Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-02-02-350-501 Specified Types Of Damage
General
This TASK gives names to specified types of damage. This is to prevent errors which can occur when different names are used for the same type of damage. Always use the correct name for the specified type of damage or condition when an inspection is made on a component.
The definition of damages contained in this section does not include the Ball and Roller Bearings. For Ball and Roller Bearing Inspection/Description of Damages refer to TASK 70-29-01-290-501.
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
NONEConsumables, Materials and Expendables
NONESpares
NONESafety Requirements
NONEProcedure
Refer to Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure, Figure.
TYPE OF DAMAGE
RELATED DATA
RELATED CONDITION
Arced
Flashed-over
The effects that can be seen (burned or fused metal) of an unwanted electrical discharge between two electrical connections
Battered
Damaged by impacts
Is damage caused to a part when it is constantly hit. Refer to Figure
Bent
Creased, folded, kinked, leaning
Is angular change from the initial shape or contour usually the cause is a lateral force. Refer to Figure
Binding
Sticking, tight
Is decreased movement such as a tightened condition which results from very hot or very cold temperatures or an unwanted particle between surfaces
Bowed
-
A curve which changes the surfaces usual shape or contour. Usually the cause is heat or a lateral force. Refer to Figure
Brinelled
-
Circular surface damage on bearing races. Usually the cause is constant shock loads given to the bearing. Refer to Figure
False Brinelling
Roller bearings: It is seen as axial lines across the roller track which are surface blemishes. This is permitted.
Ball bearings: Are two marks related to each ball that can be seen on the ball track which are surface blemishes. This is permitted
Brittle
Perished
A change in the elasticity of the material
Broken
Fractured
The separation of a part by force, into two or more pieces. Refer to Figure
Bulged
Ballooned, swollen
Internal and external local distortion. Usually the cause is too much heat or differences in pressure. Refer to Figure
Burned
Charred
A complete structural failure of the material because of very hot temperatures. Refer to Figure
Burnish
A shiny area resulting from rubbing against a hard, smooth surface; may contain scratches of no apparent depth.
Burrs
-
Rough edges or sharp projections on the surface of a material
Carboned
Carbon covered, carbon tracked, coked
A quantity of carbon particles collected on the surface of a material. Refer to Figure
Chafed
Scraped, scuffed
Friction wear damage, usually the cause is two parts that rub together with a small amount of movement
Checkered
Crazed
Surface cracks; usually the cause is heat
Chipped
-
Material broken off the edge, corner or surface. Usually caused when a material is hit
Collapsed
Crushed
The surface is pulled below its initial contour. Usually the cause is large differences in pressure. Refer to Figure
Corroded
Rusted, oxidation, etched, sulphidation
Slow deterioration of the material because of a chemical effect. Usually seen as oxide particles on the surface
Cracked
-
A linear opening that can easily be seen and which can cause the material to break. (Special fluorescent or magnetic penetrants are not necessary). Refer to Figure
Crossed
-
Material damage to a part, for example, crossed thread. Alternatively a part incorrectly assembled, for example, crossed wires
Curled
-
A rounded fold in the material such as a blade tip that has rubbed against the engine casing. Refer to Figure
Dented
-
Damage to the surface of a part when it is hit with an object. The material is distorted but not removed. Refer to Figure
Deposits
Metalized
Particles of material collected on a part from a different part or material. Refer to Figure
Disengaged
Separated, loose
This occurs only to parts that are usually permanently attached to each other
Disintegrated
Shattered
Completely broken in pieces. Refer to Figure
Distorted
Buckled, depressed twisted, warped
Is damage that changes the initial shape or contour of a material. Usually caused when the material is hit, made hot or has structural stresses applied. Refer to Figure
Eccentric
Non-concentric
Occurs when a part has the point about which it turns moved off center
Eroded
-
The flow of fluids or gases cause the material to wear; heat or grit makes this occur more quickly
Extruded
-
Plastic deformation because of high pressure between parts
Feathered edge
-
The edge of the material is made thinner
Flattened out
-
Permanent damage more than the tolerance limits. Usually caused when the material is compressed
Frayed
-
Worn (rubbed) in to strips
Fretted
-
Damage caused when two materials are rubbed together
Fused
-
When two materials become attached to each other, usually the cause is heat, friction or current flow
Galled
Fretted, spiked
Damage caused when two materials are rubbed together at high pressure. Refer to Figure
Glazed
-
This is seen as a hard glossy surface because of heat, varnish, incorrect loads or when the surface is rubbed
Gouge
-
A large rough cut of large depth with the removal of some material, caused because a sharp object has hit the part. Refer to Figure
Grooved
Furrowed, fluted
A smooth rounded score, because of wear, with rounded corners and smooth on the groove bottom
Imperfection
An interruption (non-uniformity) in the normal surface condition of a part configuration which must be evaluated for acceptance to an assigned standard.
Indications
-
Small cracks or other small defects that can not be seen without fluorescent or magnetic penetrants
Melted
-
Distortion to the initial shape or contour because of heat friction or pressure
Nicked
-
A small cut on the surface or edge of a part caused when the part is hit with an object. Refer to Figure
Overheated
Heat discolored, heated excessively, seen as a change in color or condition. hot spot
The part has become too hot, usually Refer to Figure
Part missing
Lost
Related only to a detail that is usually permanently attached
Peeled
Blistered, flaked, exfoliated
Is when the surface finish (coating, plating) breaks away. Refer to Figure
Peened
-
A group of very small dents caused when the part is hit many times
Pick-up
-
The material from one surface becomes attached to a different surface. Usually caused when two surfaces are rubbed together without sufficient lubricant. Refer to Figure
Pierced
Hole in the part
The part has a hole made in it
Pitted
-
Small irregular shaped holes in the surface of a material. Usually caused because of corrosion or electrical discharge. Refer to Figure
Plugged
Clogged, obstructed, restricted passage
The flow is decreased or prevented because of blockage
Porous
Pock-marked, perforated weld
Small empty spaces in the material usually found in welds and materials that are cast. Refer to Figure
Rolled over
Lipped, turned metal
The edges of the part become rounded. Refer to Figure
Rough
-
When the operation (not the surface) is not smooth
Rubbed
Abraded
To move with pressure or friction against a different surface. Such as compressor rub
Ruptured
Blown, burst, split
The surface of the part is broken open because of an internal stress or force. Refer to Figure
Scored
-
A scratch or scratches of large depth (with some removal of the material) made with a sharp object during the operation of the part. Refer to Figure
Scratch
-
A small surface cut with not much depth made with a sharp object or particle. Material is not usually removed. Refer to Figure
Seized
Frozen, jammed, stuck
Movement between the parts is stopped because the clearance is not sufficient. Caused because of heat or unwanted particles
Shallow imperfection
An imperfection which appears to penetrate the surface finish texture, does not have a dark bottom and would not cause a stylus having a nose radius ranging in size from 0.030 in. - 0.0365 in. (0.762 mm - 0.927 mm) to hesitate (catch) when passed over it.
Sheared
Cut
Is when two surfaces move in relation to each other along the same axis in opposite directions. This will cause the details that hold the two surfaces together to break. Refer to Figure
Skidding
-
Is surface damage to balls, rollers and races of bearings. It is seen as an intermittant matt silver effect on the surface and occurs because of intermittant loads during use. Refer to Figure
Sludged
Gummed
Very small particles of unwanted material collected in one location
Softened
Perished
Below the specified elasticity
Spalled
Plucked
A rough broken area on the surface of a material. Usually caused because of surface cracks or inclusions when a load is put on the surface. Refer to Figure
Spinning
Damage caused when a bearing race is turned too much
Stretched
Growth
The part is made larger as a result of conditions of operation
Stripped
-
The removal of material by force. Usually related to threads and insulation
Superficial imperfection
An imperfection which disrupts the surface and appears smooth-edged but does not penetrate the surface roughness texture. This condition is so slight, considered less than a shallow imperfection, that a stylus need not be used to evaluate it.
Torn
-
The material is pulled apart. Refer to Figure
Untwisted
Unwound
An unsatisfactory decrease in the angular adjustment. The part tries to become straight
Worn
-
The material of the part is erroded away because of operation or use
Wrecked
-
The damage is too bad for continued use
SUBTASK 70-02-02-350-001 The Types of Damage to Metal Parts
SUBTASK 70-02-02-350-002 The Condition of Metal Parts
TYPE OF DAMAGE
RELATED DATA
RELATED CONDITION
Acceptable
OK
Satisfactory for continued use
Not inspected
-
Class of part
-
The nozzle guide vane class is the
too low
angular deviation between the airfoil
chord and the buttresses
Class of part
-
The nozzle guide vane class is the
too high
angular deviation between the airfoil
chord and the buttresses
Clearance above
-
Unsatisfactory tolerances have
maximum
collected. (Not because of wear)
Clearance above
-
Unsatisfactory tolerances have
minimum
collected. (Not because of wear)
Clearance end
-
-
too much
Compression or
-
Compression or tension load is lower
tension below
than specified
minimum
Compression or
-
Compression or tension load is higher
tension above
than specified
maximum
Damaged during
-
-
transit
Deterioration
-
-
in storage
Dimension below
-
Below the engineering drawing
minimum
dimension or other specified
dimension
Dimension above
-
Above the engineering drawing
maximum
dimension or other specified
dimension
Emission low
-
Is the low output of electrical tubes;
it shows an unsatisfactory tube
Finish not to
-
Is the condition of the surface
specification
finish; not surface damage
Frequency out
-
The frequency of vibrations of a part
of limits
are above permitted limits
Hardness below
-
Found with Rockwell, Brinell or
limits
alternative hardnesss tests
Hardness above
-
Found with Rockwell, Brinell or
limits
alternative hardness tests
Magnetism low
-
Low or no magnetism of permanently
magnetized parts
Mis-matched
-
A condition caused because of the
incorrect relation of parts
Mis-positioned
Mis-aligned,
The incorrect installation of a part
reversed, cocked
which results in damage to the part
or related parts
Obsolete
Superseded
The part is not in use
Out of balance
-
The weight is not equally symmetrical
around the axis. This condition is to
be examined if there is no apparent
damage
Out of round
Elongated
The diameters of the part are not
constant
Out of square
-
The related surfaces are not at the
specified right angle
Part removed
-
A part removed as a precaution until
pending
an investigation is done and a
investigation
technical decision is made on its
condition
Received
-
-
disassembled
Resistance high
-
High electrical resistance in an
electrical circuit that causes
incorrect circuit operation
Resistance low
-
Low electrical resistance in an
electrical circuit that causes
incorrect circuit operation
Tension or
-
Tension or compression load is lower
compression
than is specified
below minimum
Tension or
-
Tension or compression load is higher
compression
than is specified
above maximum
Time expiration
Part retired
The part is not used because of a
time limit
Voltage erratic
-
Caused because of the intermittant
or irregular flow of current
Voltage - none
-
Caused because of an unwanted current
(circuit shorted
path to ground or between leads of
or grounded)
circuits that are usually at a
different voltage
Voltage - none
-
Caused because an electrical circuit
(circuit open)
is not complete because of a break
between electrical connections
Failure at the joint between the adhesive and the honeycomb. The adhesive stays on the surface layer but not on the honeycomb. This is usually known as pull out. Refer to Figure.
NOTE
Unbond which occurs in composites can also occur in honeycomb structures with metal perforate and non-perforate surface layers.
Adhesive failure.
This is failure at the joint between the bonded surface and the adhesive. The adhesive stays on one of the surfaces.
For honeycomb structures, adhesive failure can be divided in to two types.
NOTE
The adhesive will stay on the surface layer at the locations related to the honeycomb cells.Cohesive failure.
This is failure in the adhesive material. The adhesive stays on each surface. Refer to Figure.
Unbond (or Disbond).
The separation of two bonded surfaces. Refer to Figure. There are two types of unbond as follows:
Cracked or split.
A crack or split through a composite laminate; is seen as a small opening in the composite surface layer or the complete composite thickness. It is usually caused when the material is hit or because of distortion. Refer to Figure.
Fretted.
This is seen as a rubbed surface with the protection removed from the fibers, this can result in broken fibers. Refer to Figure.
Eroded.
This is seen as the removal of the surface resin layer caused because of the effects of weather. When the protection is removed from the fibers it can make the surface rough. It is possible for the fibers to become eroded. Refer to Figure.
Cavity.
This is an empty space that occurs usually in the surface layers with a large quantity of resin or infilled locations. Refer to Figure.
Sharp object.
Usually a split or a crack, possibly with related delamination near the damage. Refer to Figure.
NOTE
In honeycomb sandwich structures, impact damage could include other types of damage to the honeycomb.Blunt object.
Usually delamination of the layers with a possible related split, crack or unbond. Damage usually extends out of the immediate location of the damage. Refer to Figure.
Impact damage.
There are two groups of impact damage:
Torn fibers.
Strips of lifted surface fibers, pulled and peeled along the fiber length. Damage is frequently made larger because of the air flow until the fiber breaks. Refer to Figure.
Blistered.
This is bubbles on the surface caused because of local delamination below the surface layer. Refer to Figure.
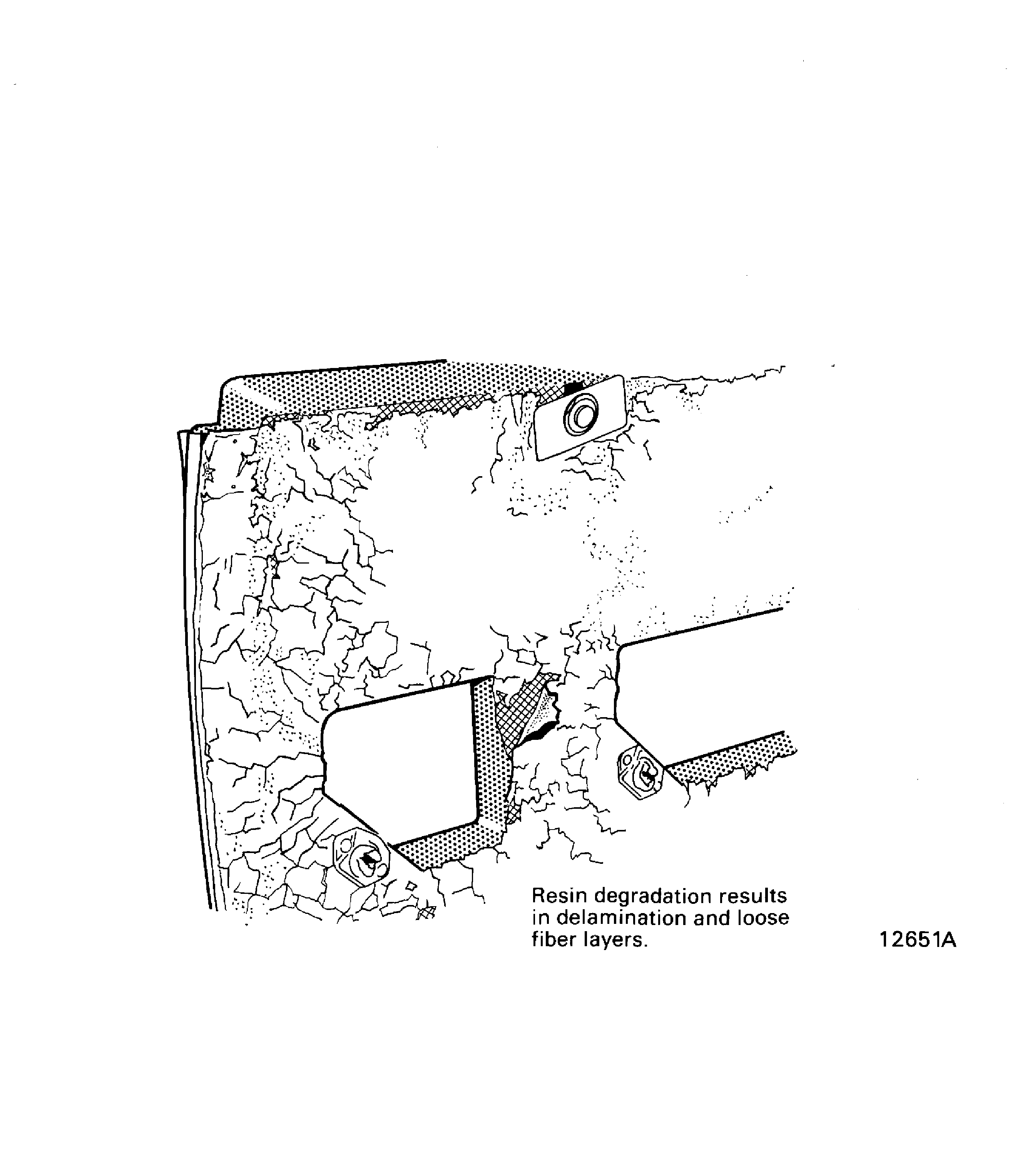
Resin degradation.
This is deterioration of the resin of a composite laminate, at the surface and also internally, which results in delamination and loose fibers. Refer to Figure.
Fire or heat damage.
