Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Description
TASK 71-00-00-990-501 Description and Operation of the Power Plant Systems
The engine has an Integrated Drive Generator (IDG) which is mounted on the external gearbox. The IDG supplies the electrical output to the aircraft pylon. The IDG has a lubrication system that is independent of the engine oil system. The oil is cooled by the IDG fuel cooled oil cooler attached to the LPC/intermediate case.
Fire Protection - Chapter 26, Figure
The engine fire and overheat detection system is pneumatically operated. It monitors the air temperature around the engine accessories and the core engine. When the temperature increases to a set value the system gives an output signal. The accessory zone fire and overheat detector and the core zone fire detector function independently of each other. Each zone fire detector has two detector units (responders) which give an output signal when a fire or an overheat condition occurs.
Hydraulic Power - Chapter 29, Figure
The hydraulic power system supplies hydraulic power to the aircraft hydraulic system. The system includes the pump, the low pressure warning switch, the case drain filter and the rigid tubes and flexible hoses. The hydraulic pump is attached to the front face of the external gearbox between the oil pressure pump and the dedicated alternator.
Ice Protection - Chapter 30, Figure
The ice protection system supplies warm air from the stage 7 of the HP compressor to the intake cowl. The flow of air is controlled by a venturi assembly and the anti-ice on/off valve. The duct goes from the HP compressor, through the aircraft pylon, around the LP compressor/intermediate case to the intake cowl distribution ring.
Pneumatic - Chapter 36, Figure
The pneumatic system gives pressure/flows for cabin pressurization/conditioning, wing anti-icing, engine cross-feed starting, hydraulic system pressurization and water system pressurization. Air is bled off from stage 10 at low engine power settings and from stage 7 at high engine power settings. The system is controlled by the Bleed Air Management Computer and will automatically select the compressor stage from which air is bled. It will also limit bleed air pressure and bleed air temperature.
The primary purpose of the fuel system is to give a completely controlled and continuous fuel supply suitable for combustion, to the combustion system. Control of the fuel system is by the Electronic Engine Control Unit (EEC) through the Fuel Metering Unit (FMU).
High pressure fuel is also used for servo pressure for some actuators.
The primary components of the fuel system are:
High and low pressure fuel pumps
Fuel cooled oil cooler
LP fuel filter
Fuel metering unit
Fuel distribution valve
Fuel nozzles
Fuel diverter valve
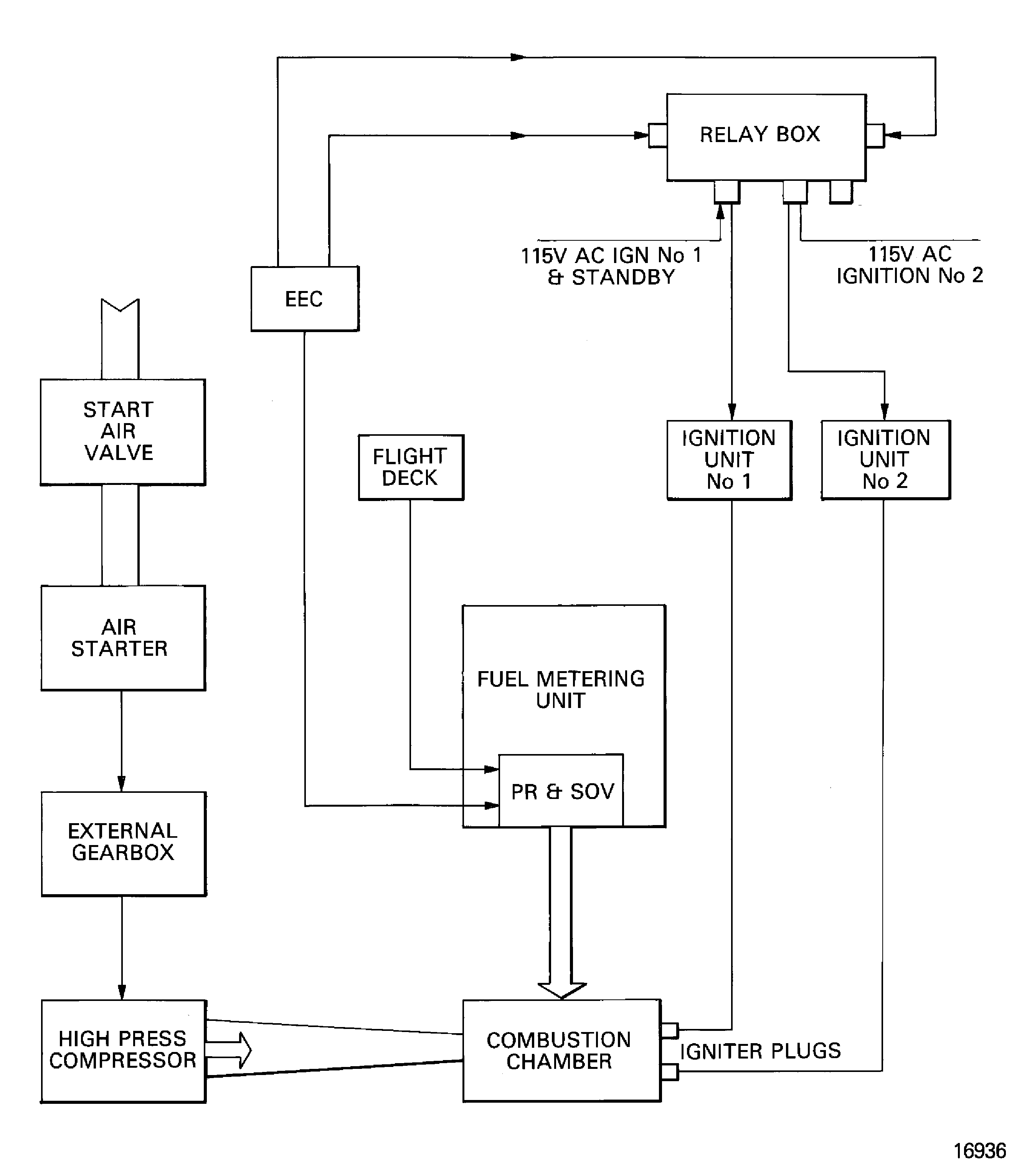
Engine Ignition - Chapter 74, Figure
There are two independent ignition systems, each with an ignition exciter unit, on the HP compressor case, an igniter plug and an air cooled HT ignition connector lead. Dual ignition is automatically selected for all in-flight starts, manual start attempts and continuous ignition. Single alternate ignition is automatically selected for ground starts.
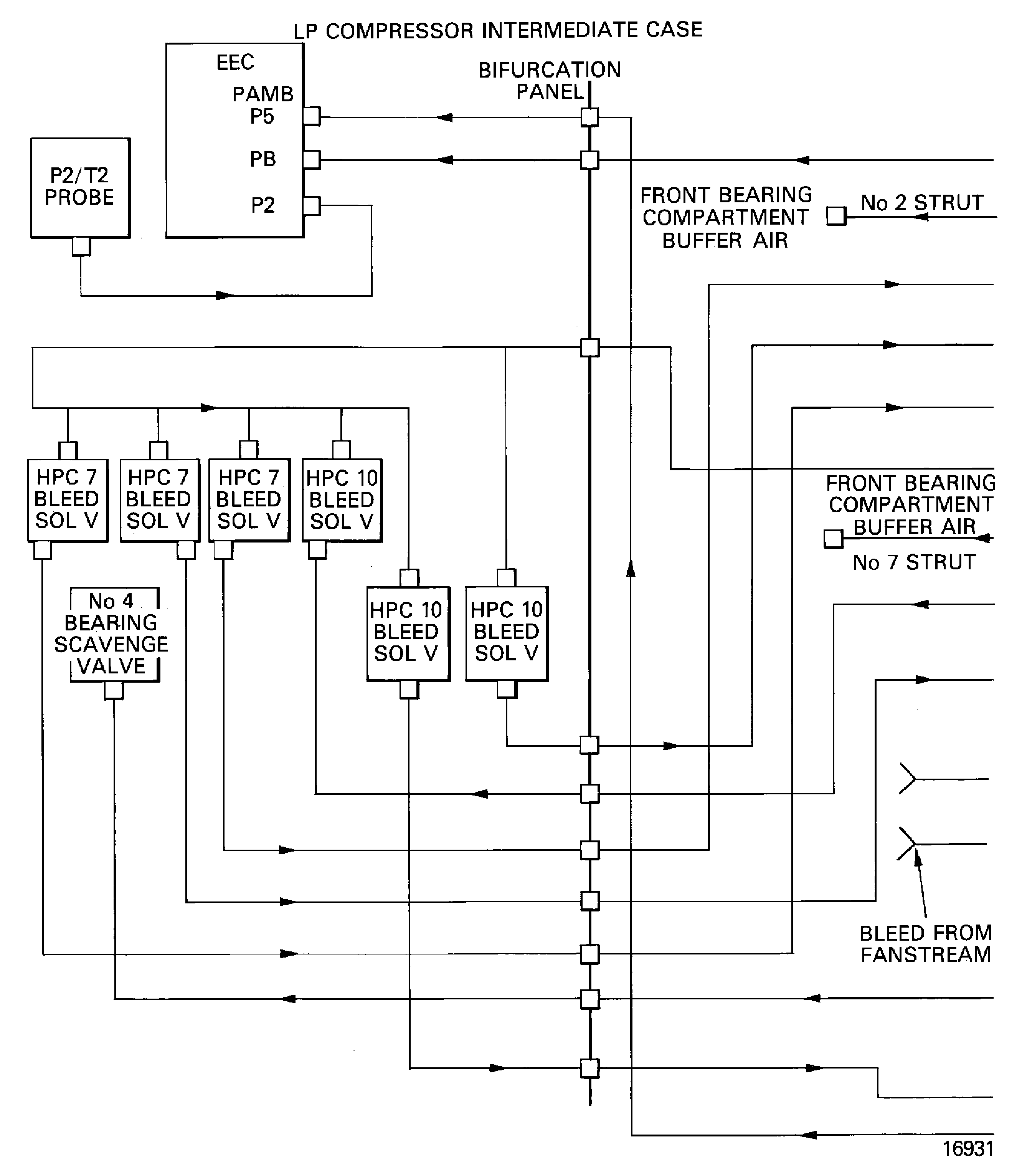
The engine air systems use air from a number of places for different control and cooling functions:
Ambient air goes through openings in the cowls and is used for Nacelle Compartment and Accessory Cooling (75-21-00) and the EEC Cooling Systems (75-28-00).
