Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Description
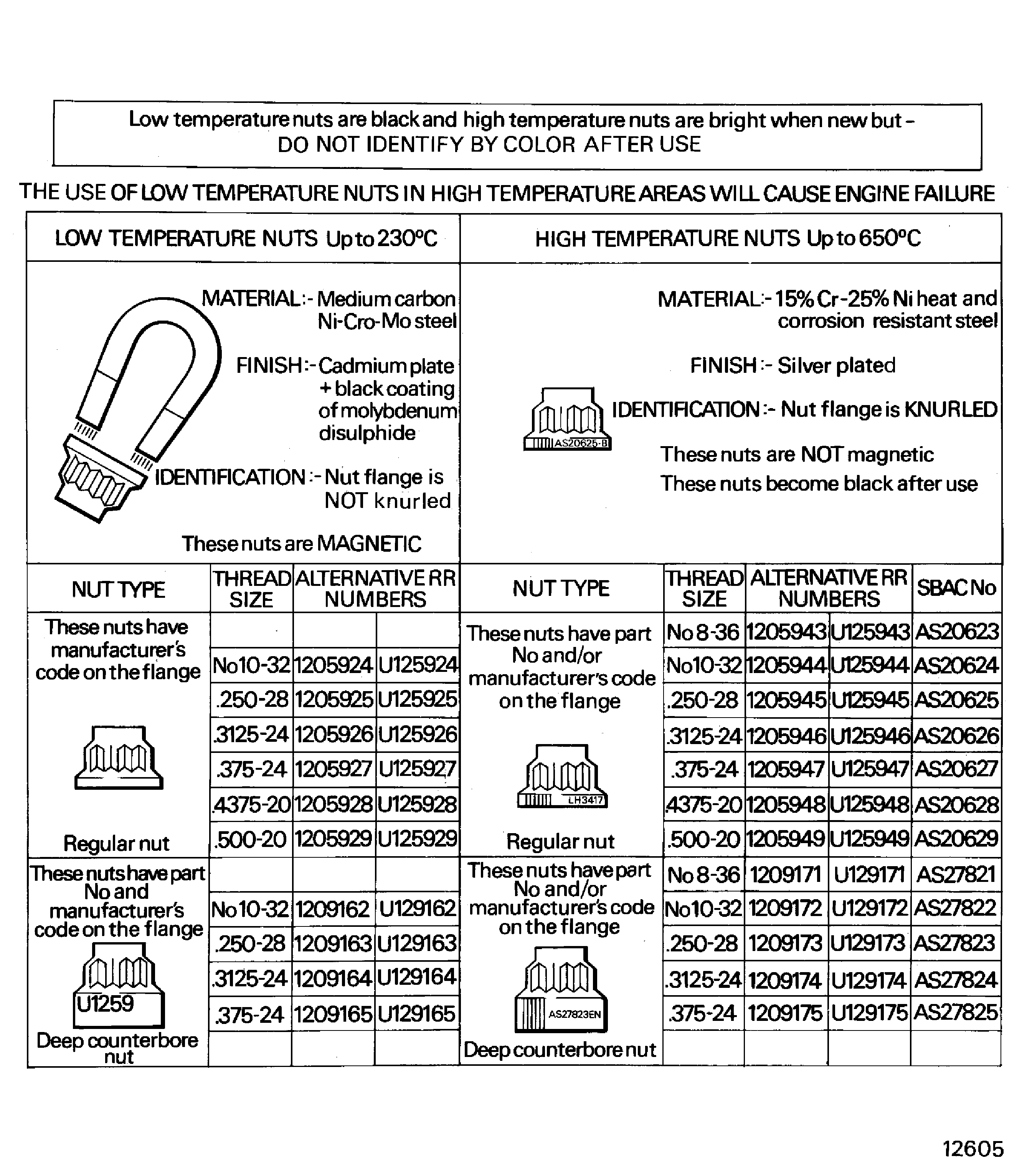
TASK 70-42-02-220-501 Identification Of 12-point Self-locking Nuts For High And Low Temperature Use
General
Although these two types of self-locking nuts look almost the same, they can easily be identified as follows:
Nuts that are used in the hotter parts of the engine (i.e. At temperatures of between 446 to 1202 deg F (230 to 650 deg C)) are not magnetic; but are silver plated and have knurled flanges (Refer to Figure).
Nuts that are used in the colder parts of the engine (i.e. At temperatures of up to 446 deg F (230 deg C)) are magnetic. They are also cadmium plated, have a layer of molybdenum disulfide and have flanges which are not knurled (Refer to Figure).
Always make sure that the correct self-locking nuts are used, as specified in the Illustrated Parts Catalog; because high temperature type nuts are frequently specified for use in the colder parts of the engine.
NOTE
The positive identification of used self-locking nuts is only possible, by the use of a magnet.
Figure: Identification of self-locking nuts
Identification of self-locking nuts