This can cause one or all of the conditions that follow:
SUBTASK 70-02-02-350-003 Types of Damage to Composite Materials
Figure: Battered
Battered
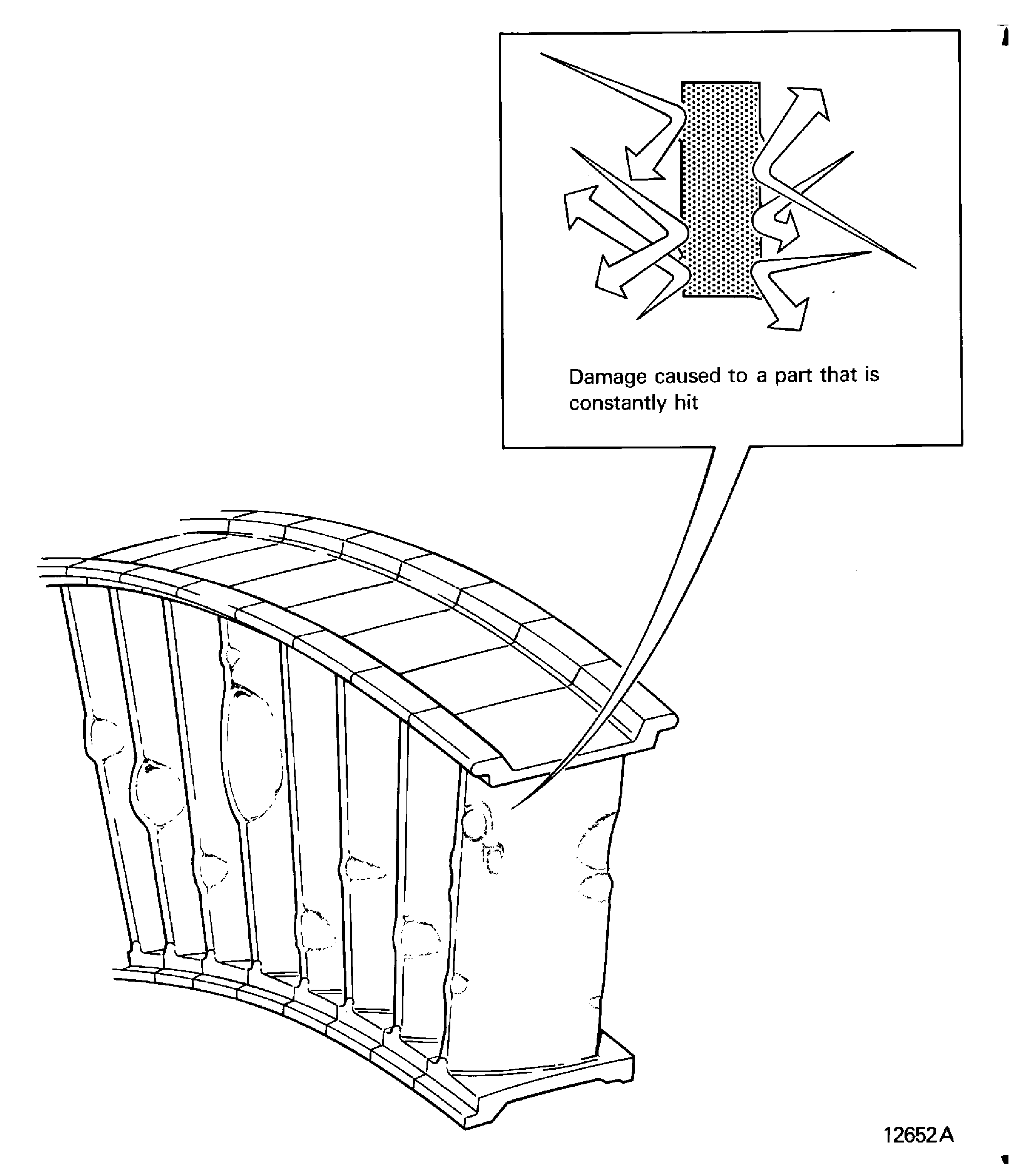
Figure: Bent
Bent
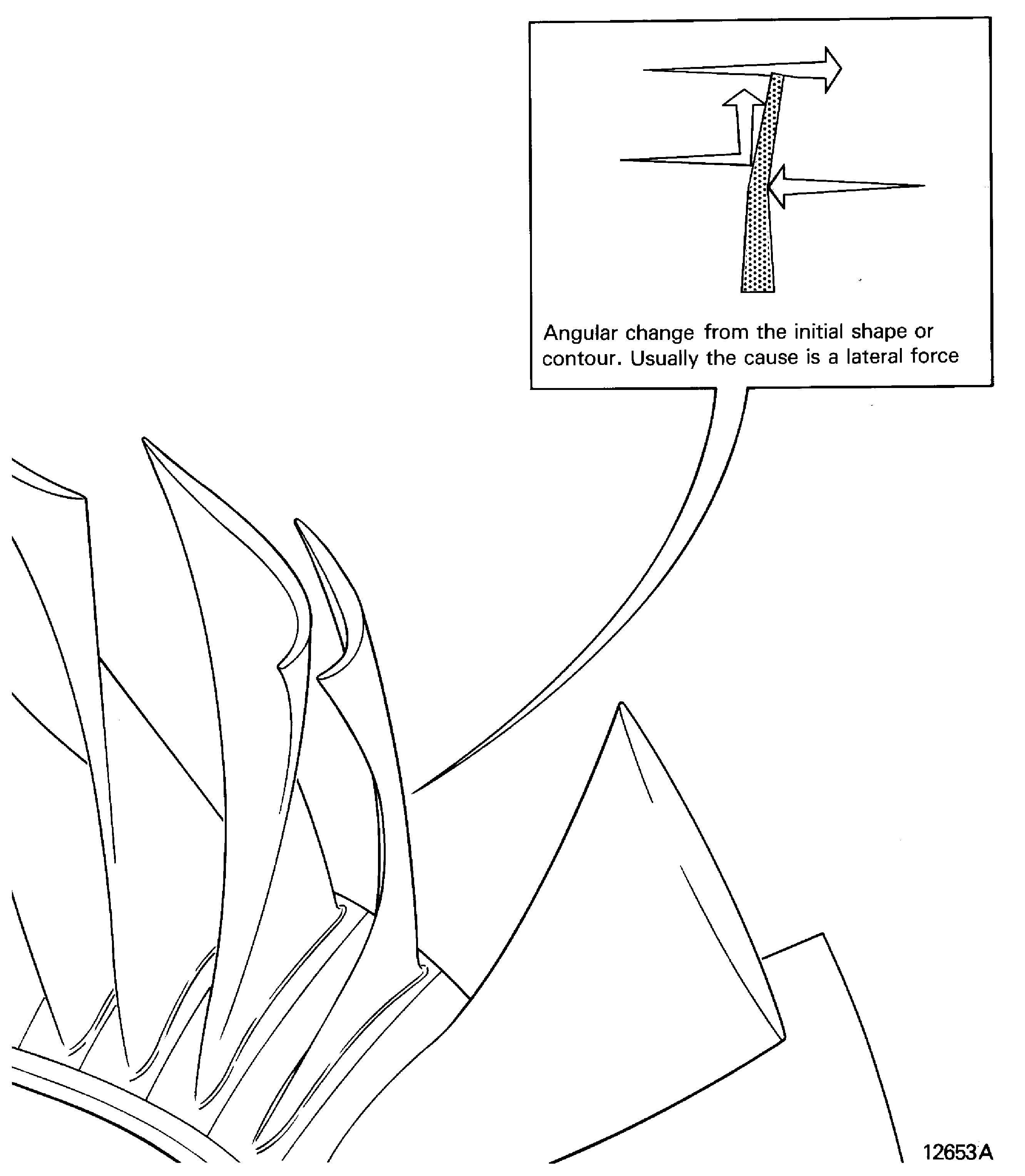

Figure: Bowed
Bowed
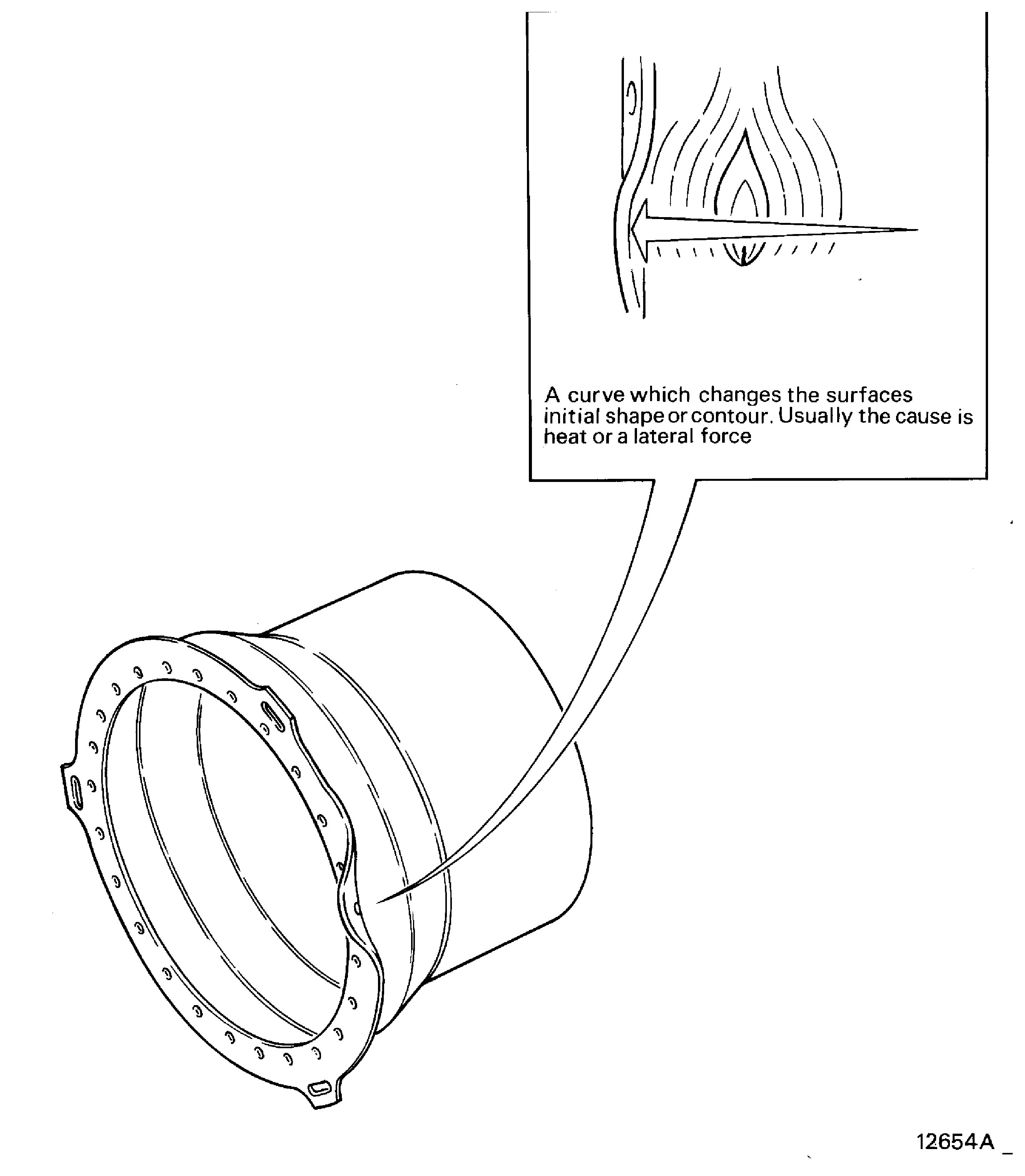