Fan stream air is used in the LP/HP Active Clearance Control system (75-24-00). It is also used for the Ignition System Cooling (75-27-00).
Air is bled from the HP compressor stage 5 for use in the Front Bearing Compartment Sealing system (75-22-00).
Air from the HP compressor stage 12 is used for No.4 Bearing Compartment Cooling (75-22-00) and the HP Turbine Cooling system (75-23-00).
Additional off-takes from stage 7 and stage 10 of the HP compressor are used for Engine Intake Ice Protection (30-21-00) and for aircraft services such as cabin conditioning.
Air is bled from the LP compressor (75-31-00) and the HP compressor (75-32-00) for engine starting and handling purposes.
A Temperature Indicating system (75-41-00) is installed to monitor the temperature of the air around the core engine.
Engine indicating is used by the EEC to monitor the engine operation conditions and help in engine control. The EEC also sends signals to show the data in the cockpit.
Engine indicating includes:
N1 rotational speed indicating system
N2 rotational speed indicating system
Engine pressure ratio system
Exhaust gas temperature system
Engine vibration indicating system
Exhaust - Chapter 78
The exhaust system collects the hot and cold gas streams and ejects them through the common nozzle to atmosphere.
The cold gas stream is also used to give reverse thrust. The thrust reverser is an integral part of the 'C' ducts and is of an angular outlet type with fixed cascade segments.
