Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-39-02-390-501 Hot Squeeze Riveting
General
Hot squeeze riveting is used to shape rivets that do not give to cold working. An example for this procedure is for riveting bearing cages. It must only be used when specified in the Engine Manual.
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
NONEConsumables, Materials and Expendables
NONESpares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
Procedure
A riveting machine gives a low-voltage high-amperage electric current to heat the rivet shank while at the same time a pressure is applied to shape the rivet head. The electric current and the pressure are applied through an electrode which can be replaced.
The control value necessary for any special job must be made by trial and error.
An example of a hot squeeze riveting machine is shown in Figure.
Description.
Hot squeeze riveting - riveting machine.
Description.
A resistance welding machine, with applicable electrodes, which gives the necessary electrical current and pressure values can be used for hot squeeze riveting.
Tools necessary to adapt the machine will be specified in the Engine Manual.
The control value necessary for any special job must be done by trial and error.
Hot squeeze riveting - resistance welding machine.

CAUTION
ALL ELECTRODES MUST BE MATTHEY 20W3 TIPPED.Matthey 20W3 is a sintered alloy of copper tungsten. It is available from Johnson Matthey Metal Joining, York Way, Royston, Hertfordshire SG8 5HJ.
SUBTASK 70-39-02-300-001 General
Hot squeeze riveting is used to shape rivets that do not give to cold working. An example for this procedure is for riveting bearing cages. It must only be used when specified in the Engine Manual.
The equipment for hot squeeze riveting can be a resistance welding machine with applicable electrodes, if the necessary electrical current and pressure values can be made. Alternatively, there are available a number of machines specially made for this type of riveting.
Prepare.
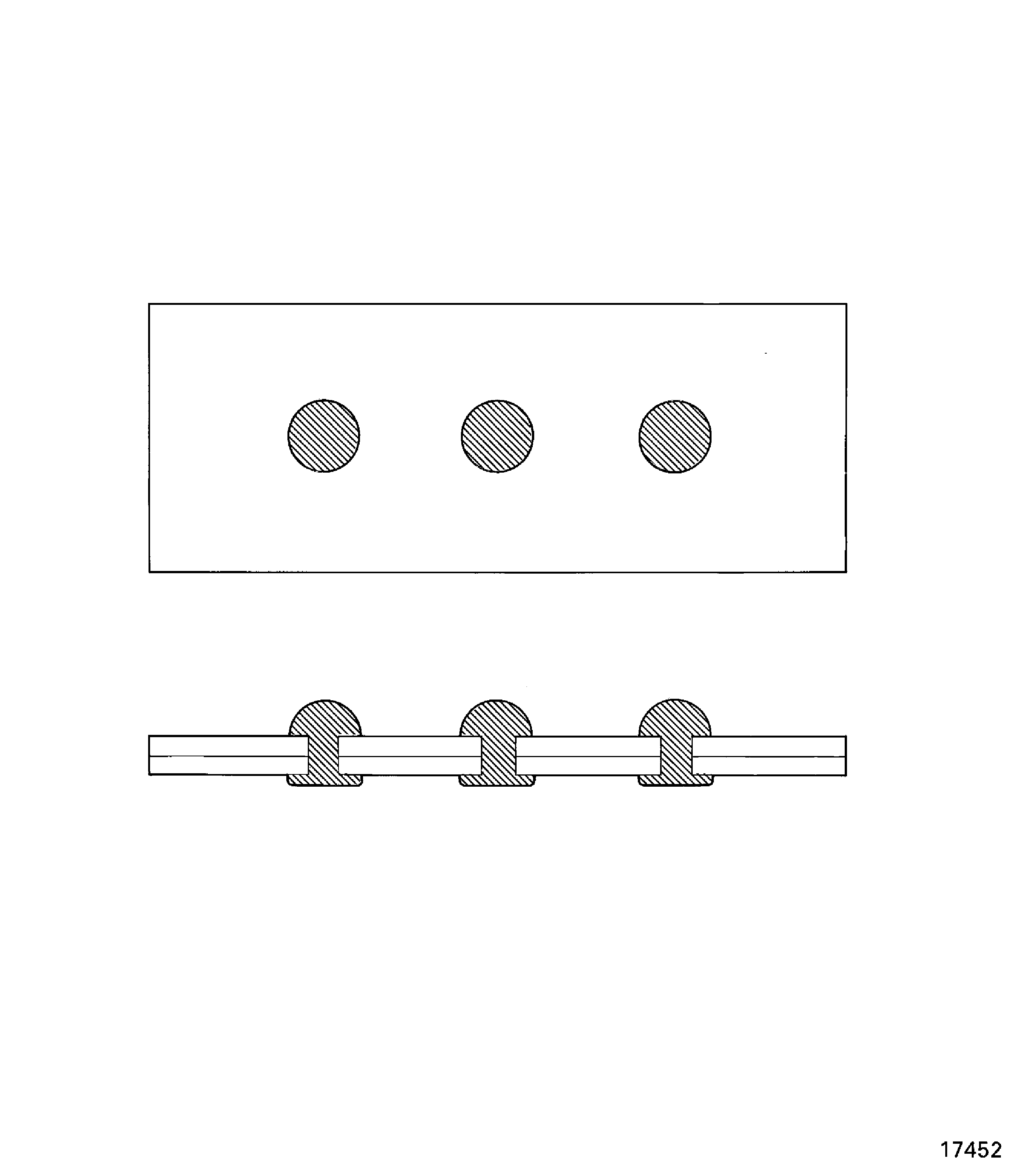
Test pieces must be near the rivet and hole size, and of the thickness and materials of component parts being attached. An example test piece is shown in Figure.