Figure: Brinelled
Brinelled
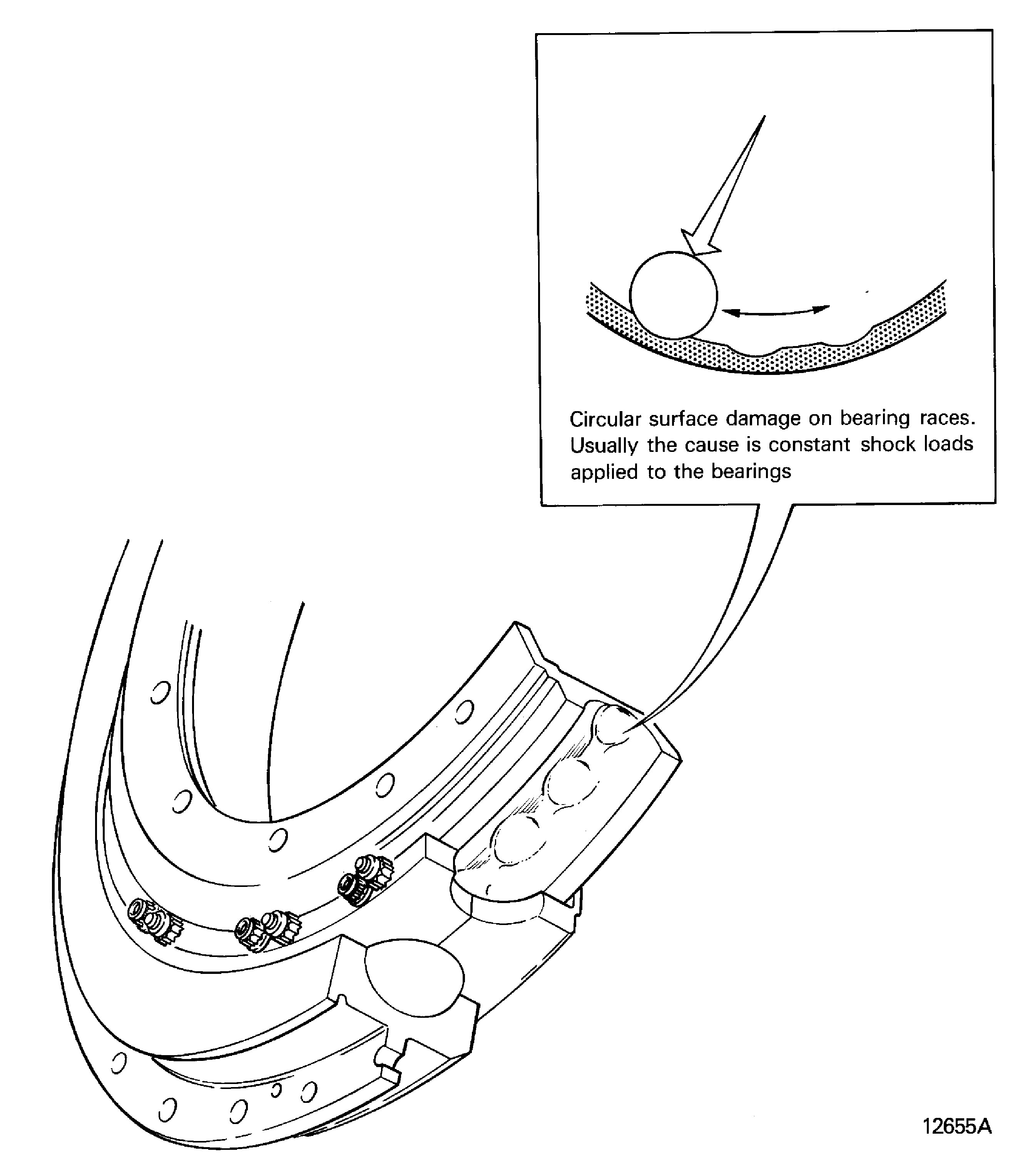
Figure: Broken
Broken
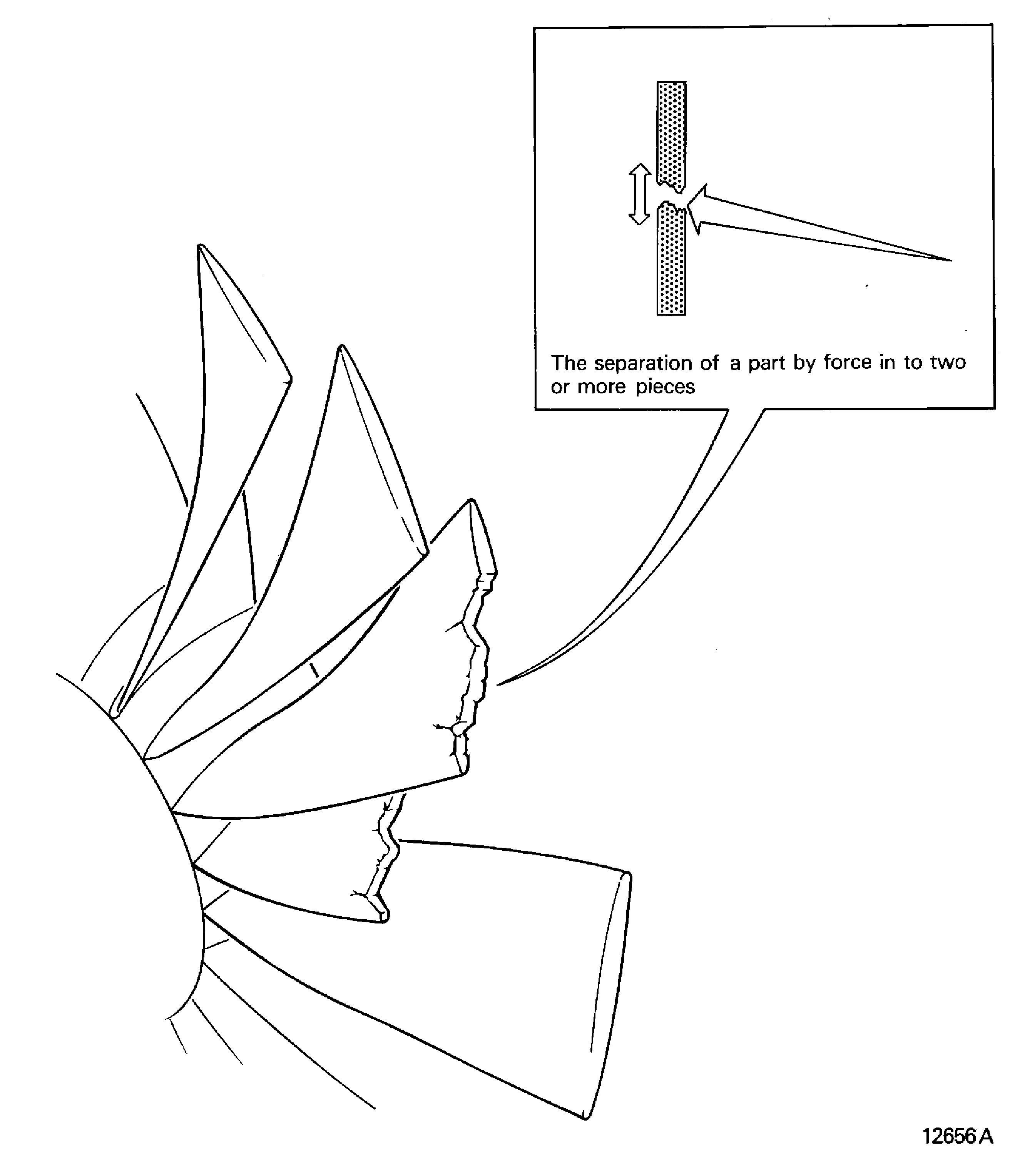
Figure: Bulge
Bulge
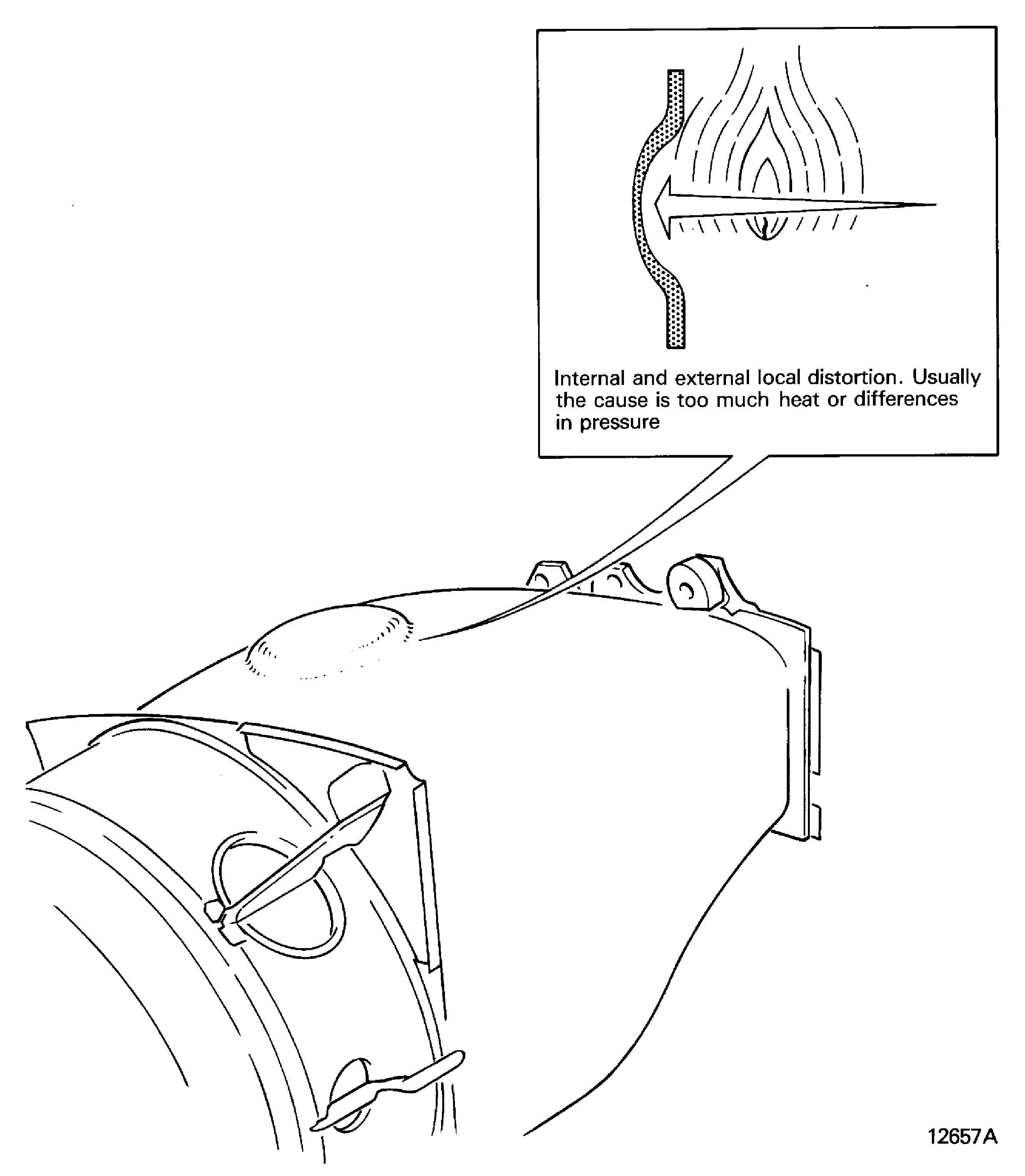
Figure: Burned
Burned
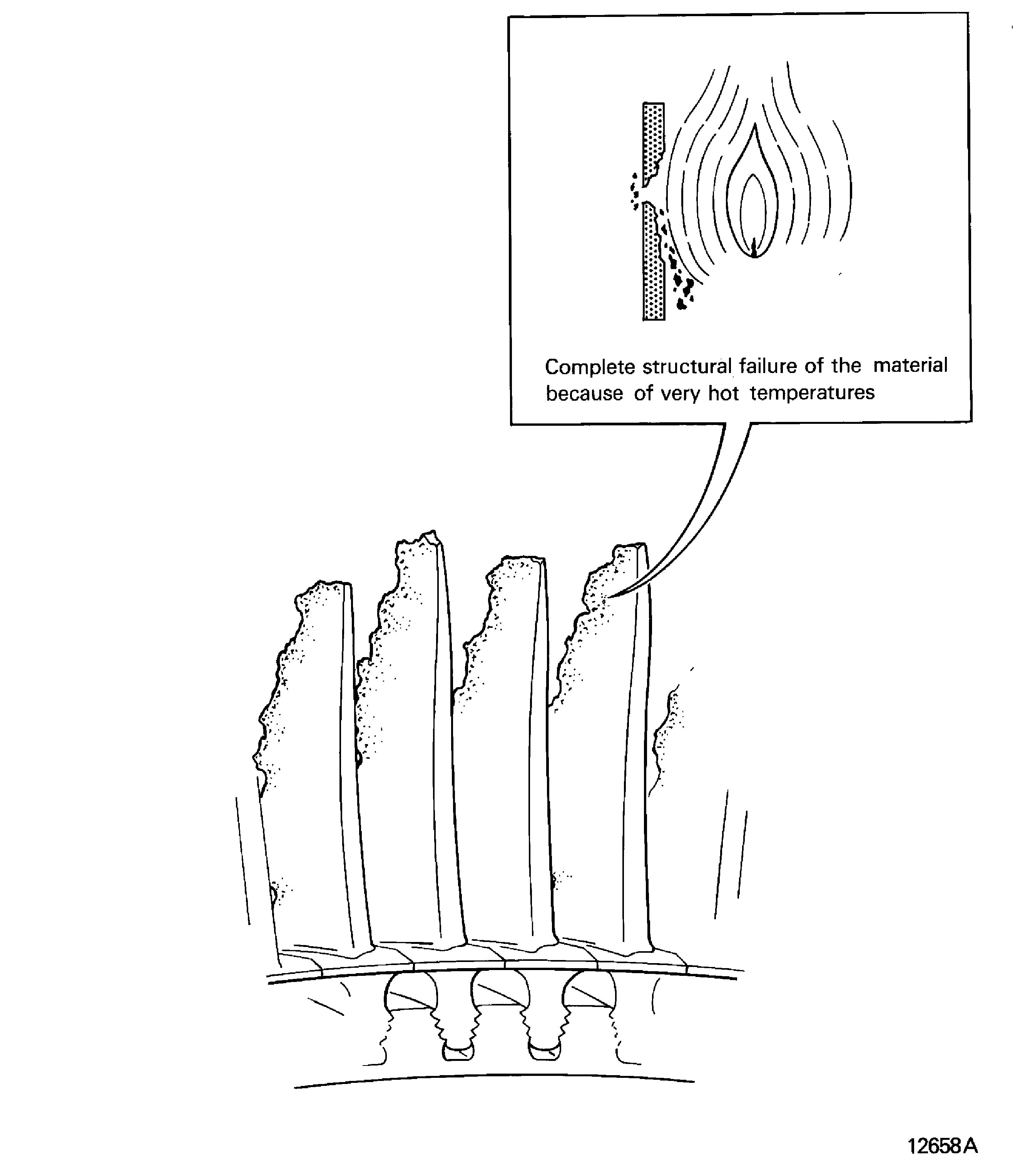
Figure: Carboned
Carboned
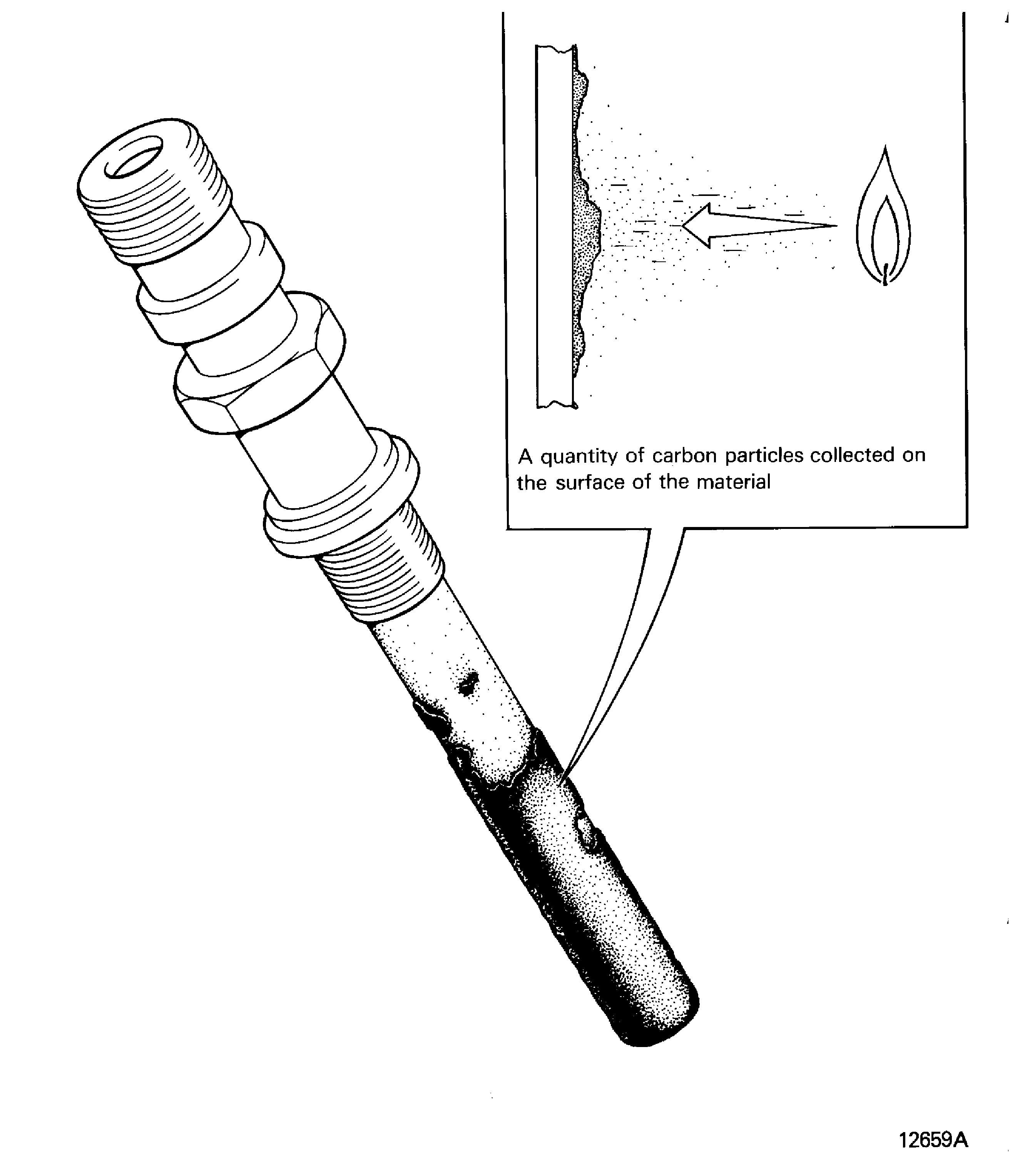
