Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
V2500-A5
Common Information
TASK 71-00-00-700-050-B00 Engine Safety Precautions, Testing-000
Engine Safety Precautions
The properties of operation of jet engines make it necessary to prevent:
Injury to the person who operates the engine.
Damage to the engine.
Engine Safety Precautions for the Persons who Operate the Engine
Engine noise
Ear protection must be worn by all persons who work near the engine while the engine operates.
The air intake. Refer to Figure.
Stay away from the danger areas at the front and the sides of the engine during operation.
The exhaust
The engine ignition system high voltage
Hot engine parts
After engine operation, do not work or make an inspection on the hot section or the exhaust areas for one half hour (preferably longer).
The compressor bleed valve discharge
Fuel and oil
Pressurized oil system
The oil tank is pressurized during operation. The pressure slowly decreases after shutdown. Do not remove the oil tank cap for a minimum of five minutes after engine shutdown.
Precautions and Procedures for Safe and Correct Engine Operation
The air intake
Clean the area in front of the air intake before the engine is operated.
The exhaust
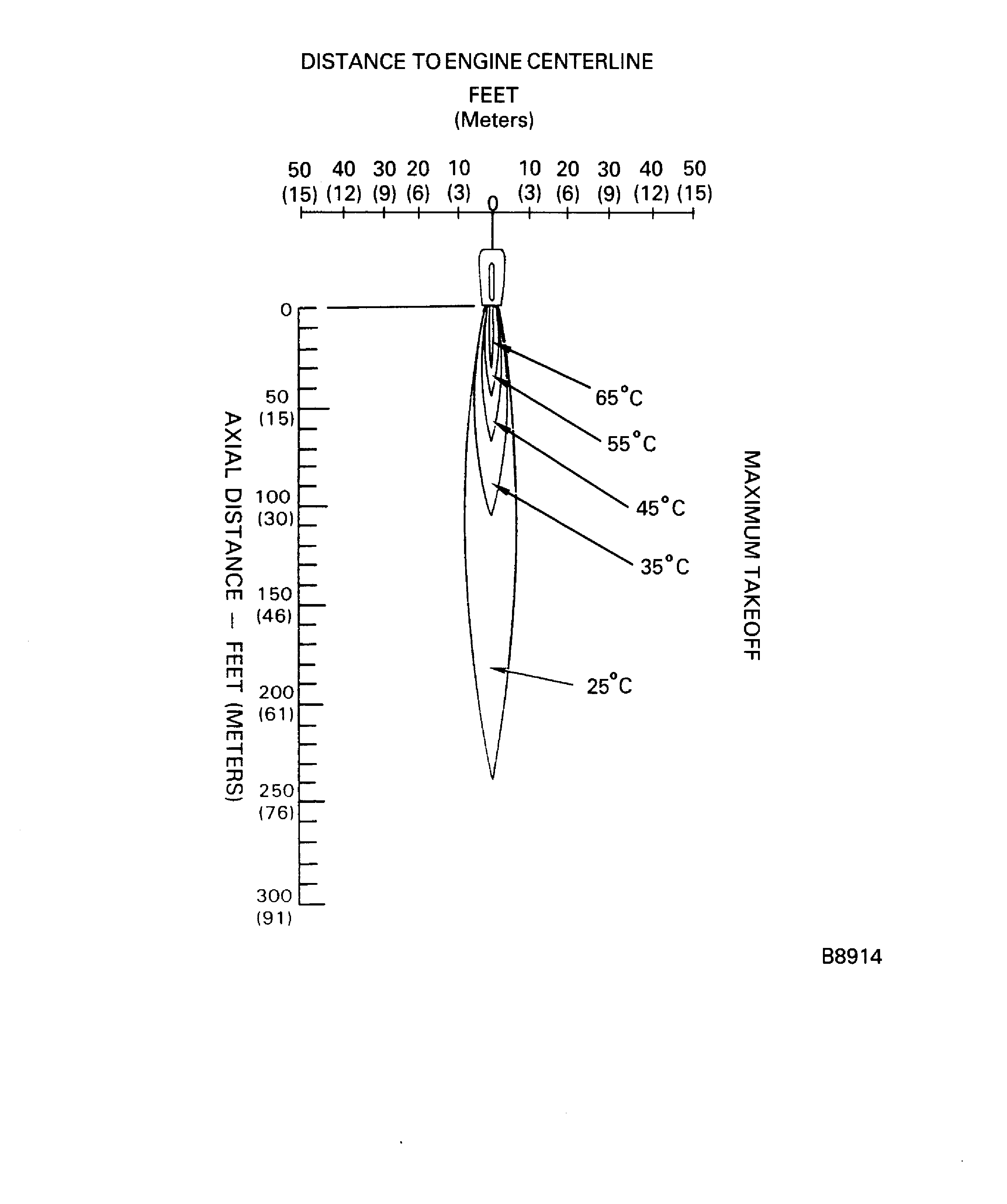
The jet wake diagrams are at standard sea level static conditions.