The oil system is a self contained, full flow and re-circulatory system. It supplies the oil flow to lubricate and cool the engine bearings, gears and splines.
The primary components in the system are:
Oil tank
Pressure pump
Six scavenge pumps
Pressure filter
Scavenge filter
Deoiler
The oil is cooled by a fuel cooled oil cooler and an air cooled oil cooler.
Starting - Chapter 80, Figure
The starter is a pneumatically driven turbine that accelerates the HP rotor to the required speed for engine starting. The starter is mounted on the front face of the external gearbox.
The primary components of the system are:
Pneumatic starter motor
Starter air control valve
Pneumatic ducts
Figure: Integrated drive generator
Integrated drive generator
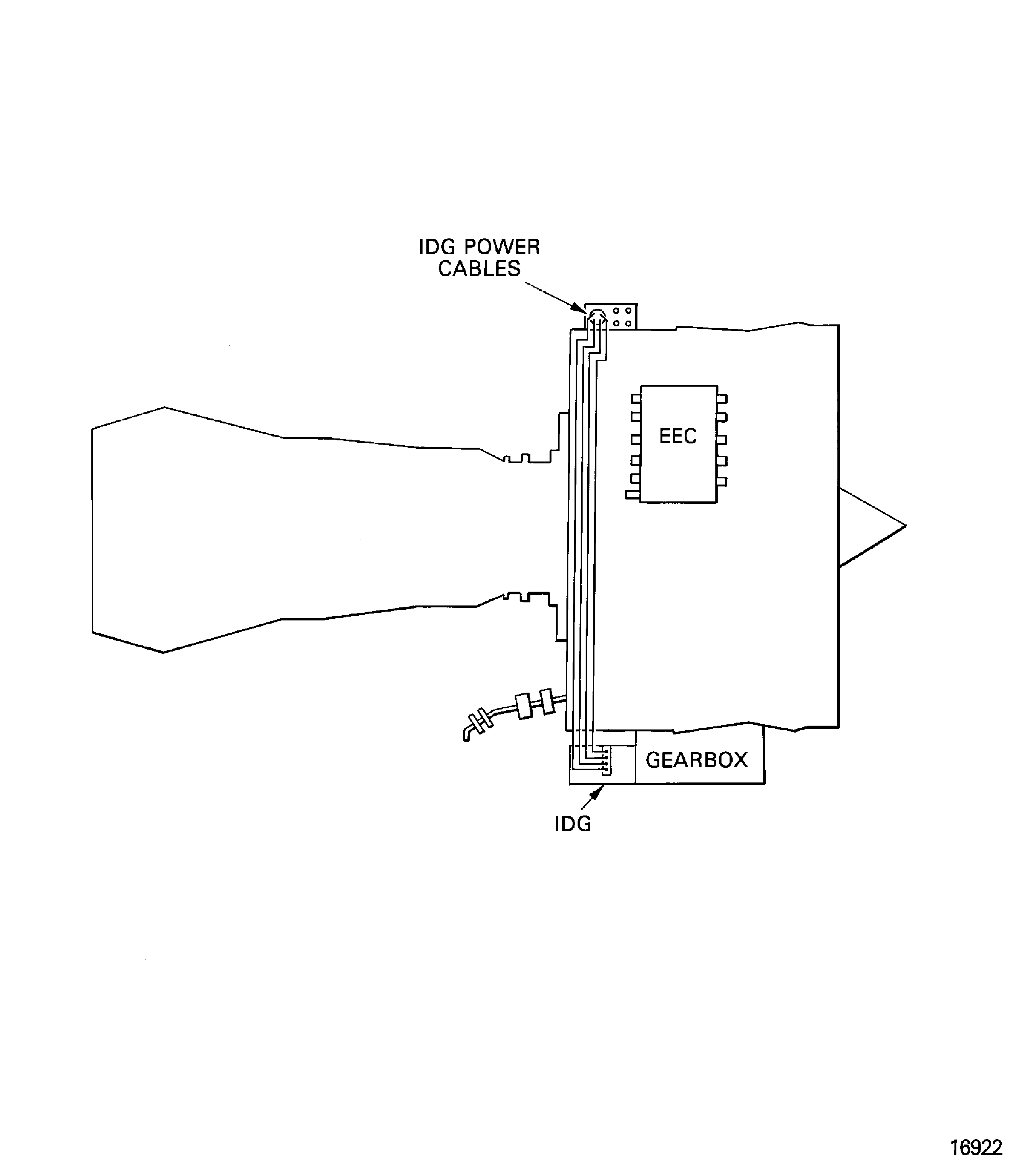
Integrated drive generator
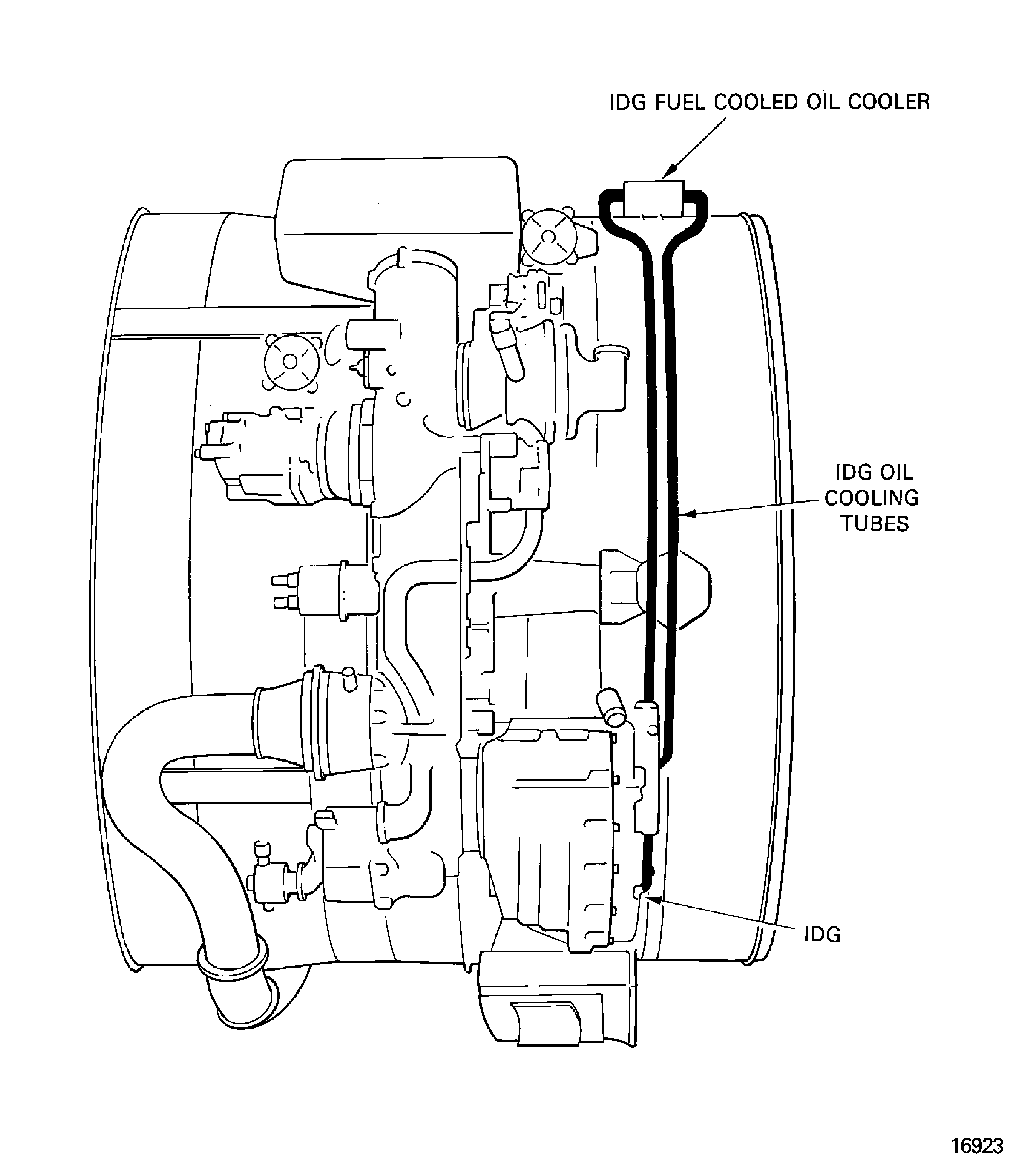
Figure: Fire and overheat detection system
Fire and overheat detection system