Figure: Collapsed
Collapsed
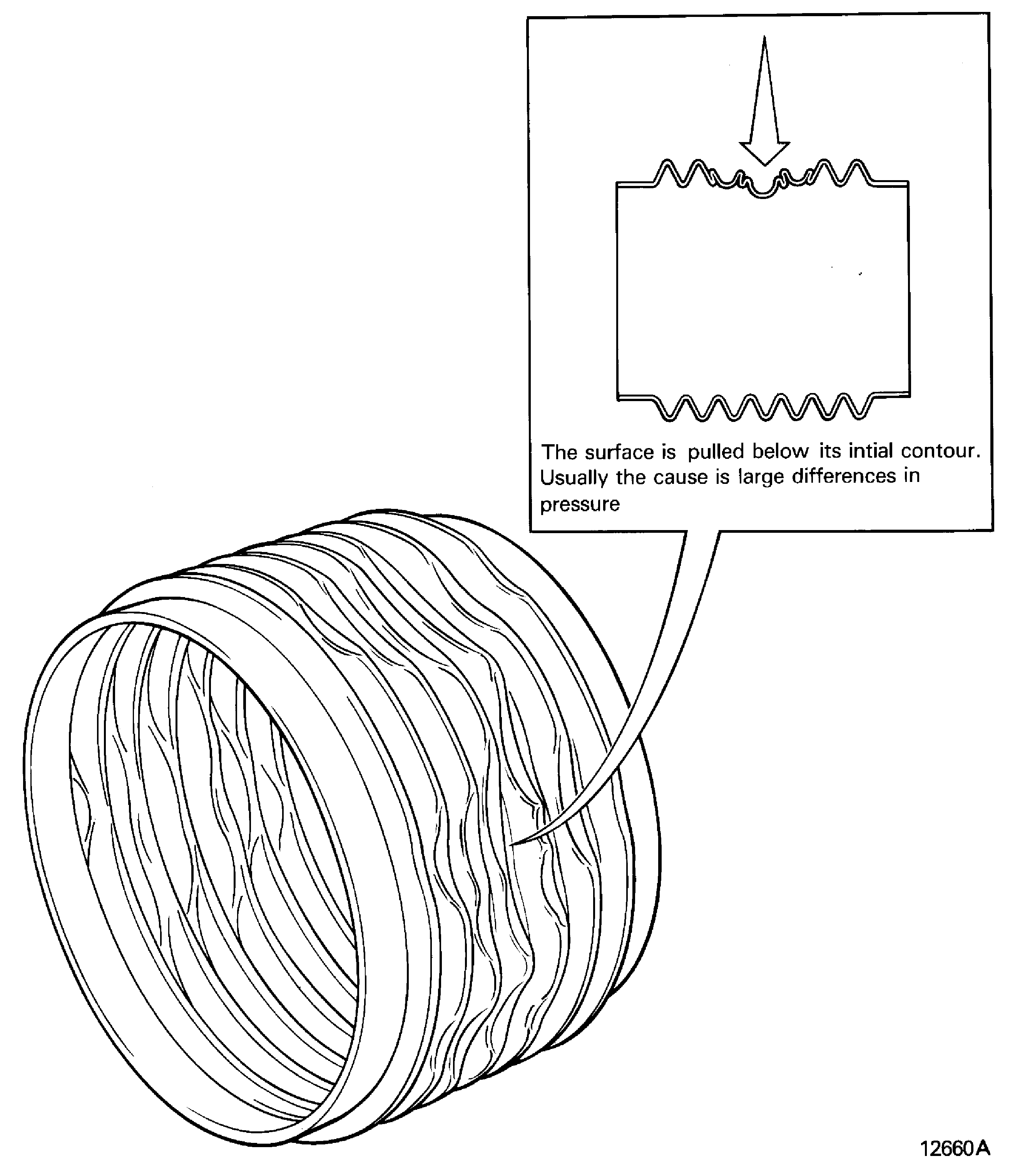
Figure: Crack
Crack
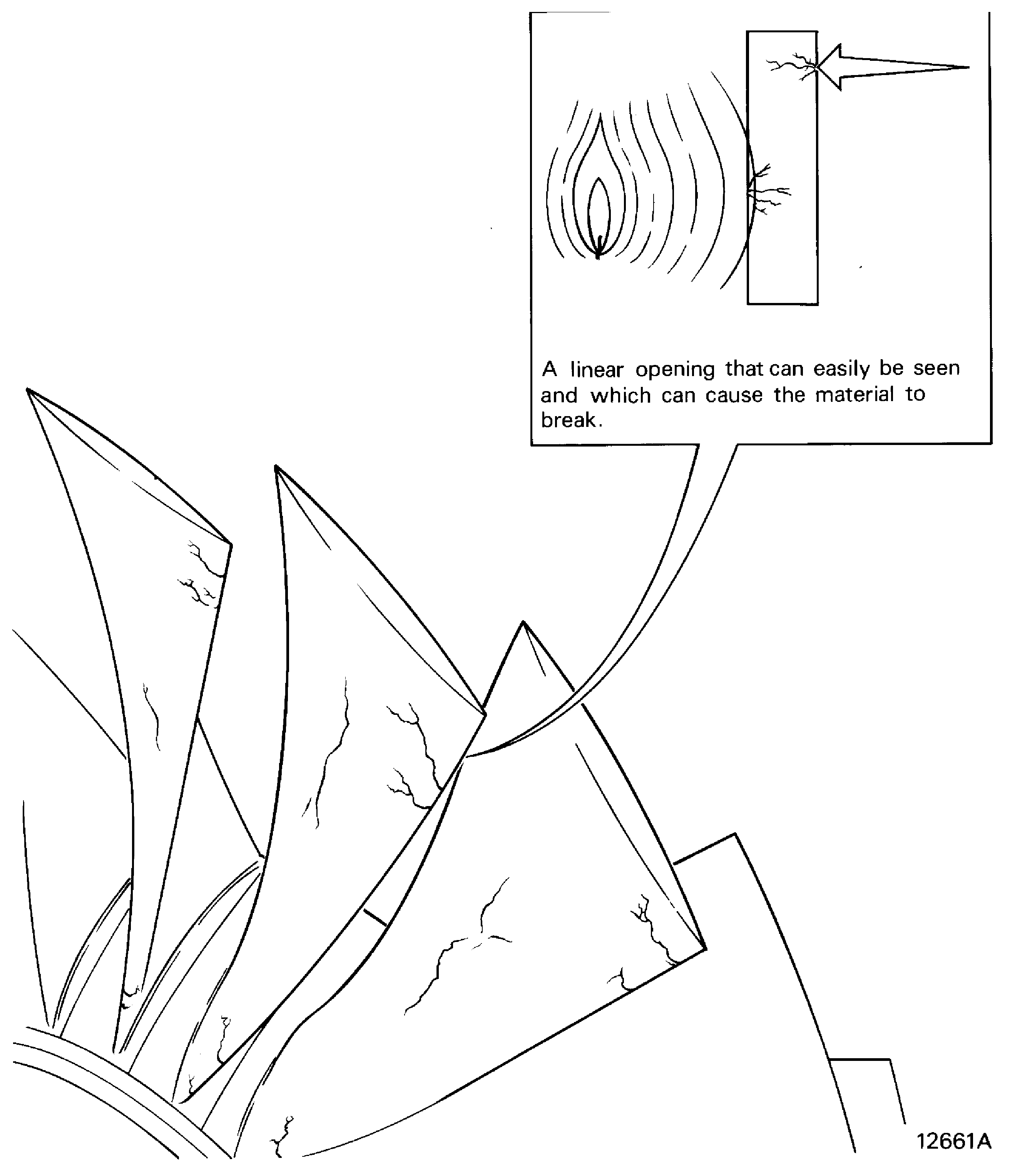
Figure: Curled
Curled
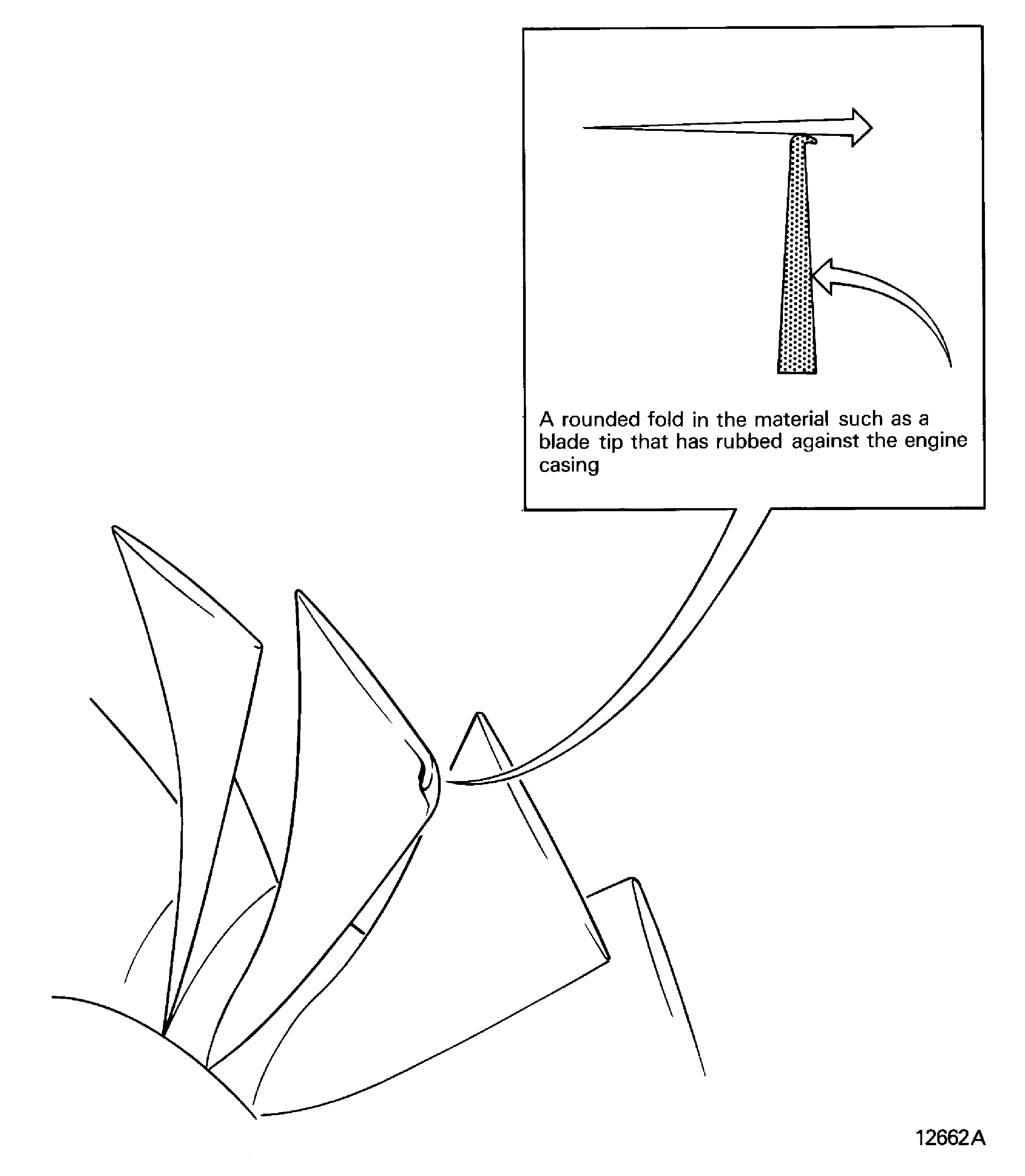
Figure: Dent
Dent
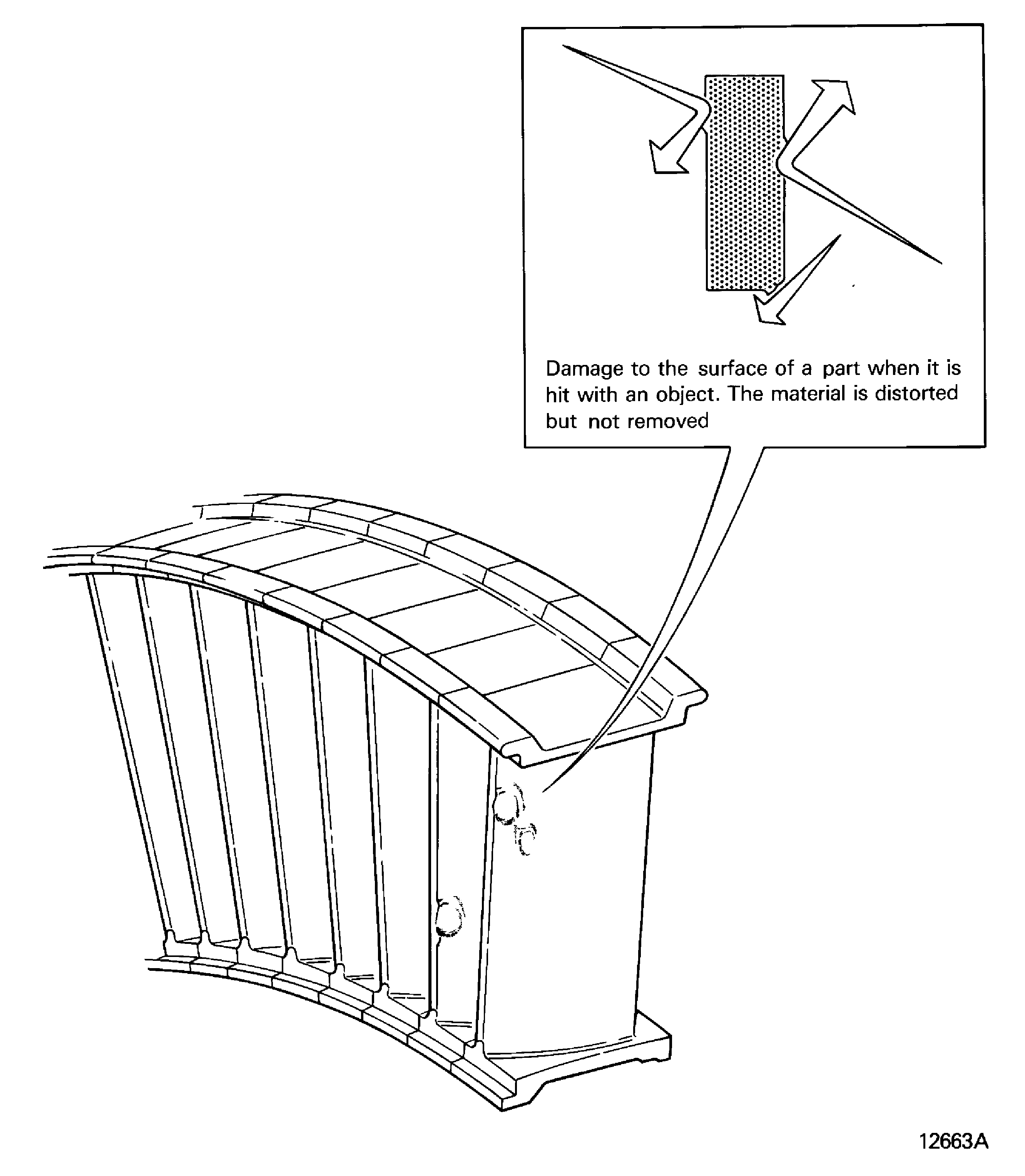
Figure: Deposits
Deposits