Test piece procedure.
SUBTASK 70-39-02-390-001 Procedure Control
Figure: An example of a Hot Squeeze Riveting Machine
An example of a Hot Squeeze Riveting Machine
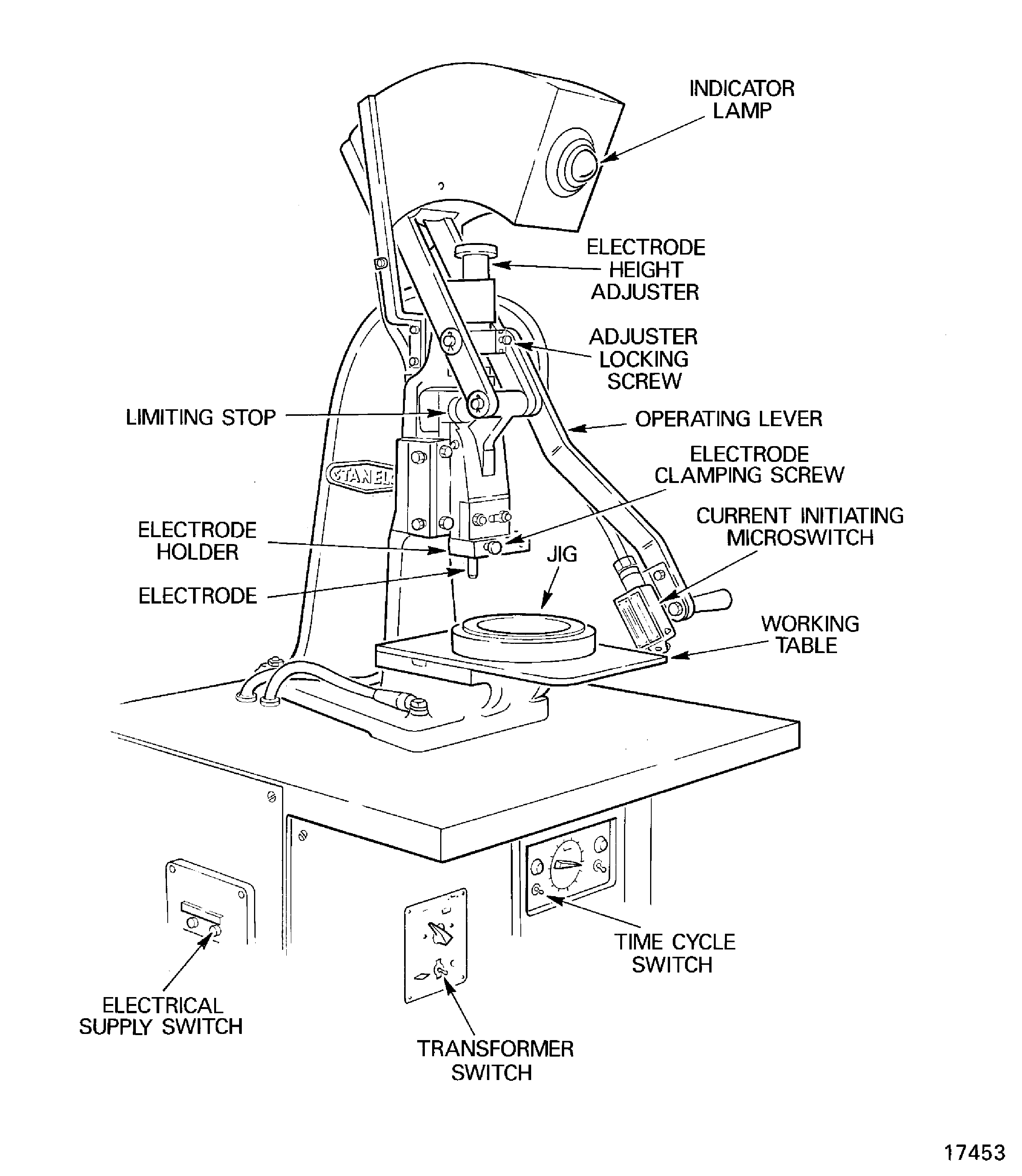
Figure: An example of a Test Piece
An example of a Test Piece