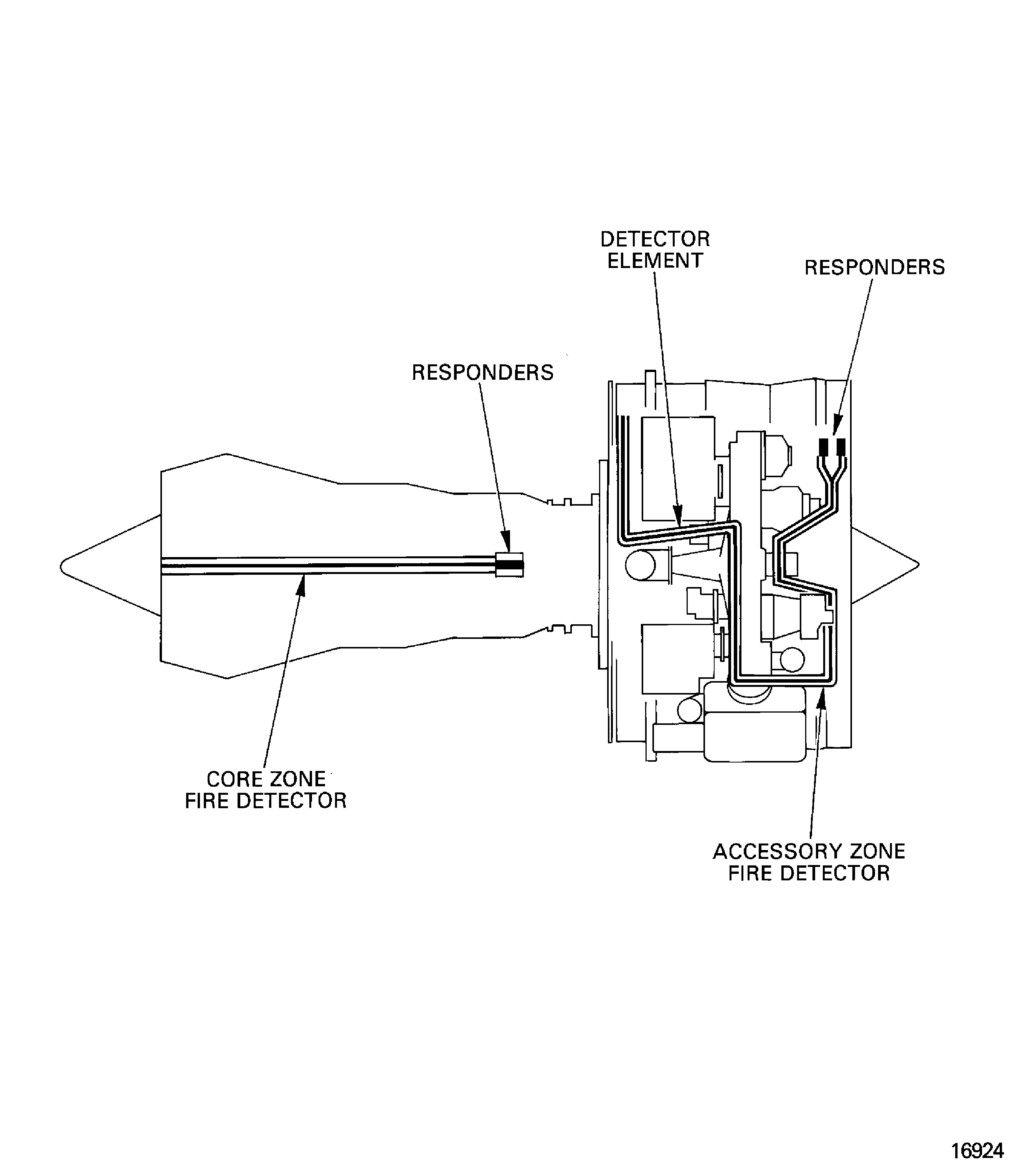
Figure: Hydraulic power system
Hydraulic power system
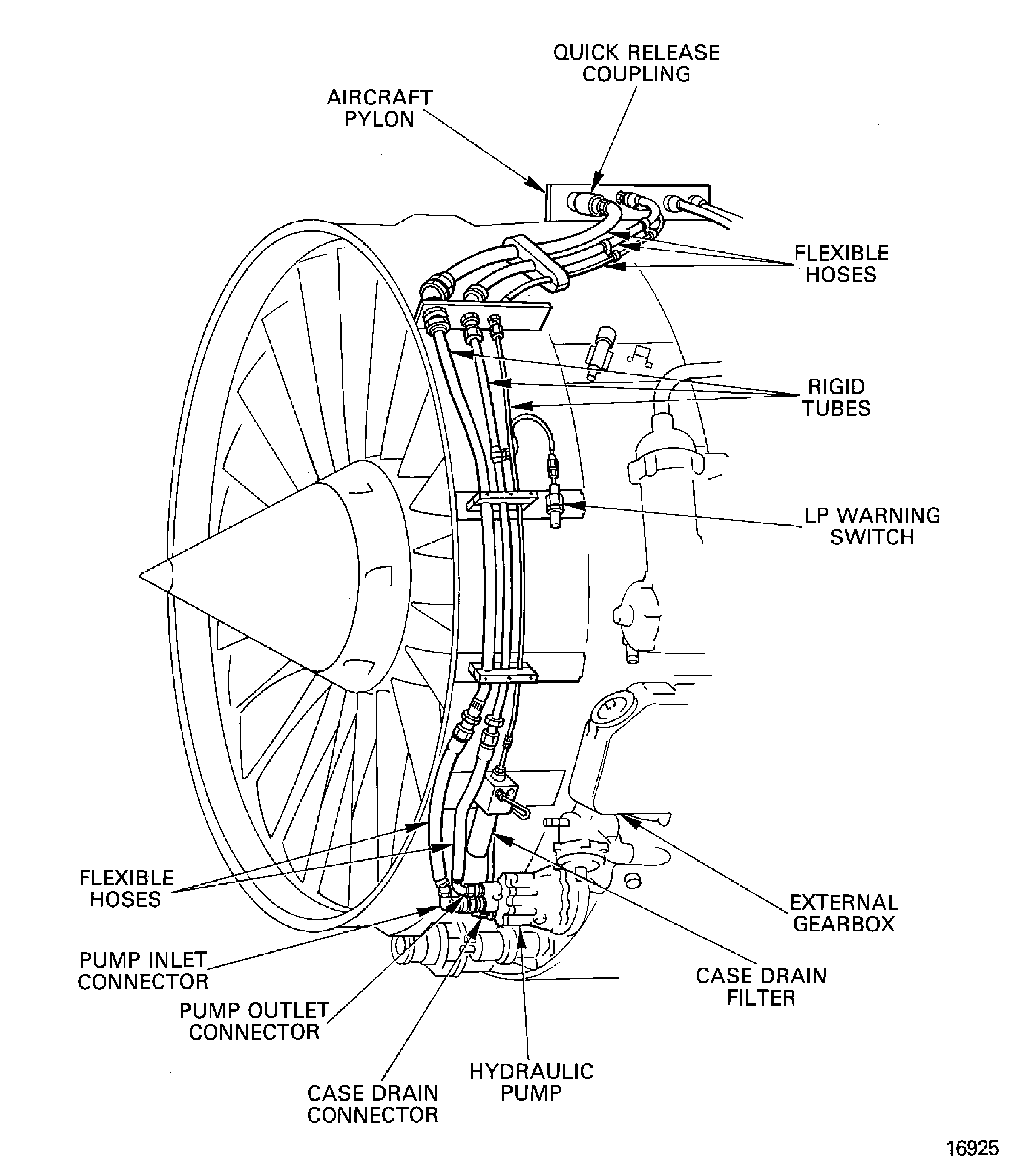
Figure: Ice protection system
Ice protection system
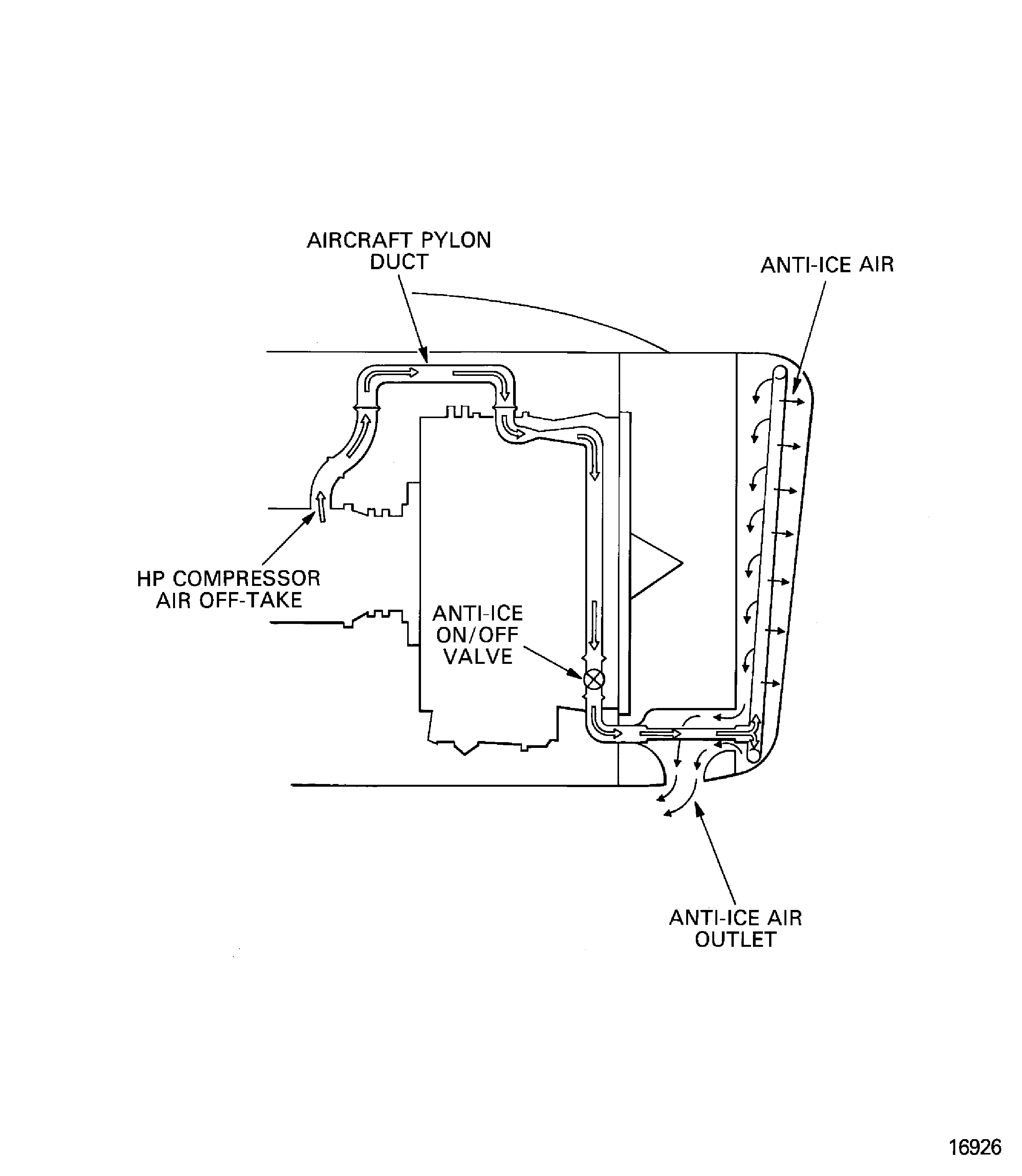
Figure: Pneumatic system
Pneumatic system
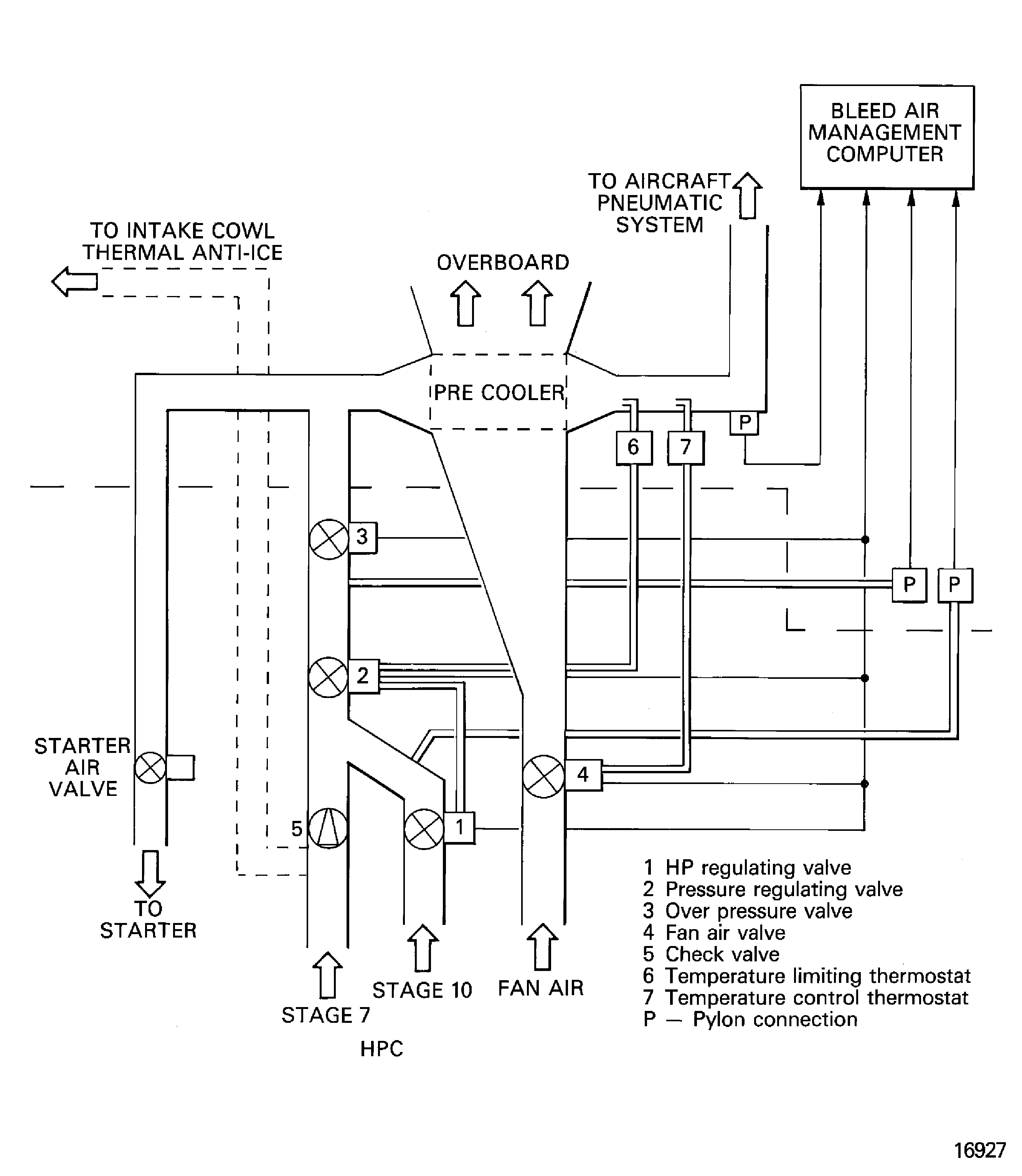
Figure: Fuel system
Fuel system
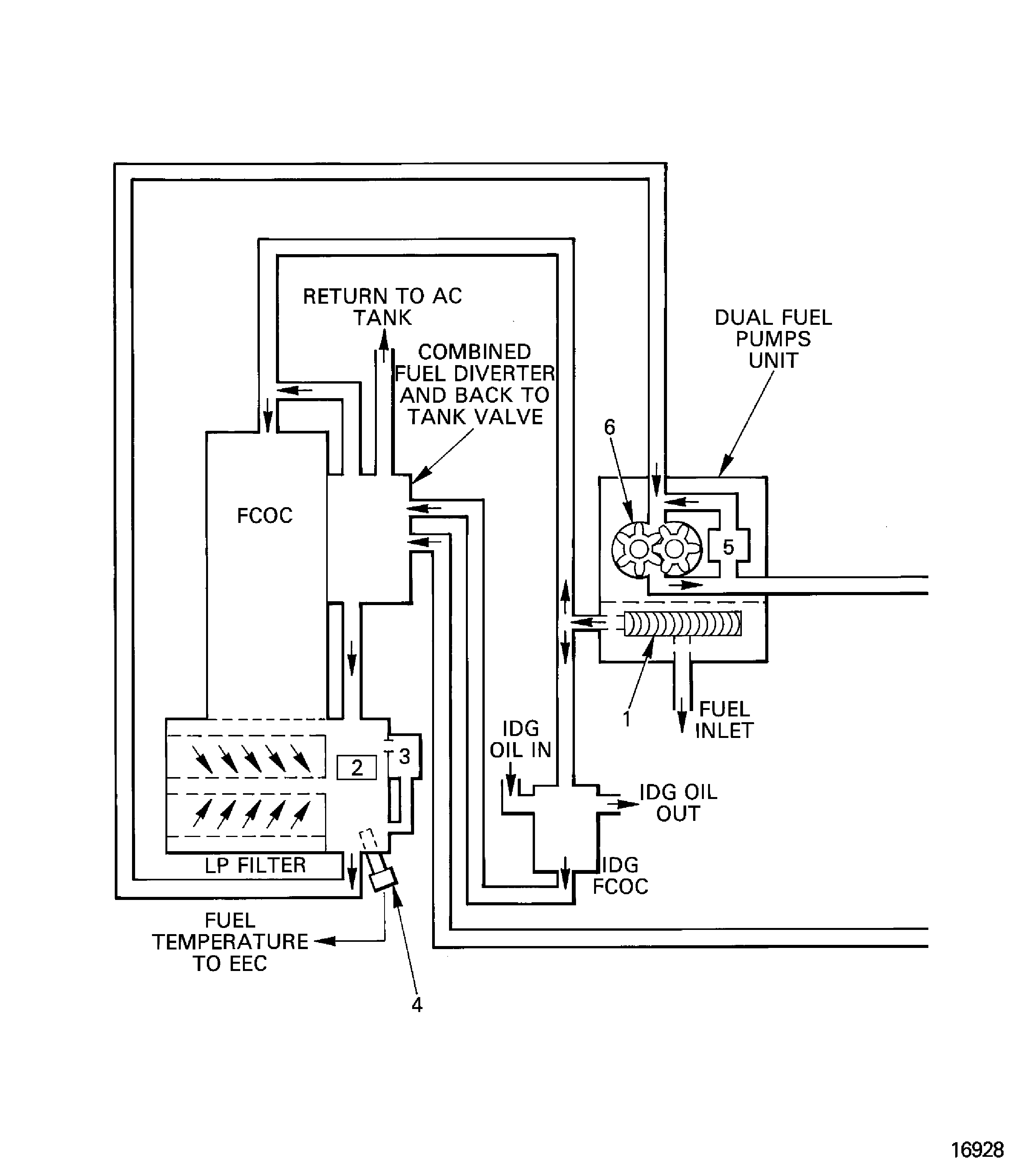
Fuel system
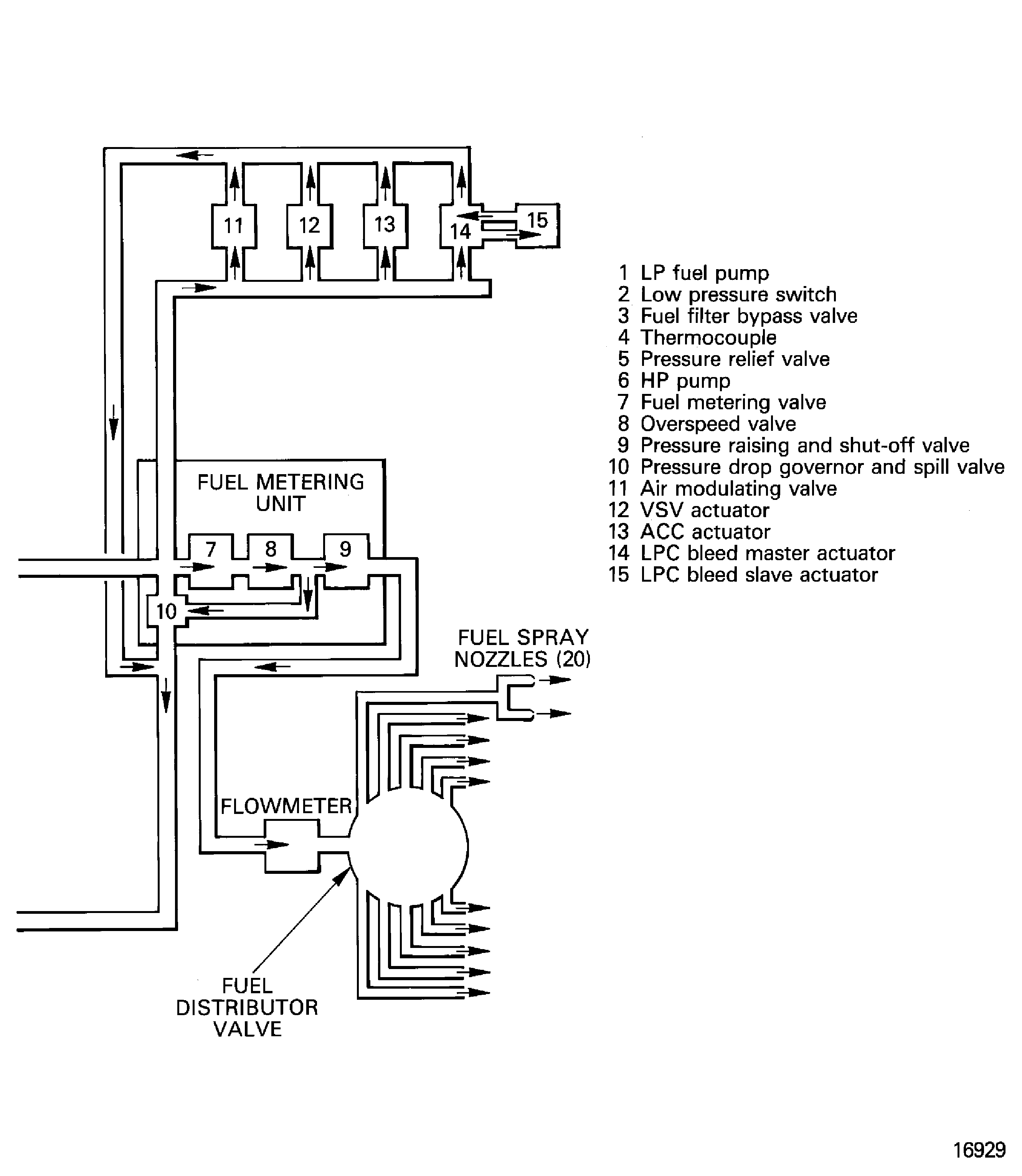
Figure: Ignition system
Ignition system