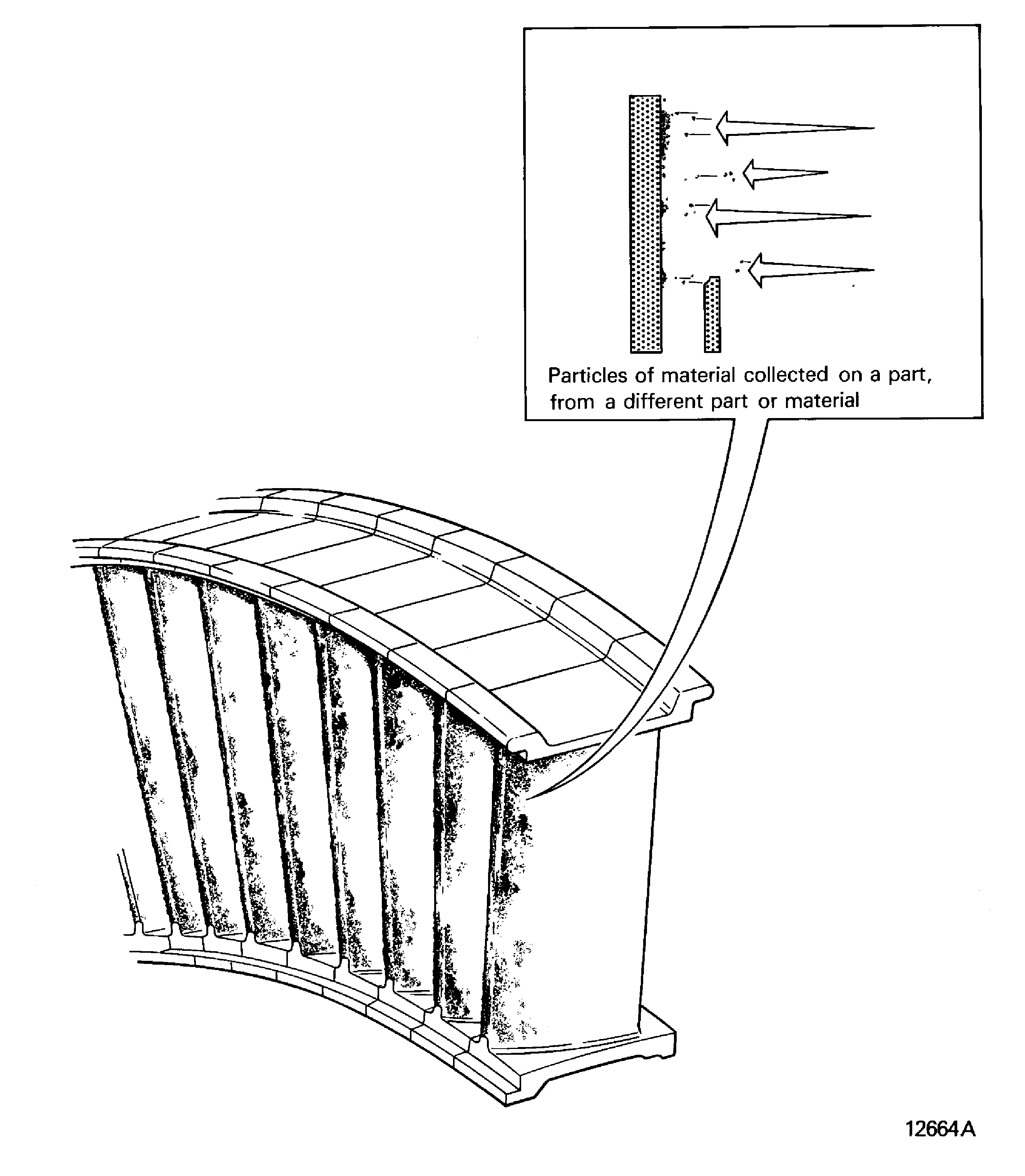
Figure: Disintigrated
Disintigrated
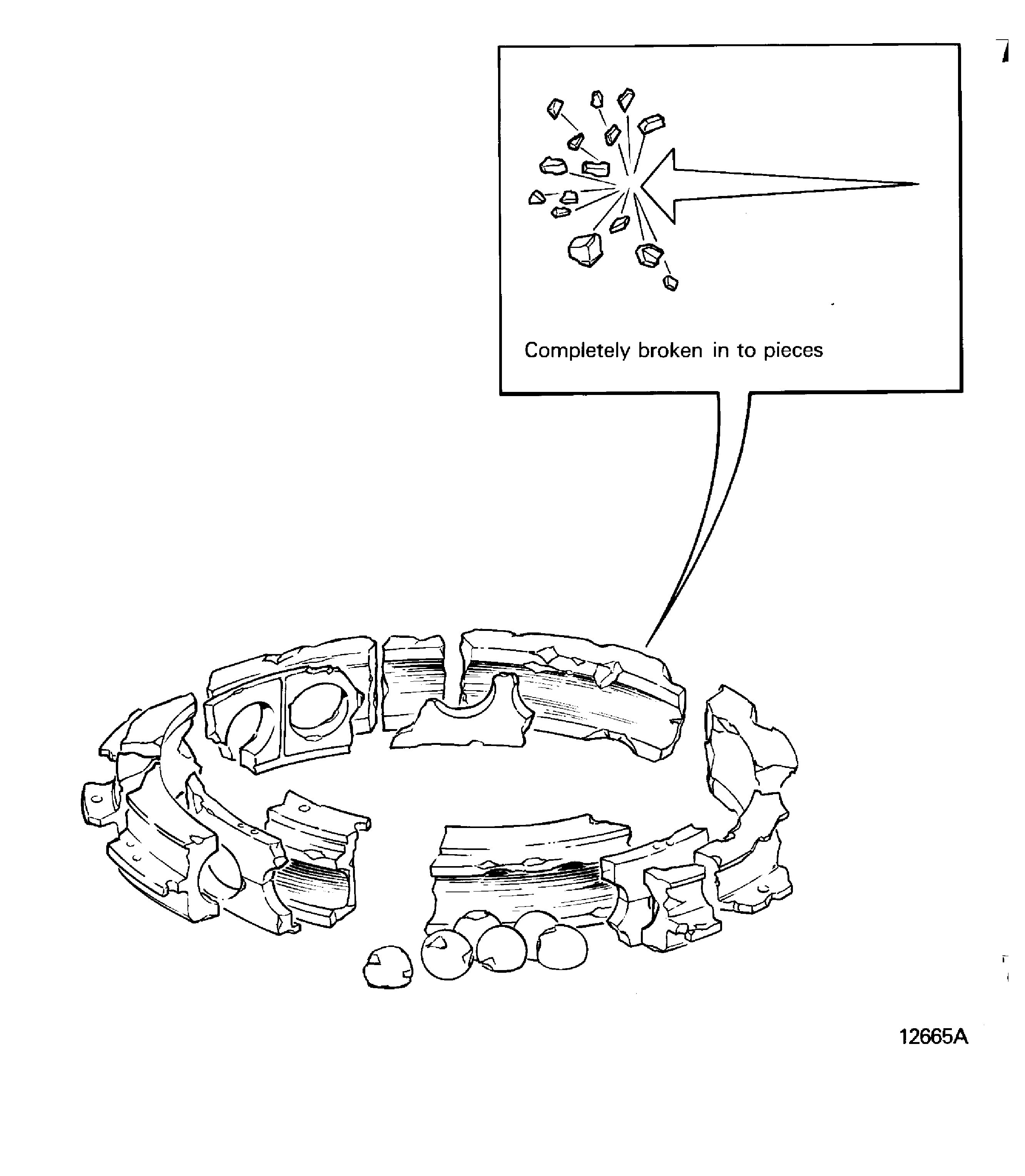
Figure: Distorted
Distorted
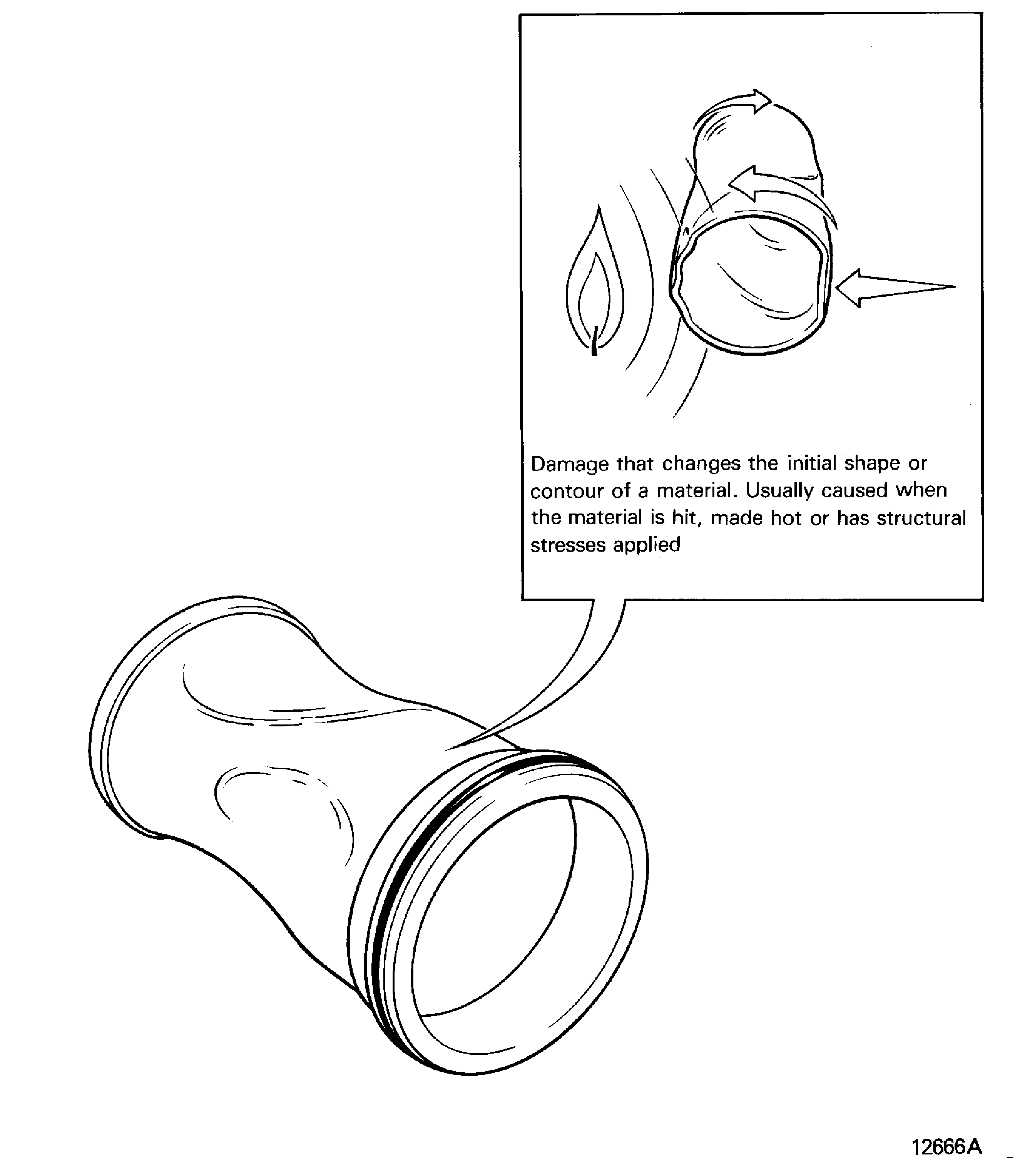
Figure: Galled
Galled
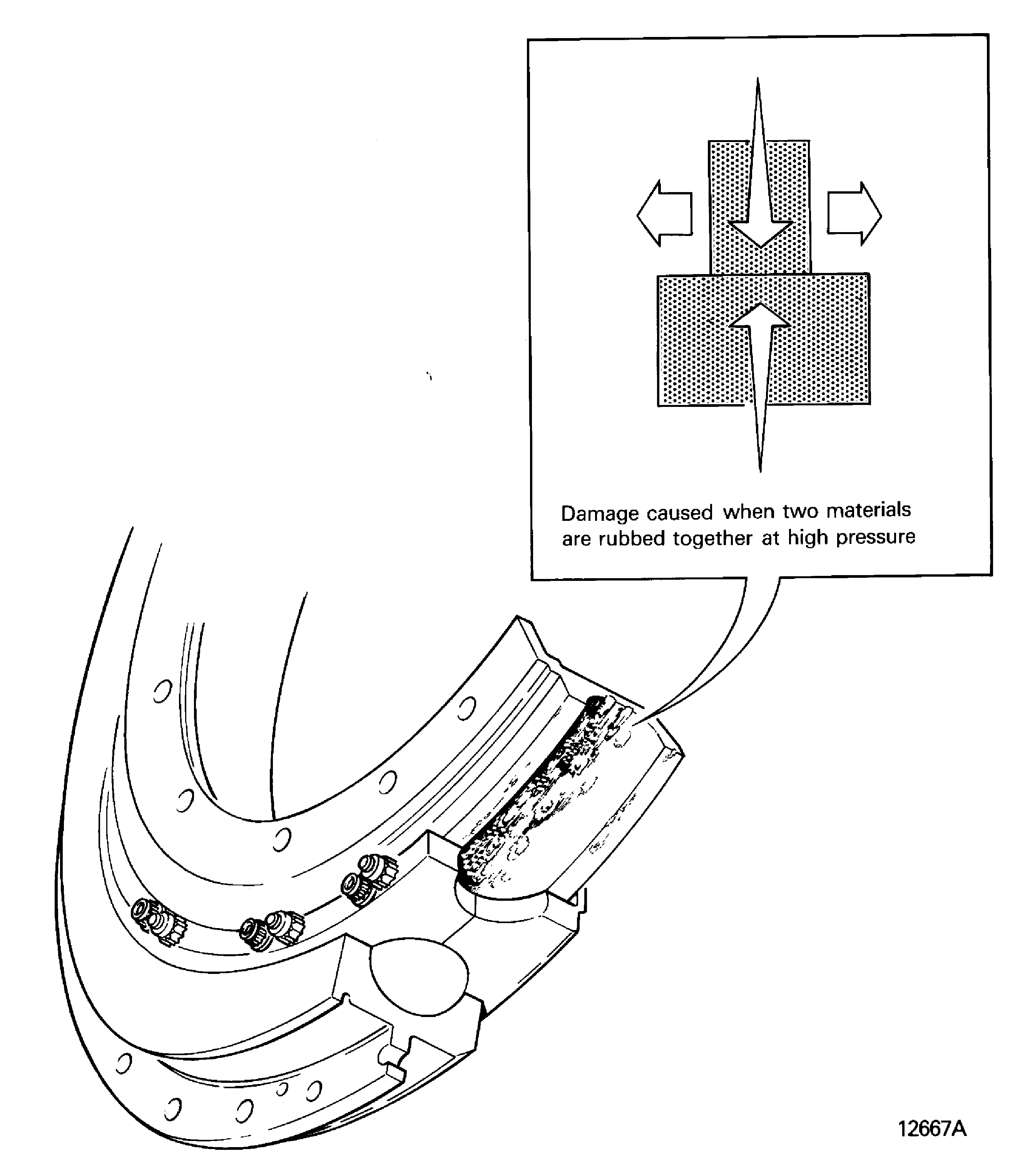
Figure: Gouge
Gouge
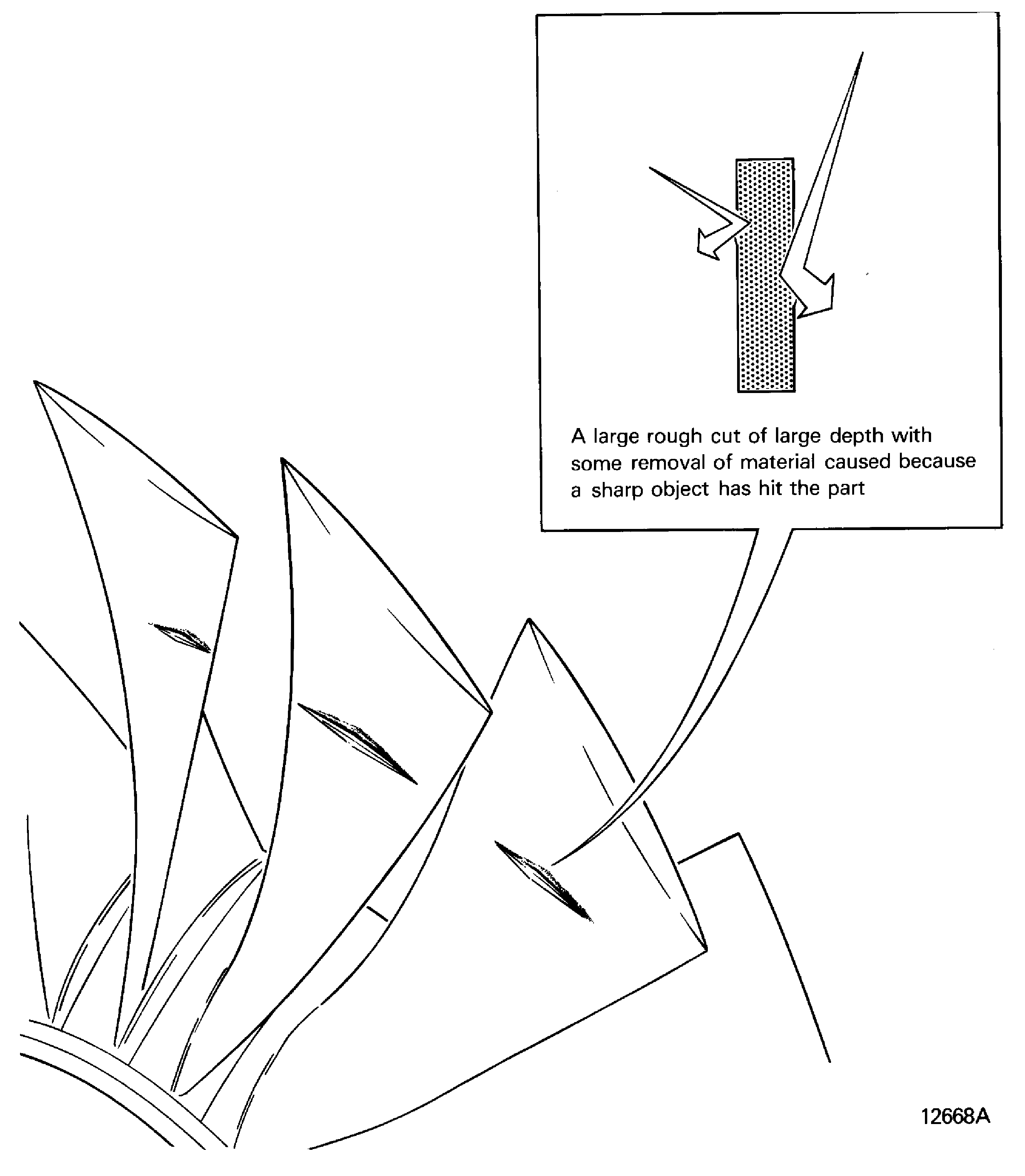
Figure: Nick