X-rays
Thrust lever movement
When possible, all thrust lever movements must be slow and smooth.
Snap accelerations and decelerations will not cause a deterioration of the engine performance if you obey the instructions which follow:
Before a snap acceleration, operate the engine at APPROACH IDLE for a minimum of five minutes after the first engine start.
After a fast deceleration, operate the engine at APPROACH IDLE for a minimum of five minutes before an engine shutdown.
If the engine has operated at high power (higher than 1.33 EPR) for more than 30 seconds (which includes usual acceleration time), and then operated at APPROACH IDLE for more than one minute, the engine must be operated at APPROACH IDLE for a minimum of 10 minutes before you make a snap acceleration.
Tailpipe fires during engine start
If a tailpipe fire occurs during engine start, shutoff the fuel and motor the engine to blow out the fire and decrease the internal engine temperature.
Dry chemical fire extinguishing agents
Dry chemical fire extinguishing agents are not recommended, but if these agents are used, special precautions are necessary to prevent corrosion to the engine parts. Refer to TASK 71-00-00-700-060-B00 (TESTING-000, CONFIG-001).
Water is not recommended to remove dry chemical fire extinguishing agents. These agents are not water-soluble. Water can cause the agents to build-up and bond to the parts, which can increase the possibility of corrosion.
NOTE
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
NONEConsumables, Materials and Expendables
NONESpares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
CAUTION
Procedure
Figure: Air intake (ground idle)
Air intake (ground idle)
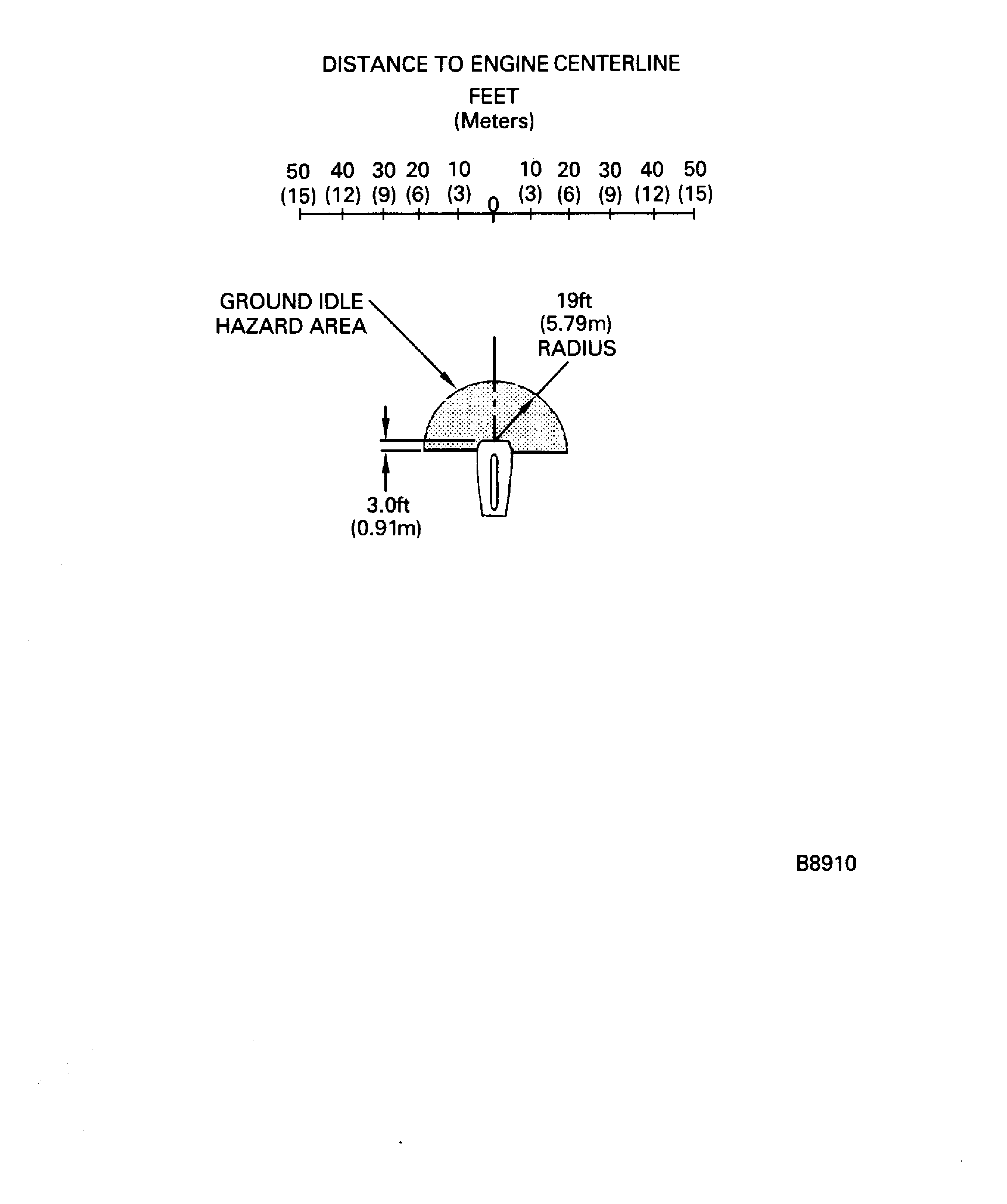