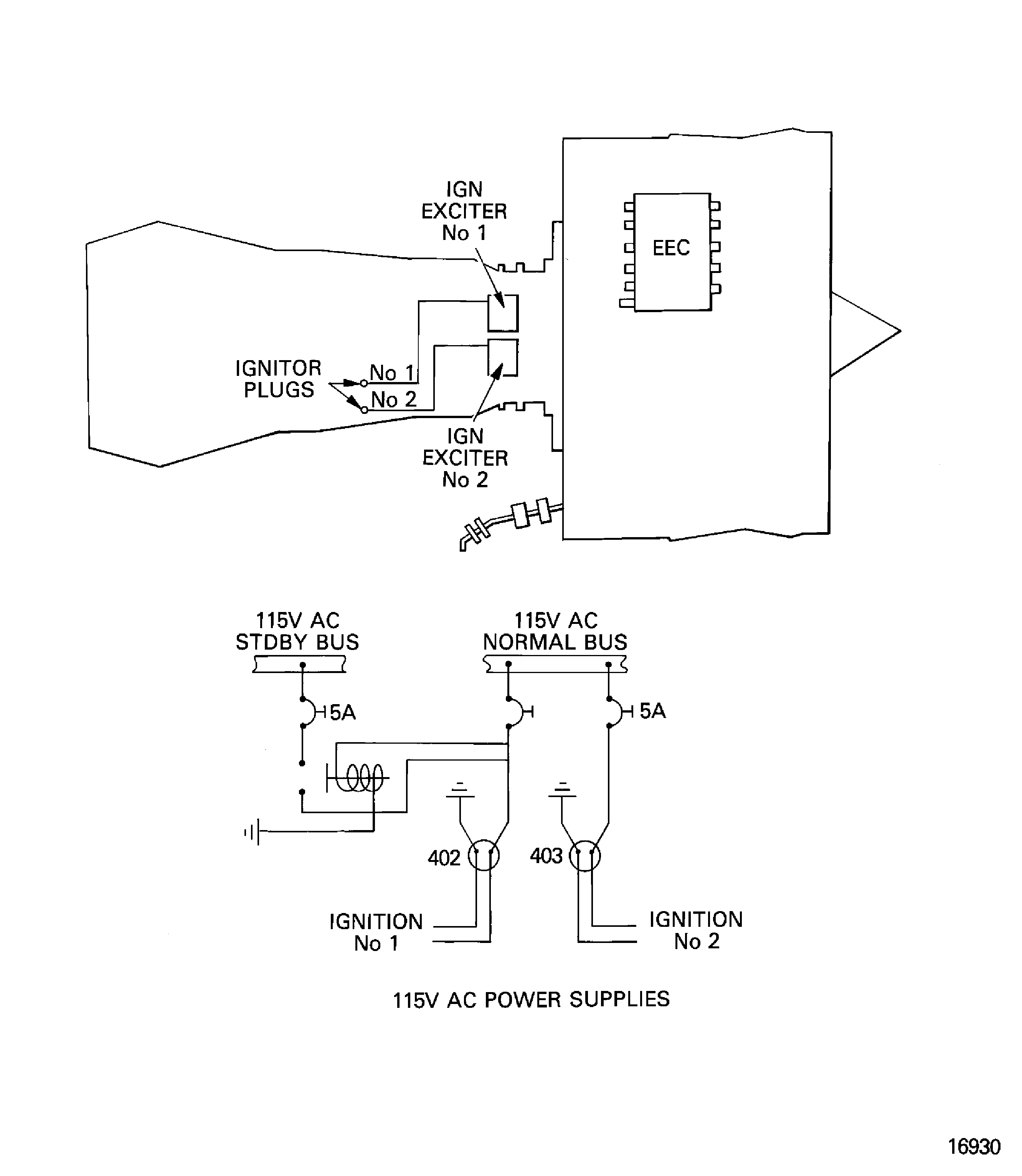
Figure: Air systems
Air systems
Air systems
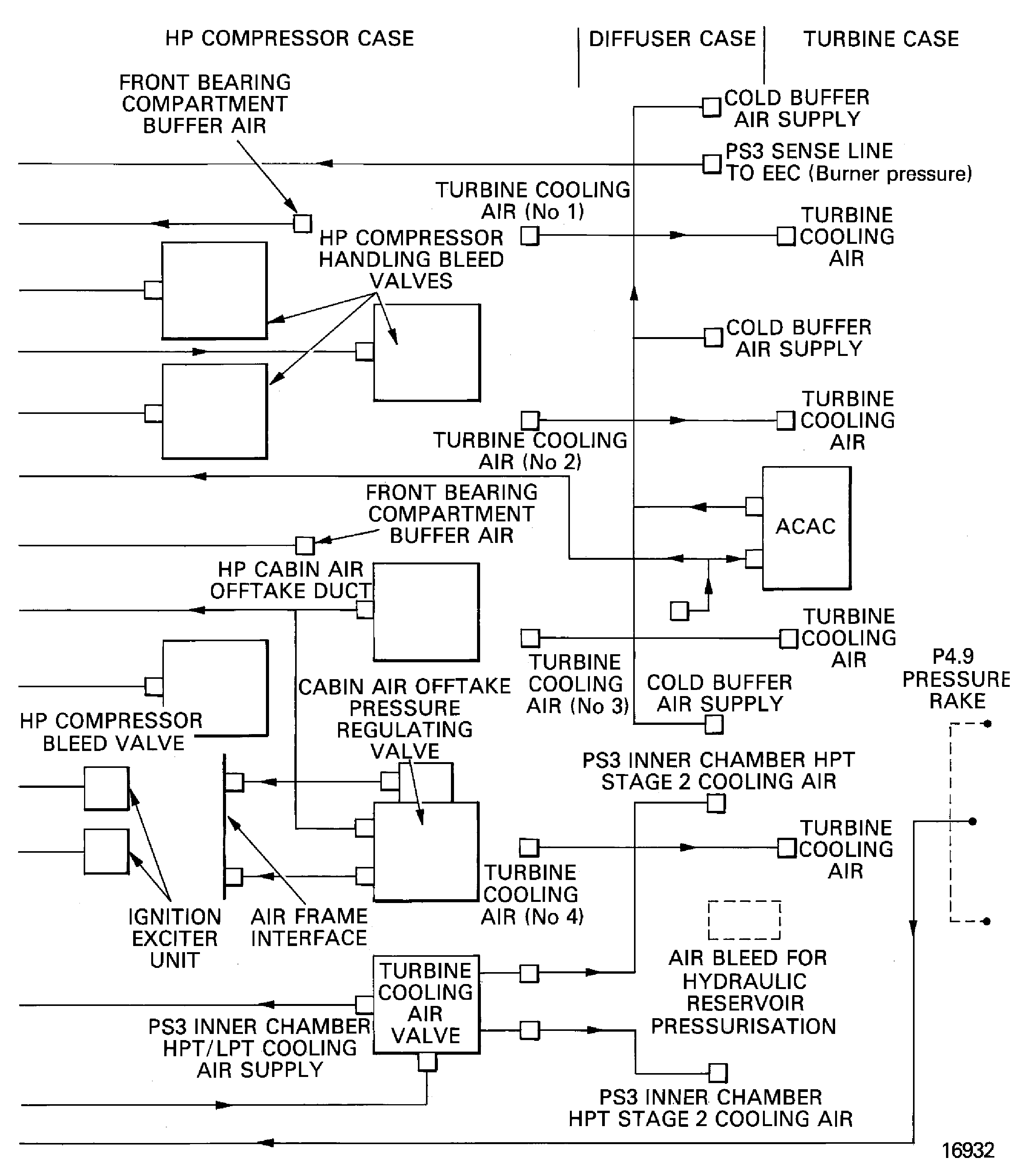
Figure: Engine indicating
Engine indicating
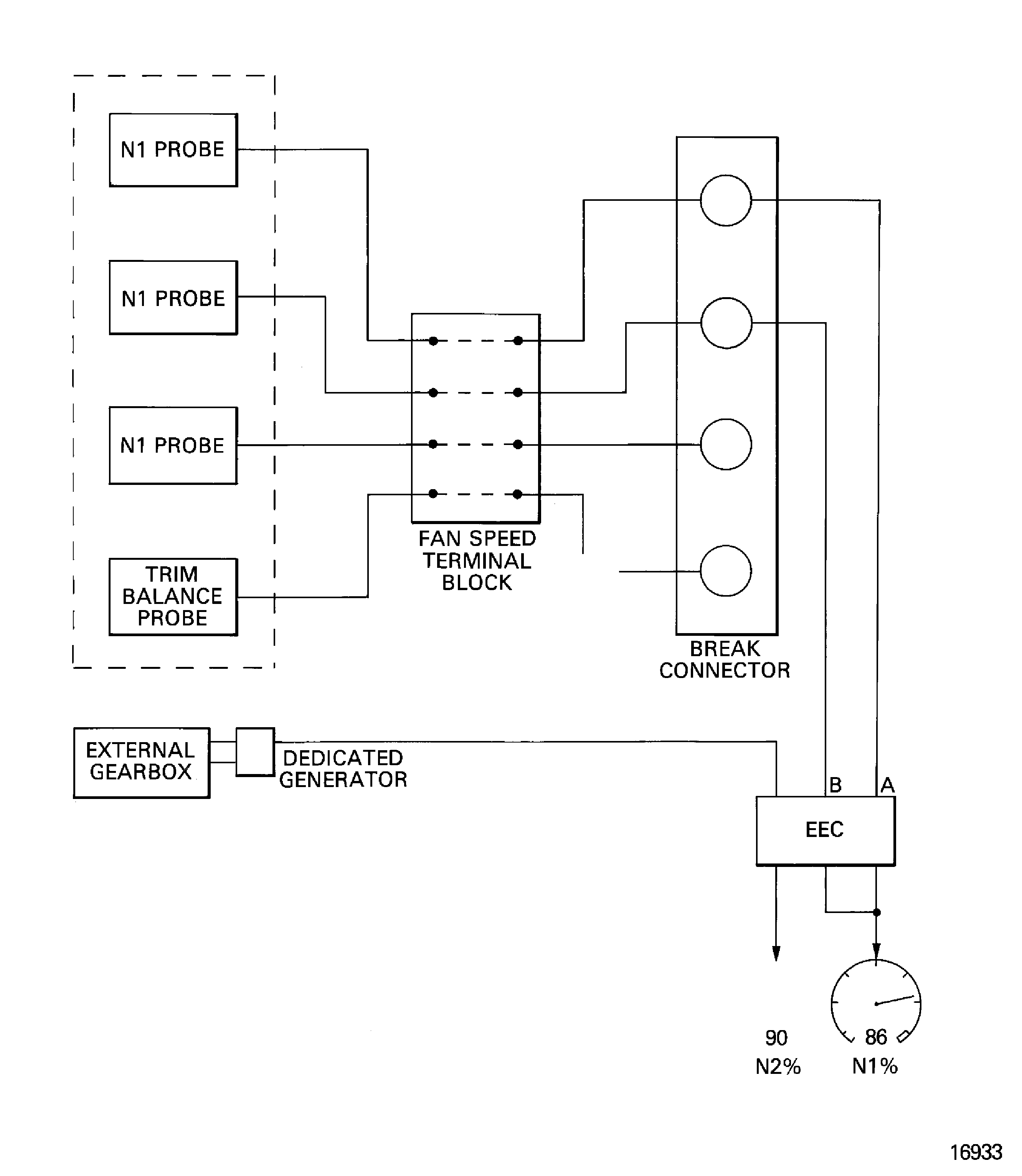
Engine indicating
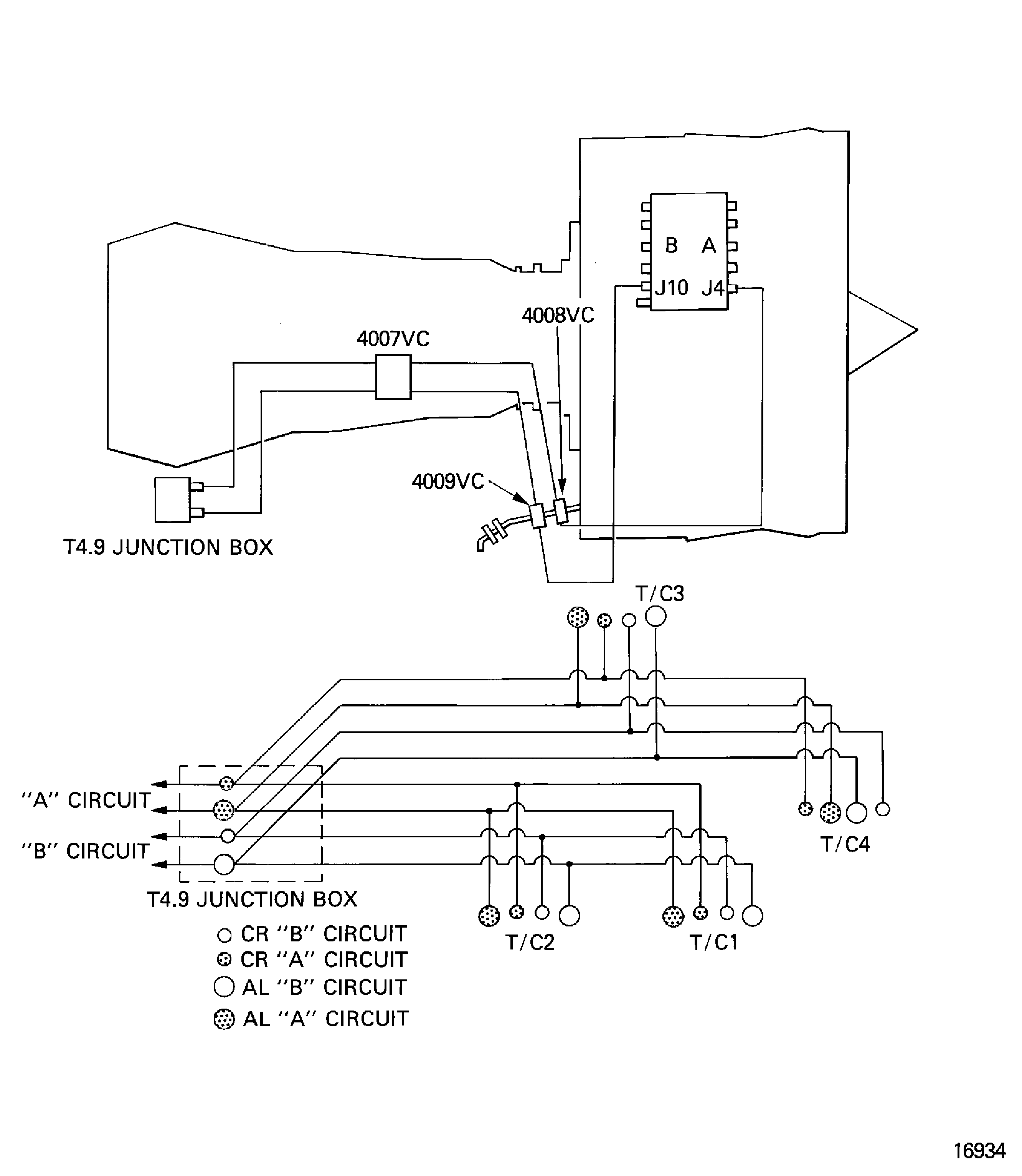
Engine indicating
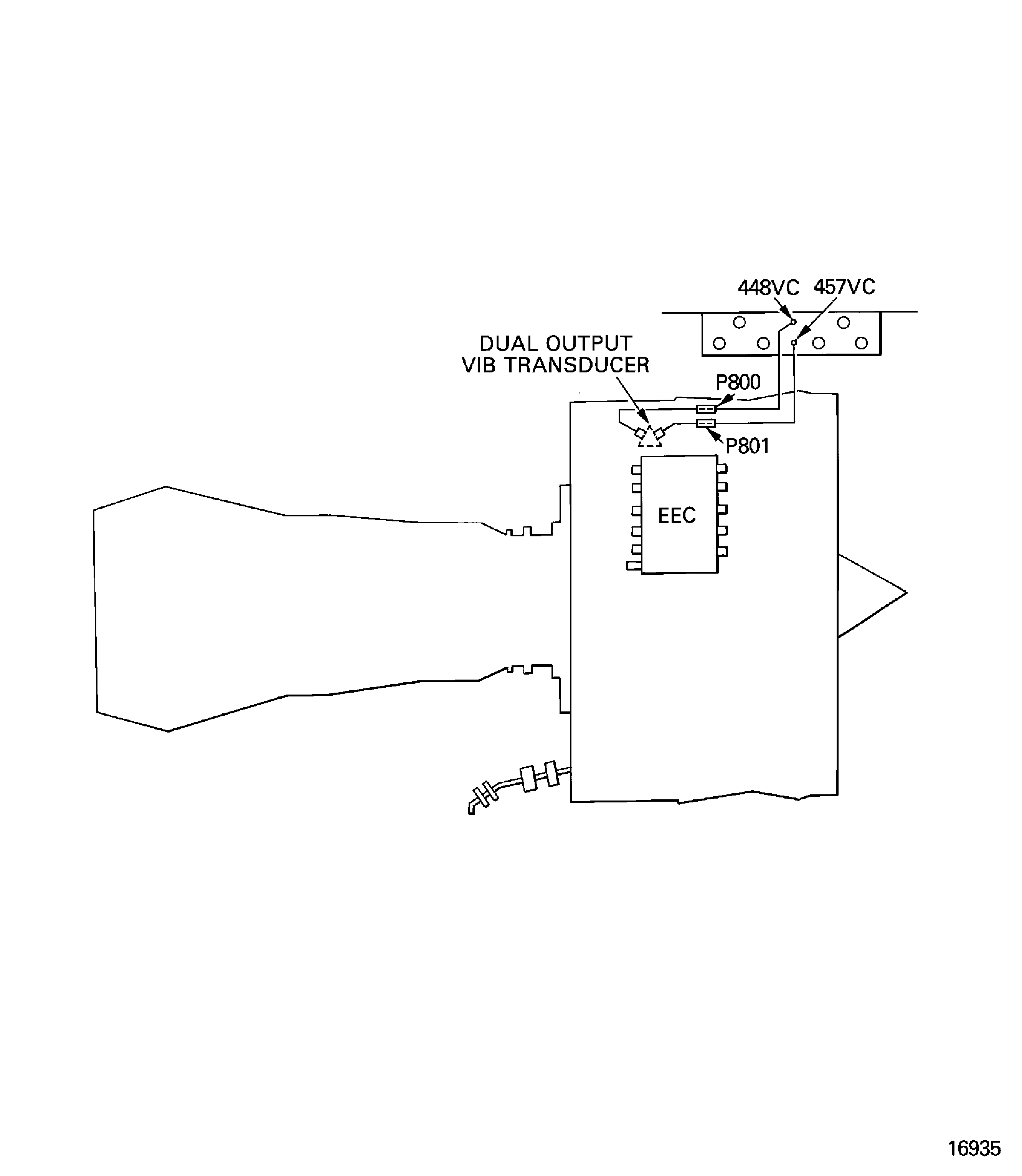
Figure: Oil system
Oil system
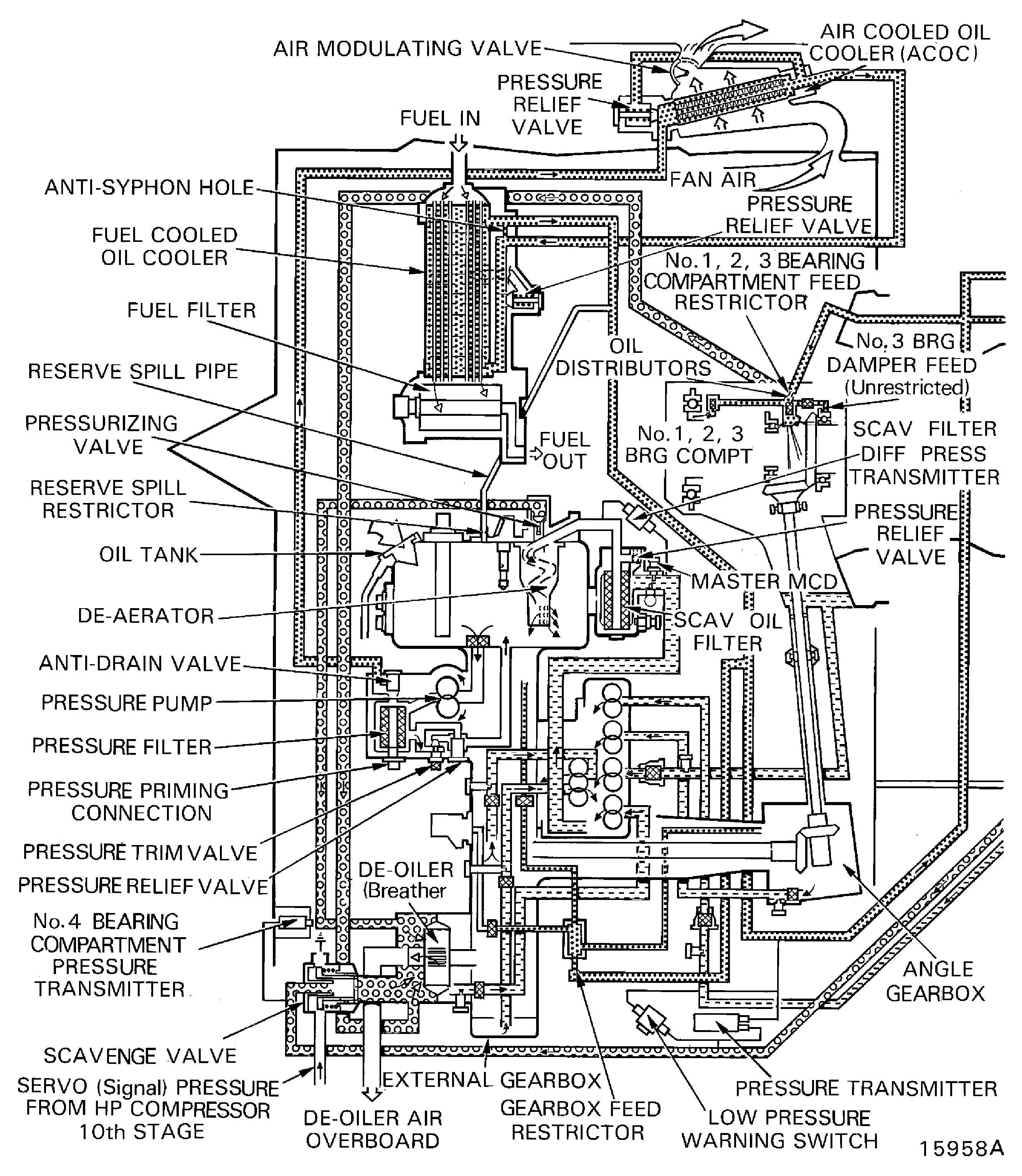
Oil system
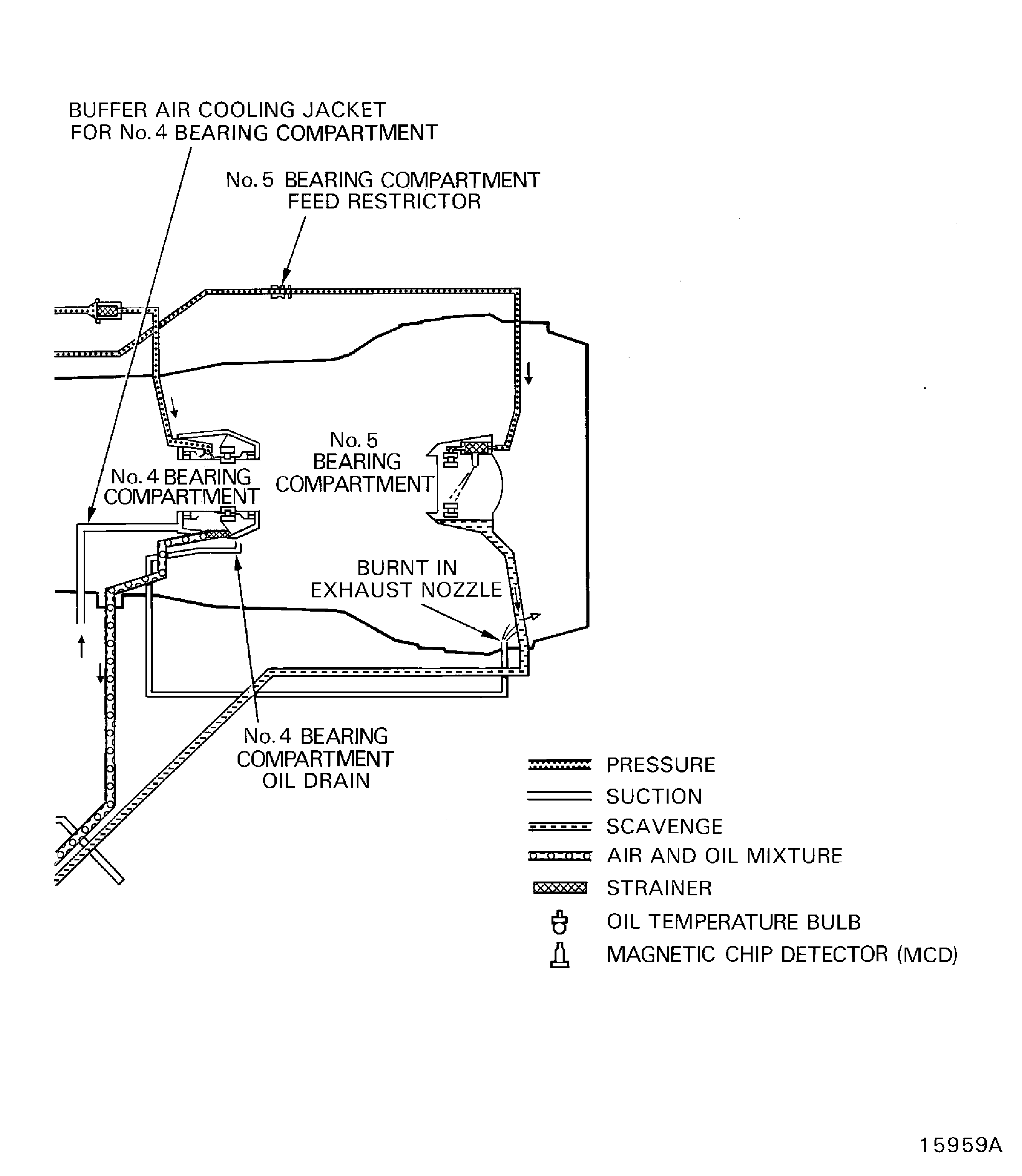
Figure: Starting system
Starting system