Nick
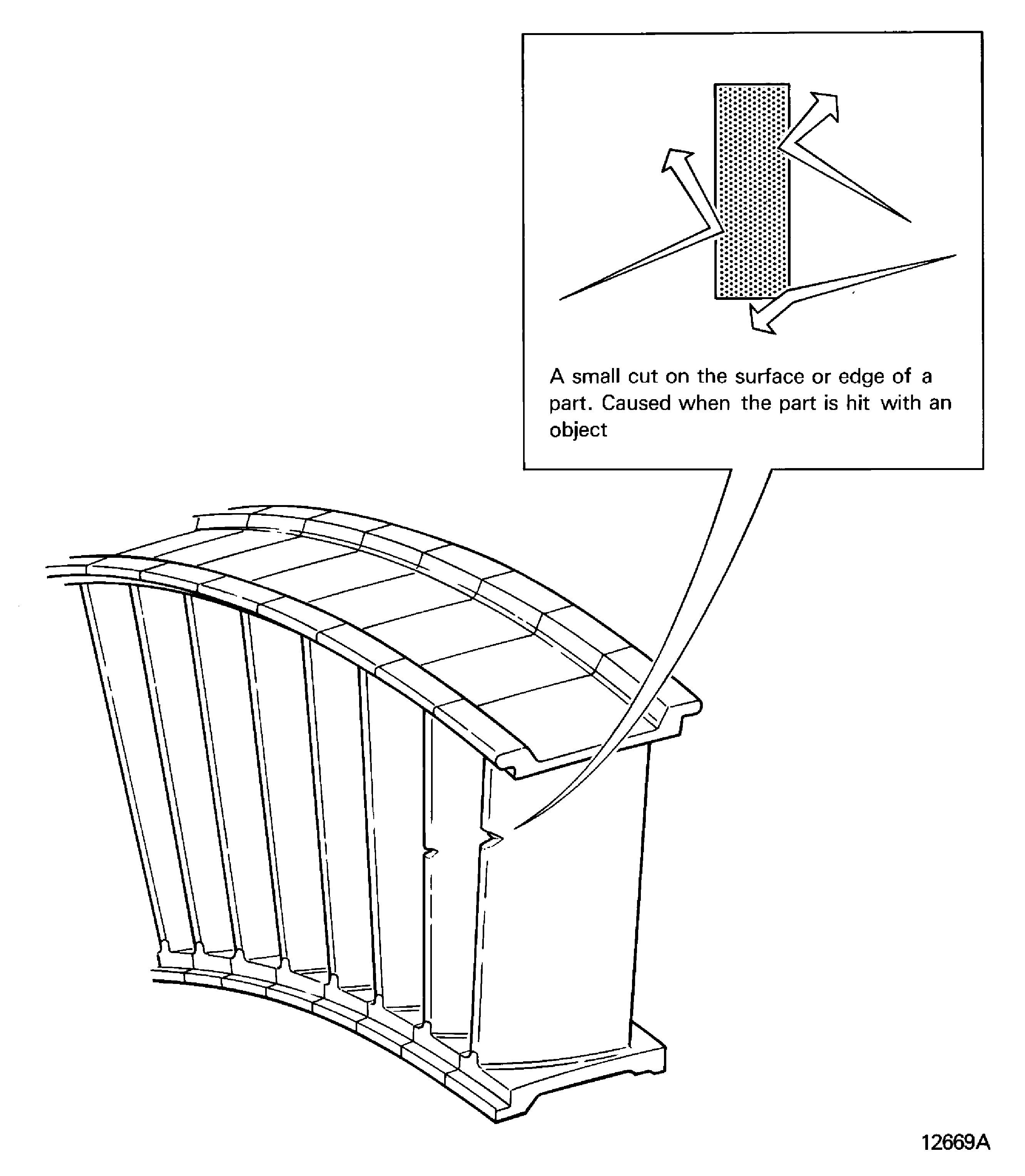
Figure: Overheated
Overheated
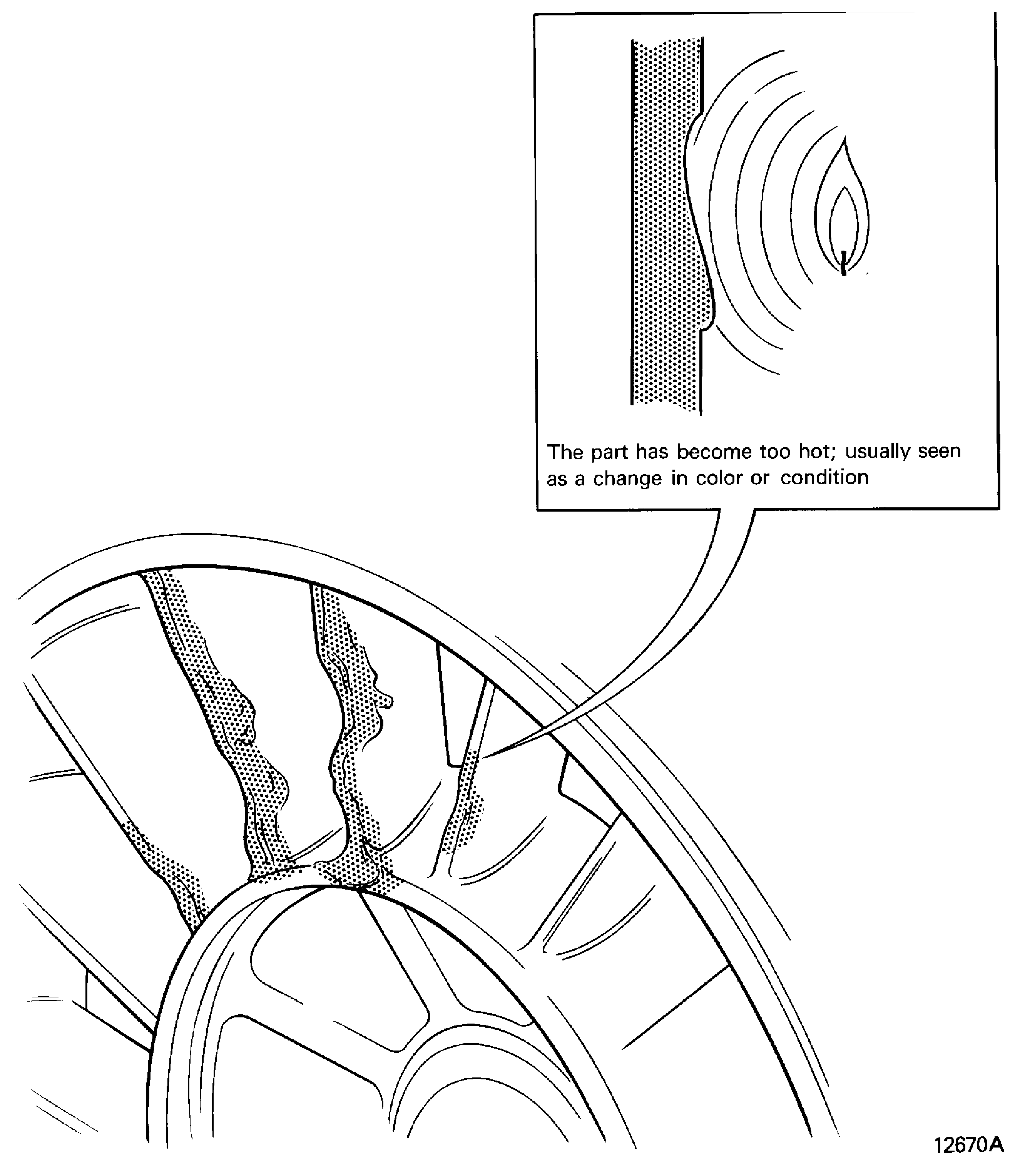
Figure: Peeled
Peeled
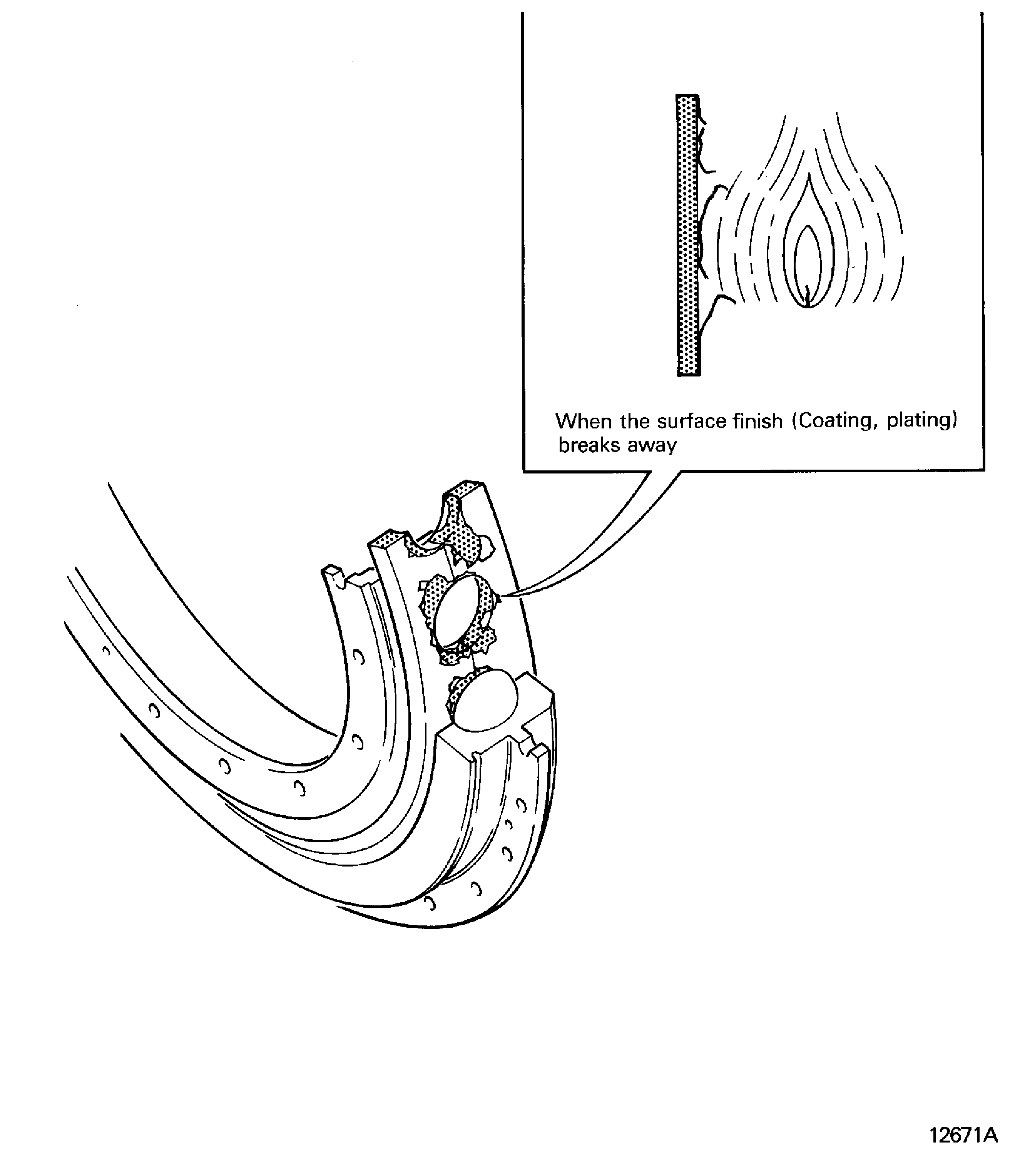

Figure: Pick-up
Pick-up
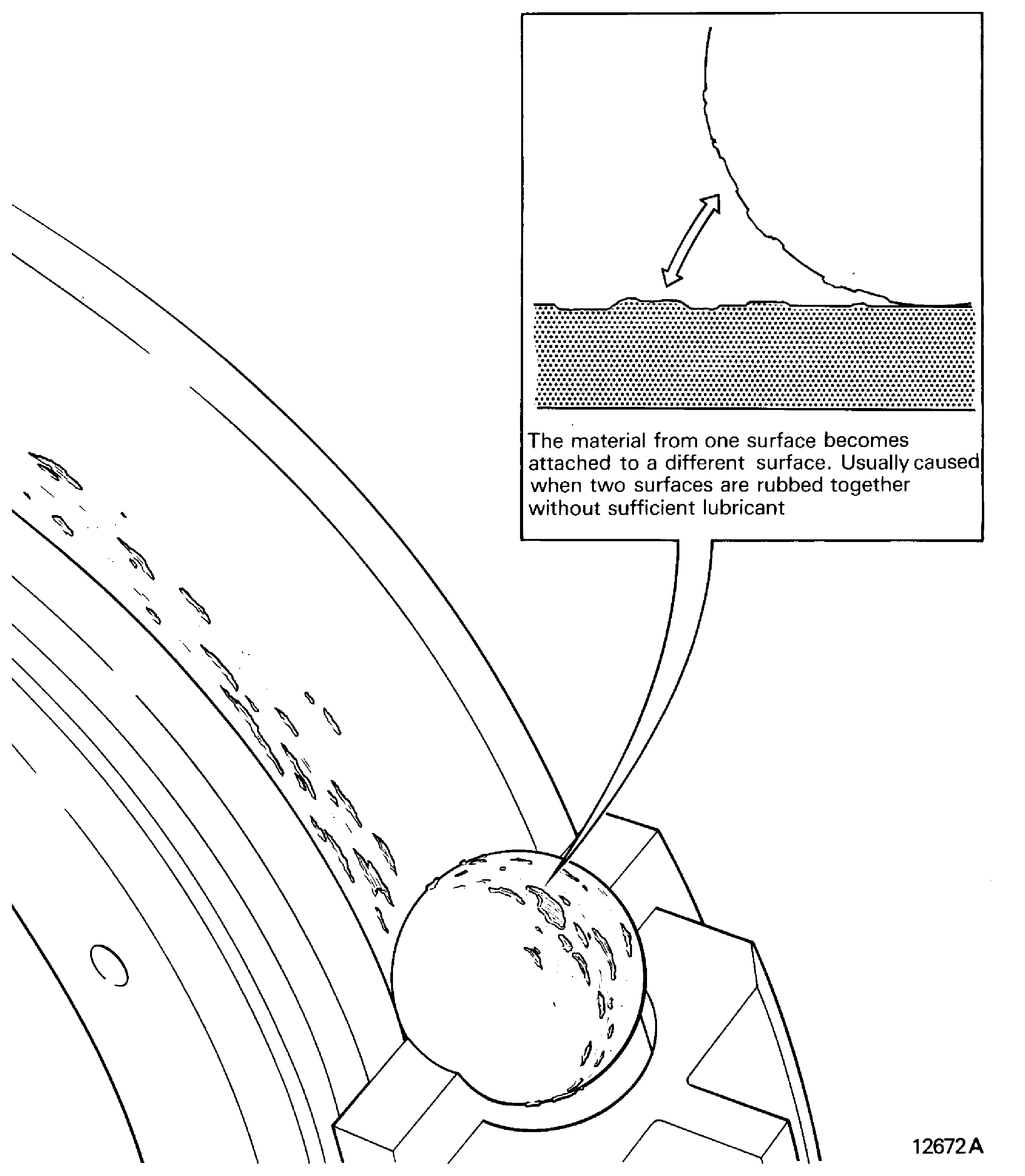
Figure: Pitted
Pitted
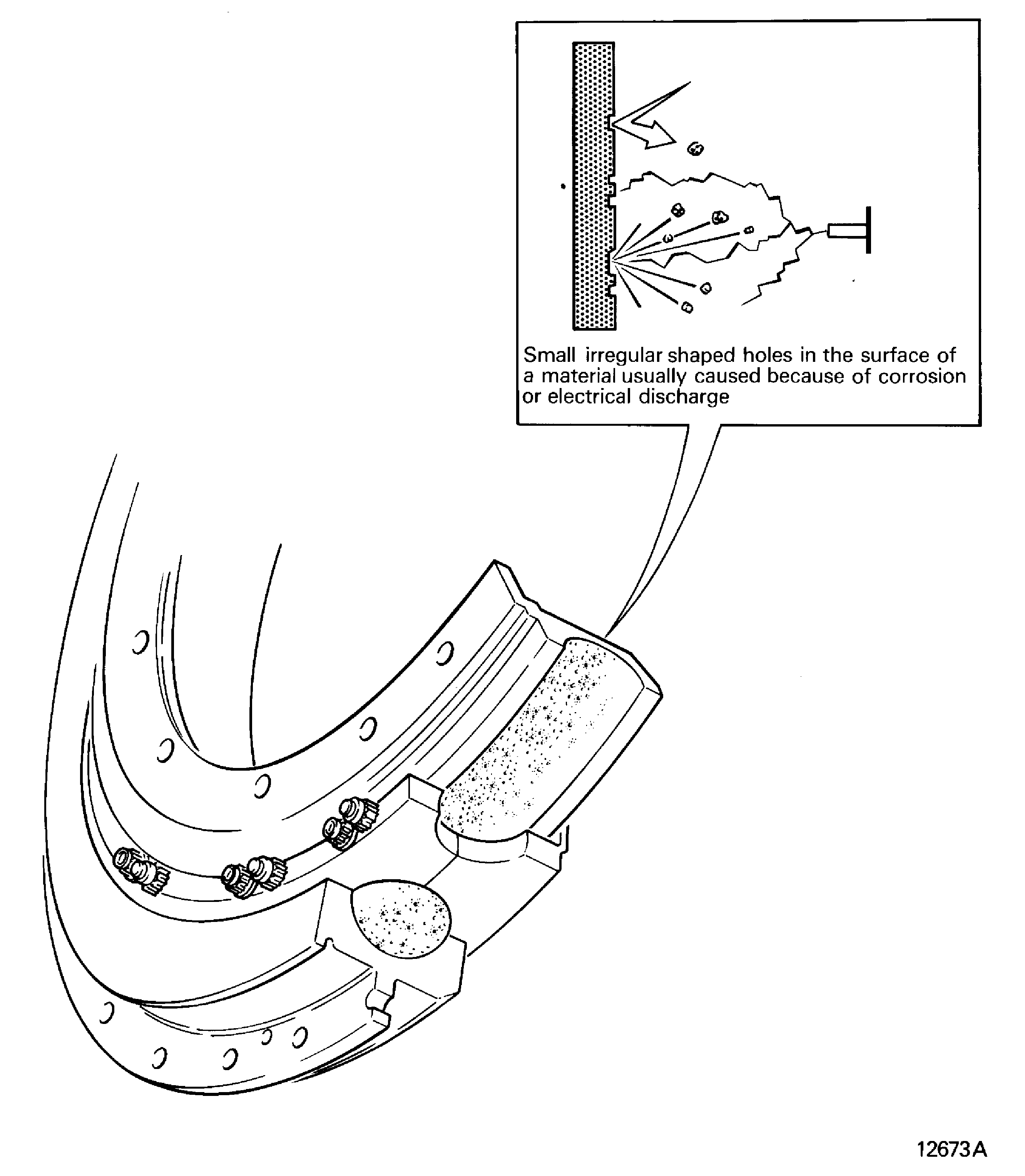