Figure: Jet wake velocity contour air intake (maximum takeoff thrust)
Jet wake velocity contour air intake (maximum takeoff thrust)
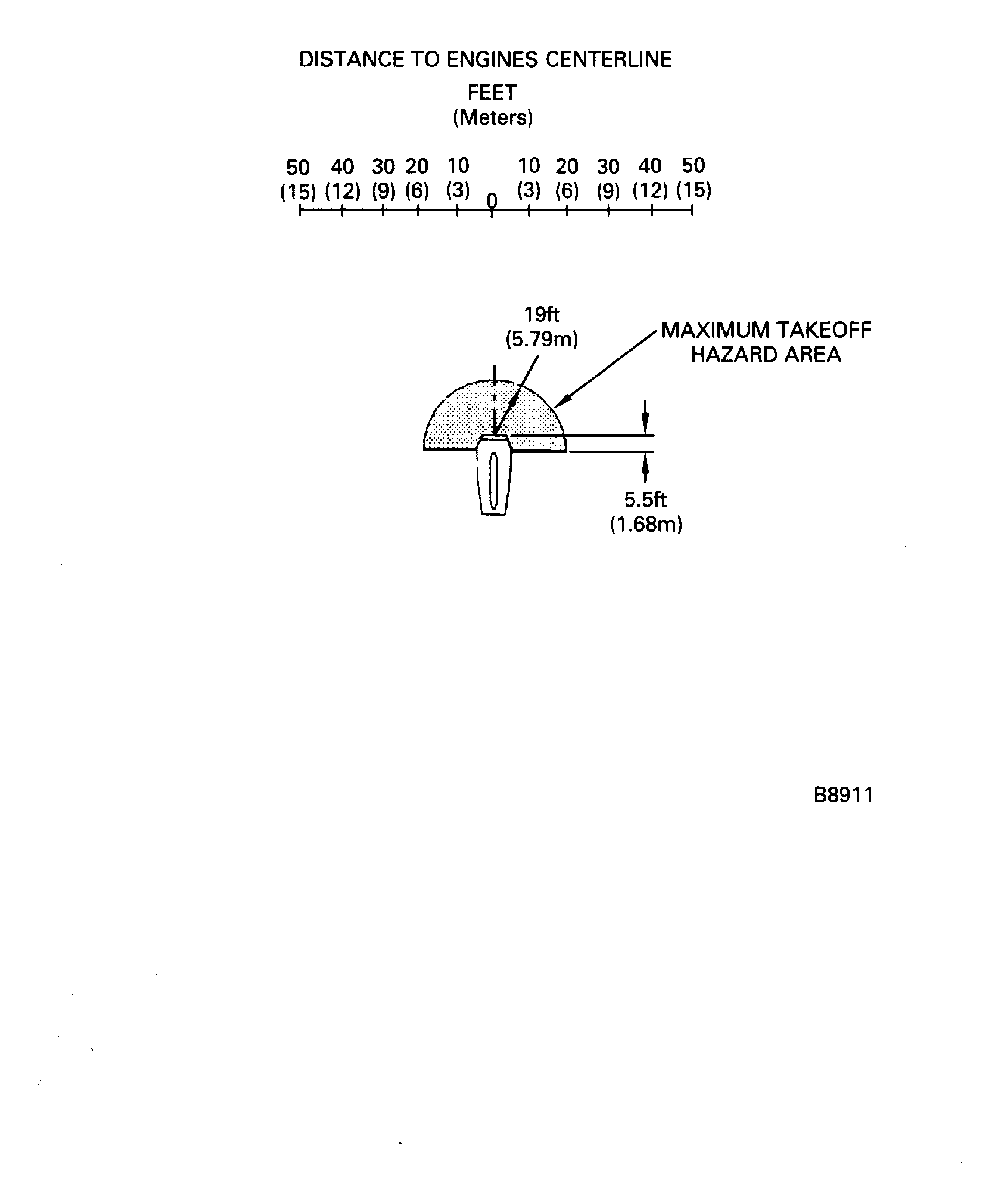
Figure: Jet wake velocity contour (ground idle thrust)
Jet wake velocity contour (ground idle thrust)
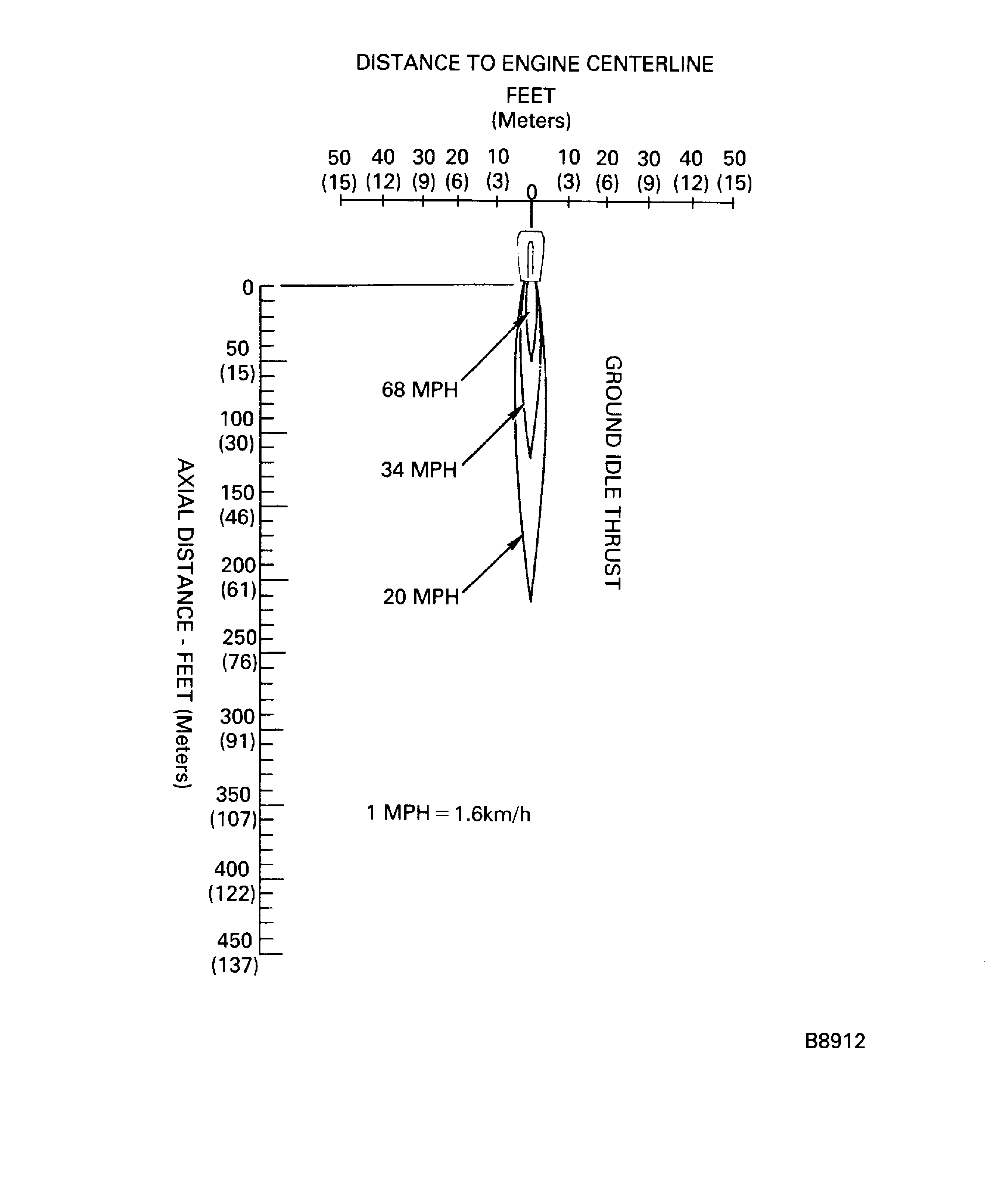
Figure: Jet wake velocity contour (maximum takeoff thrust)
Jet wake velocity contour (maximum takeoff thrust)
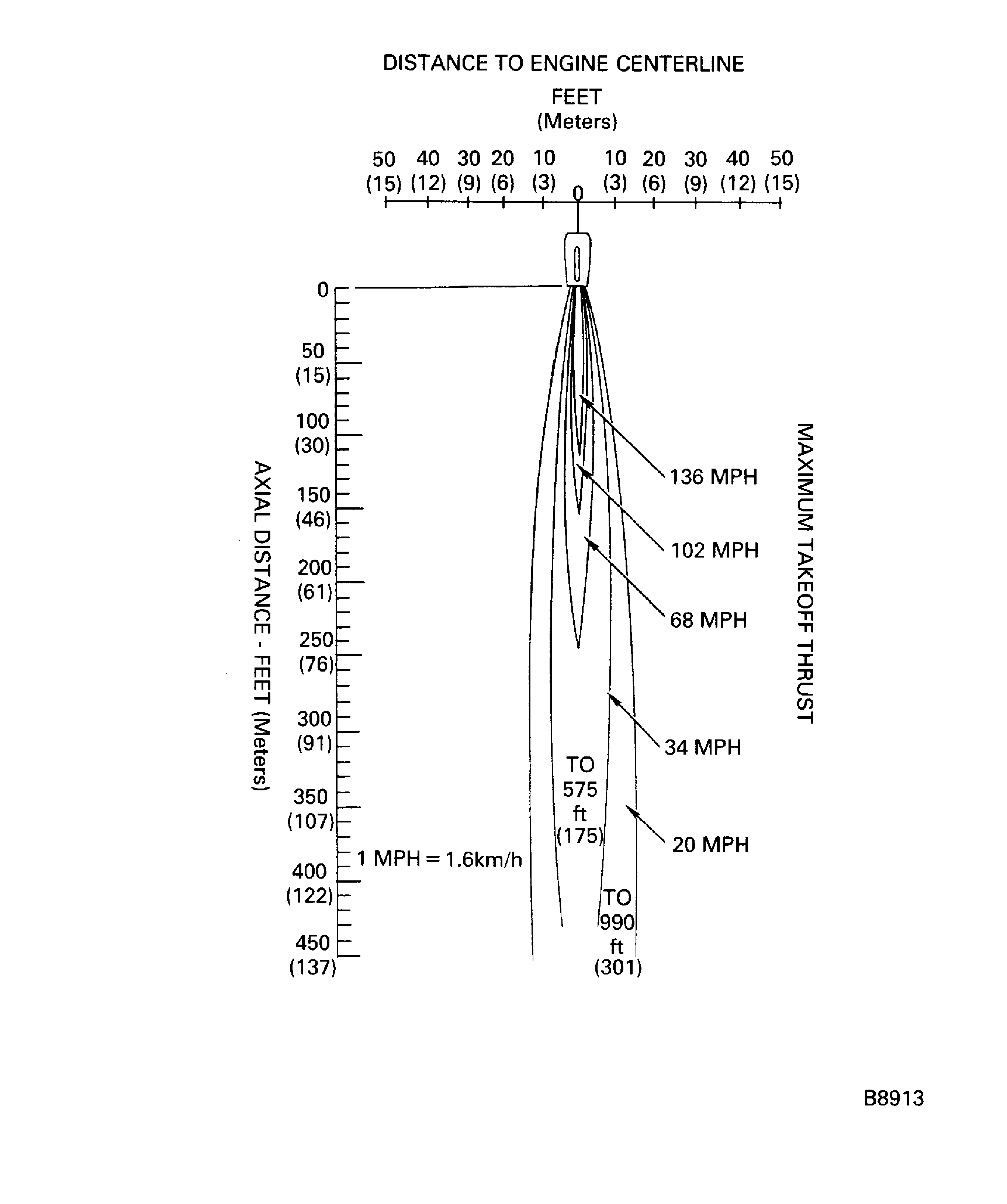
Figure: Jet wake temperature contour (maximum takeoff thrust)
Jet wake temperature contour (maximum takeoff thrust)