Figure: Porous
Porous
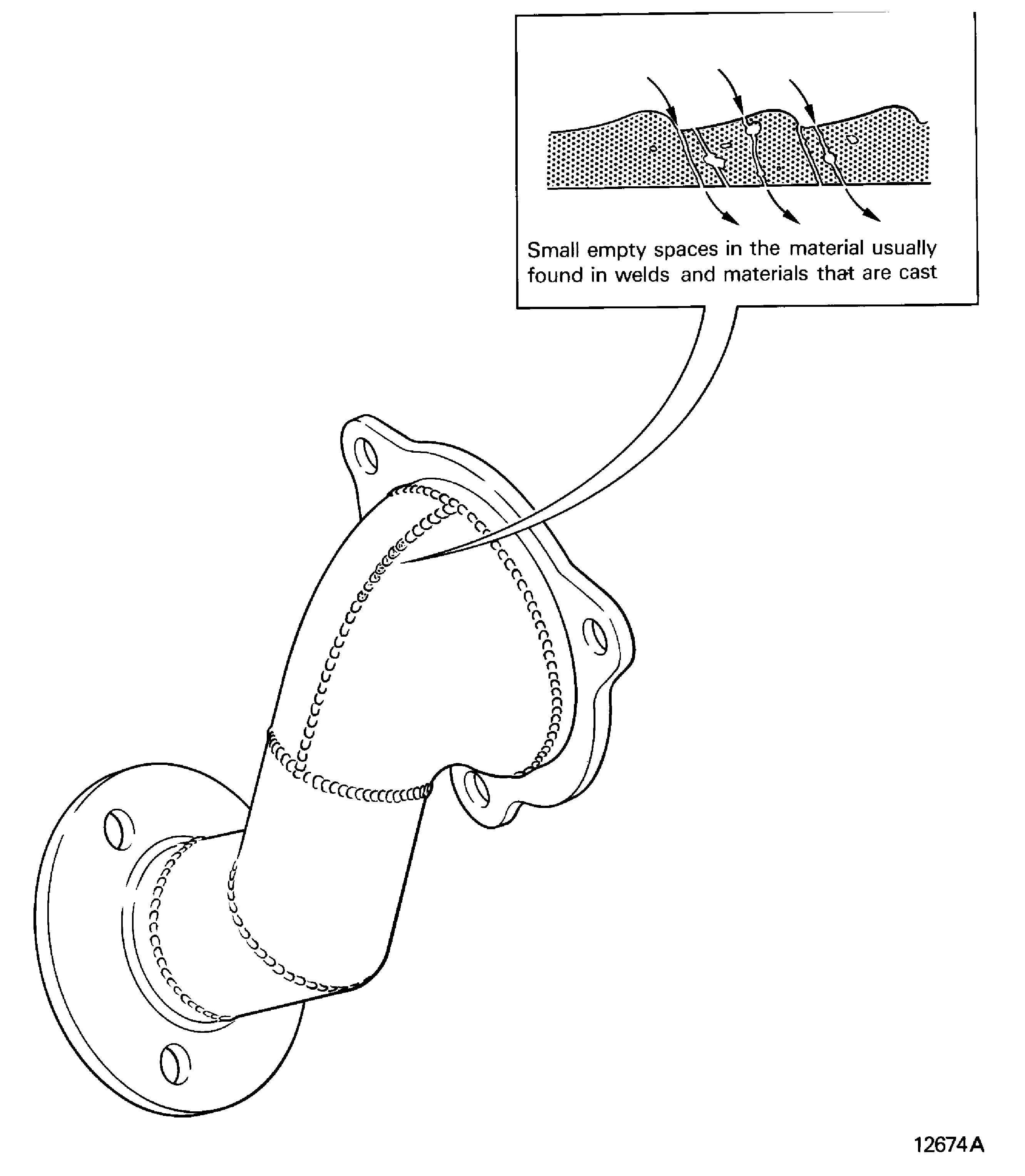
Figure: Rolled-over
Rolled-over
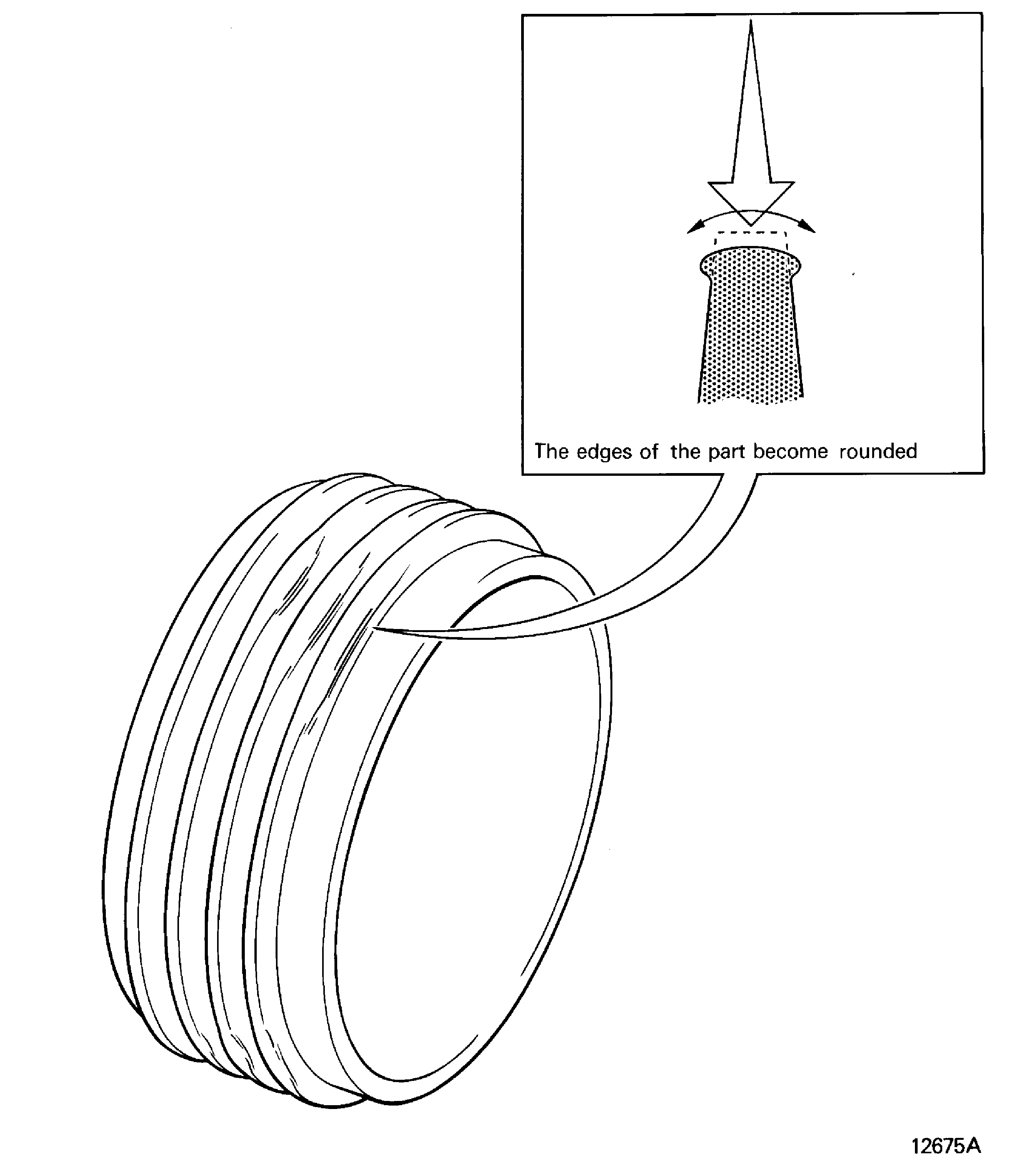
Figure: Ruptured
Ruptured
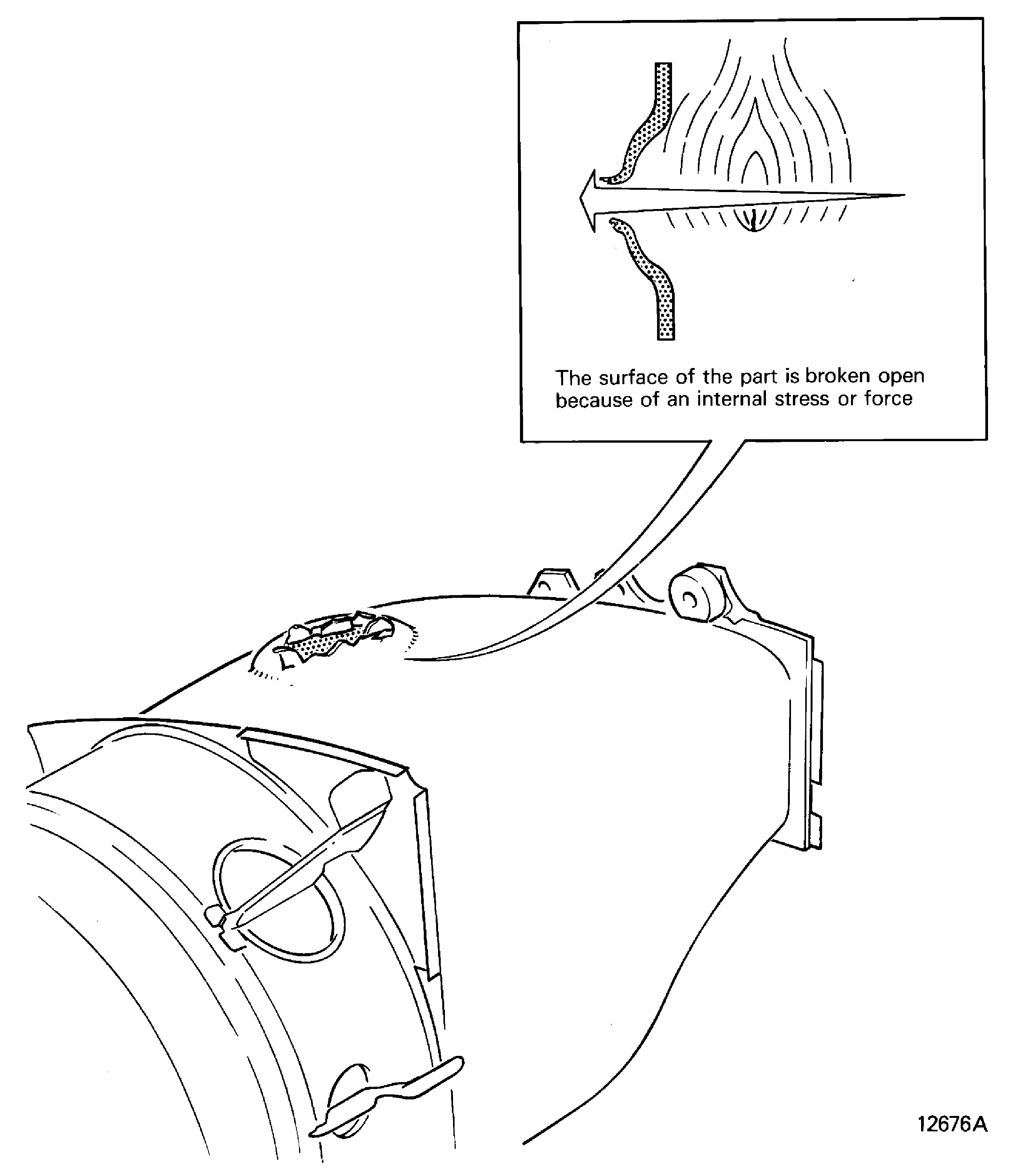
Figure: Scored
Scored
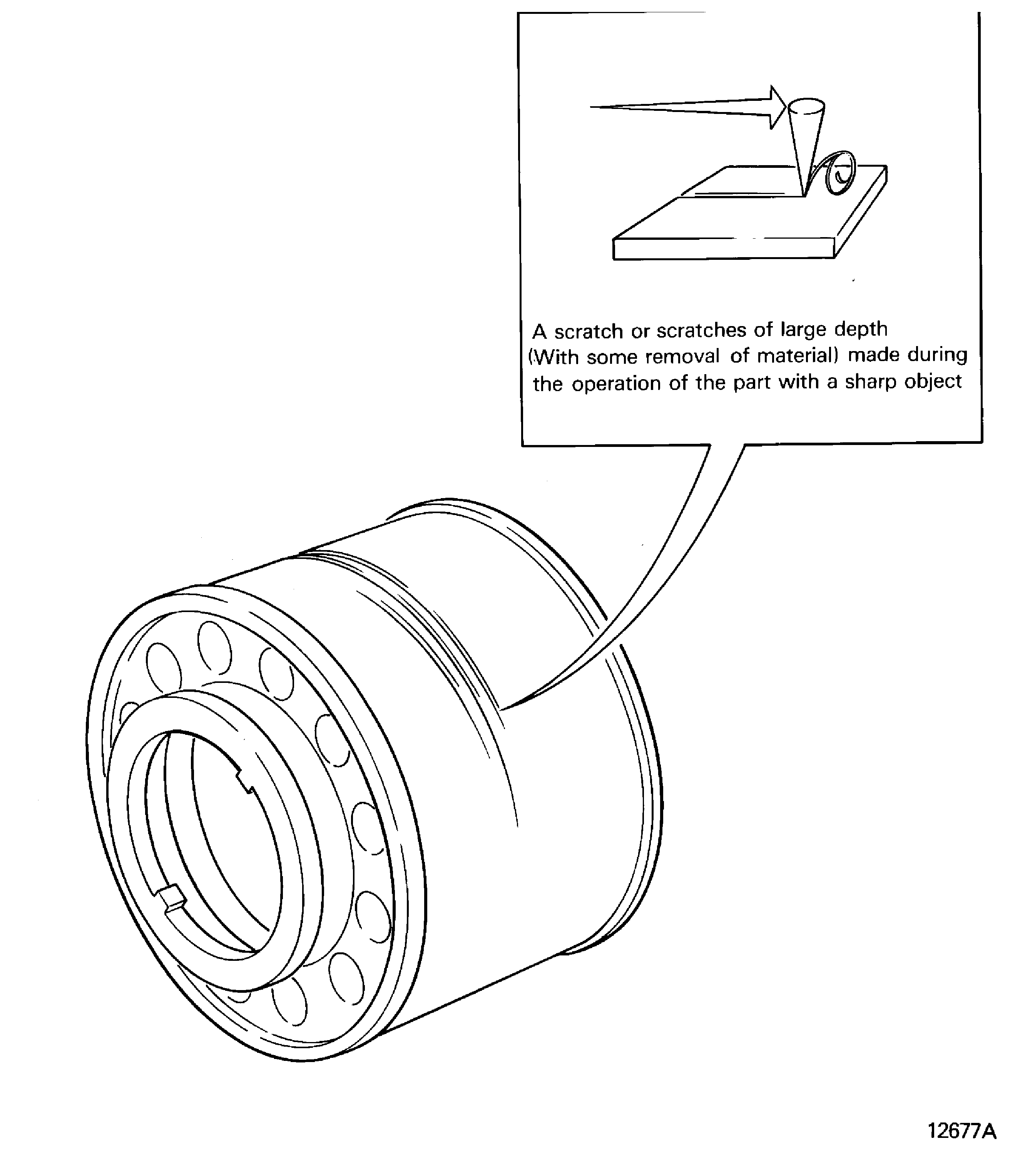
Figure: Scratch
Scratch
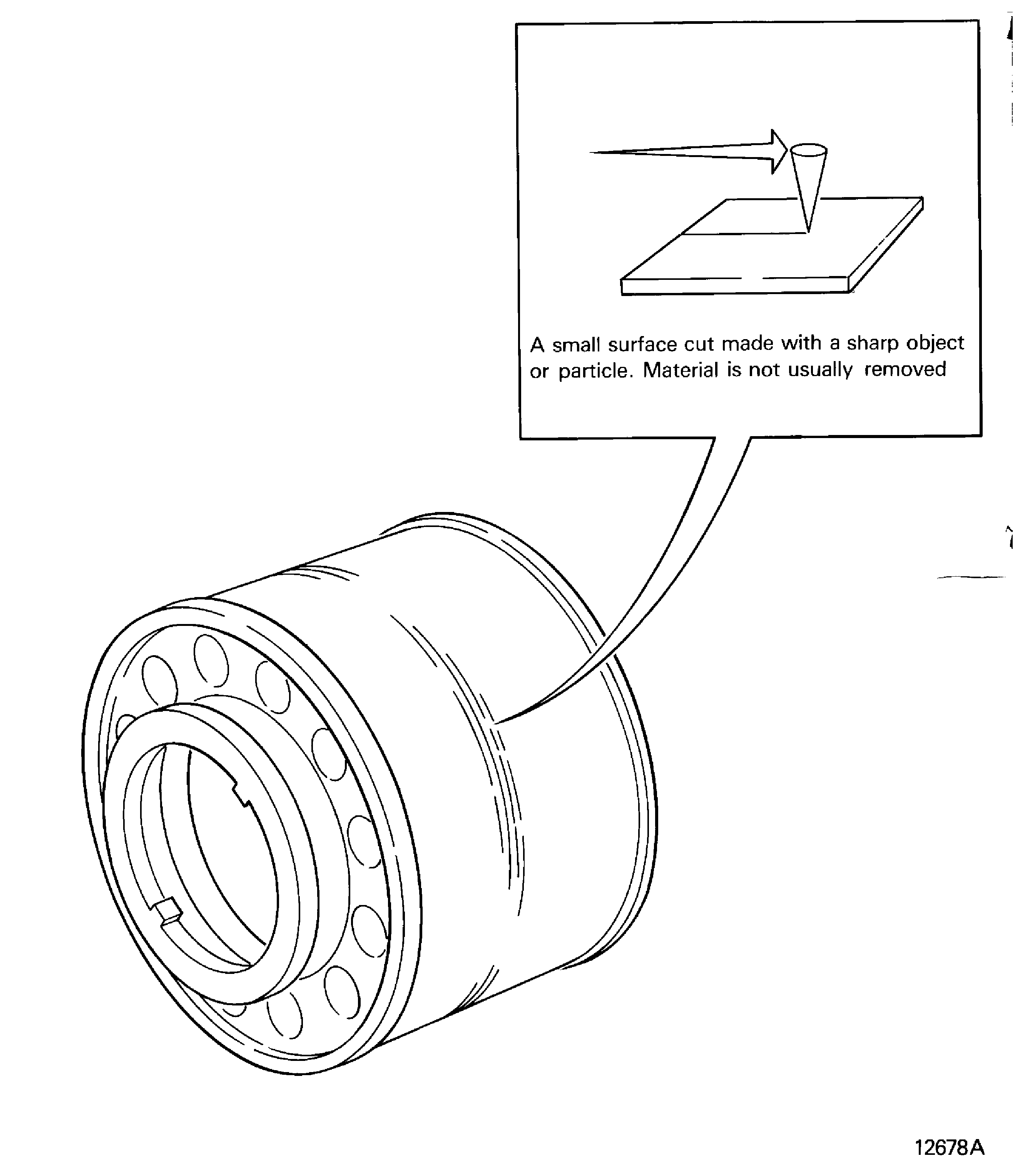
Figure: Sheared
Sheared
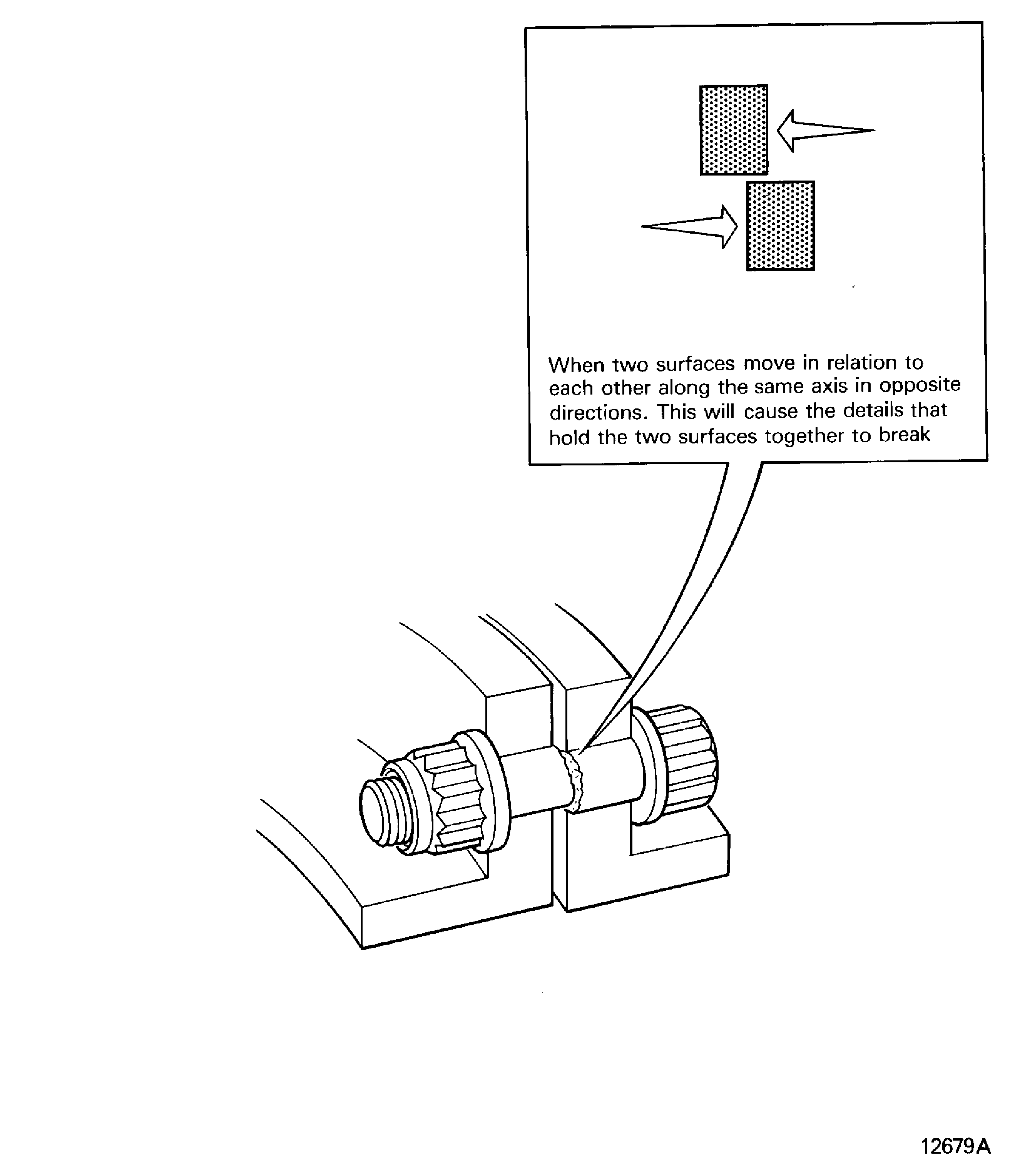
Figure: Skidding
Skidding
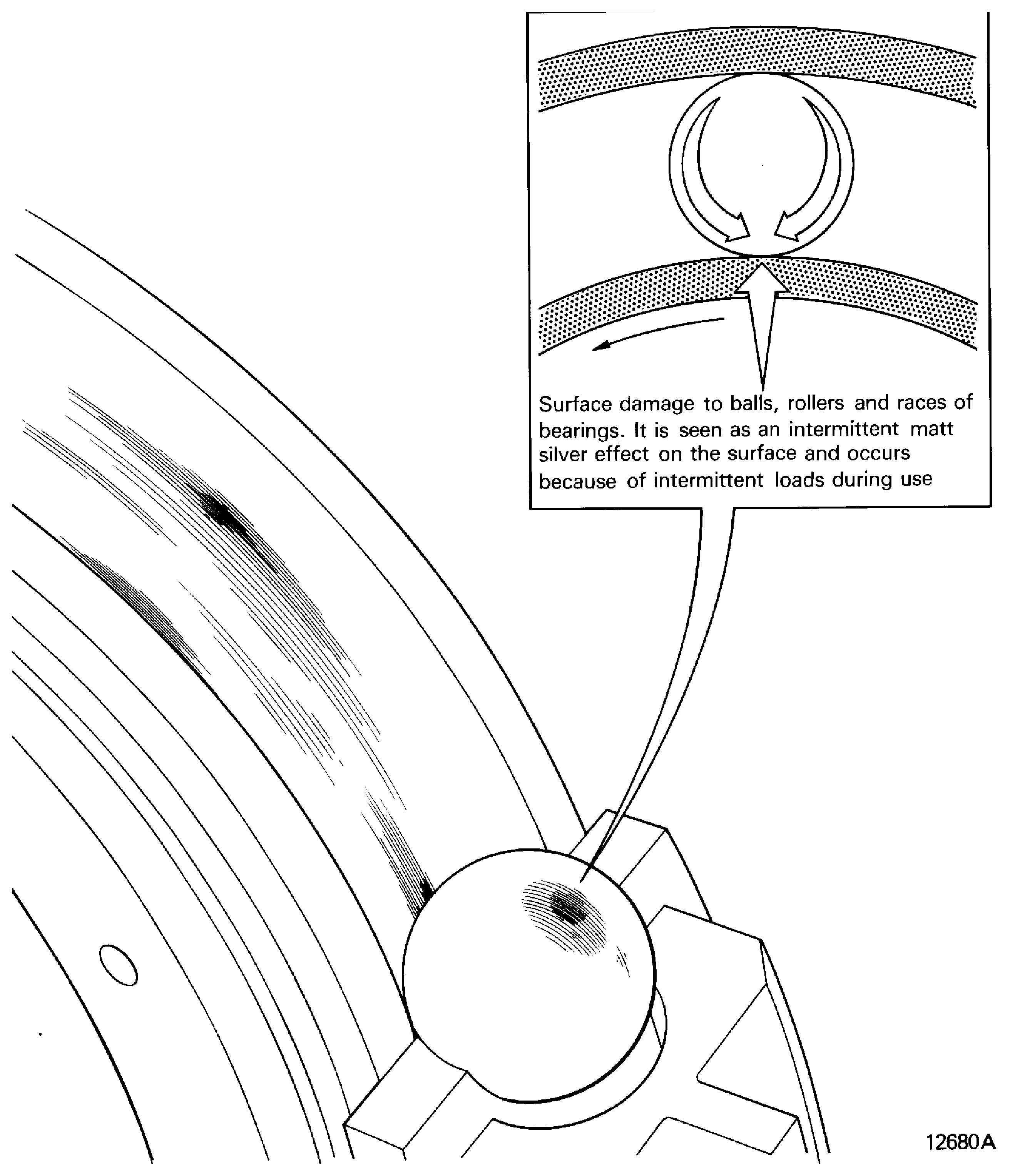
Figure: Spalled
Spalled
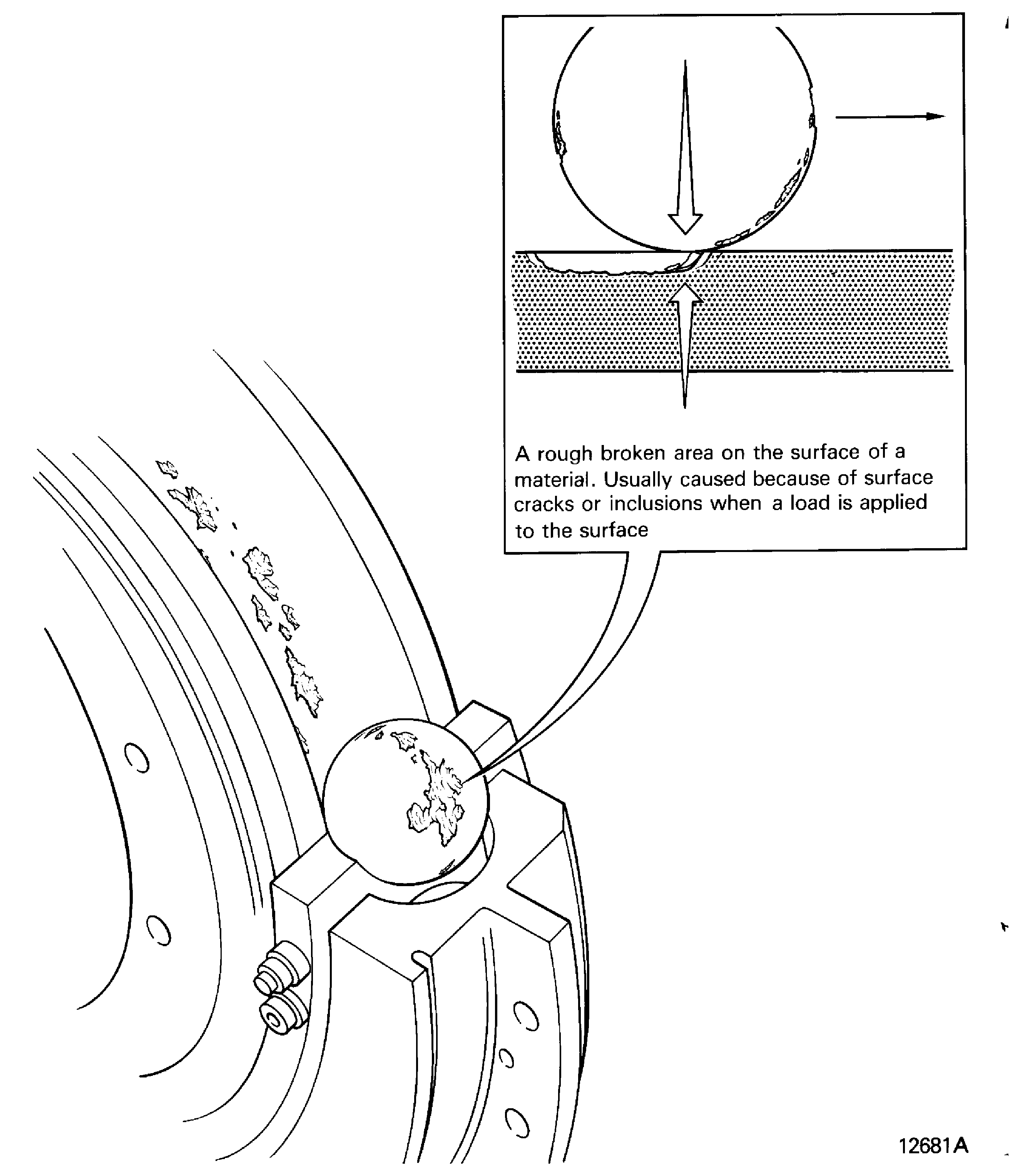
Figure: Torn
Torn
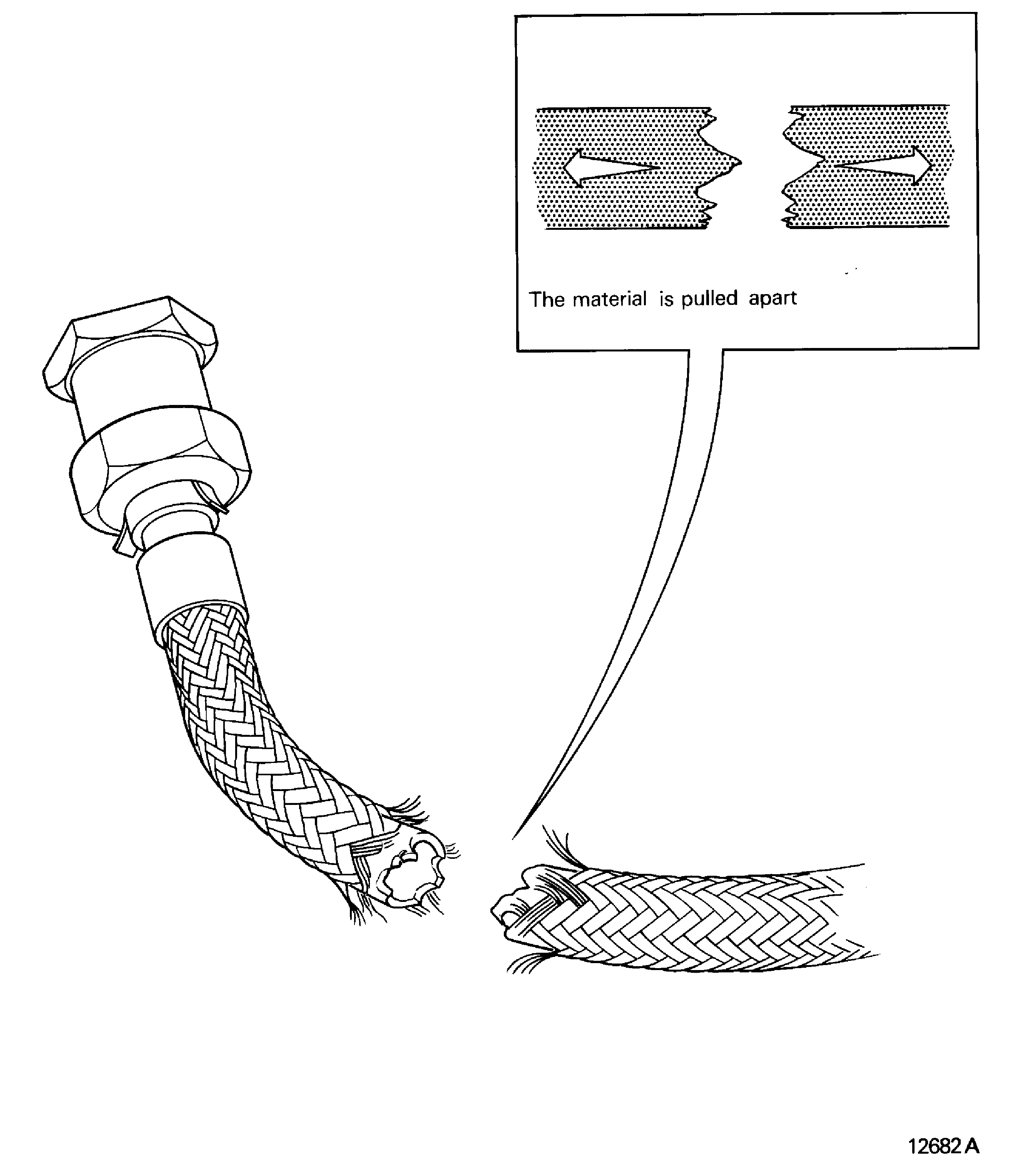
Figure: Unbond
Unbond
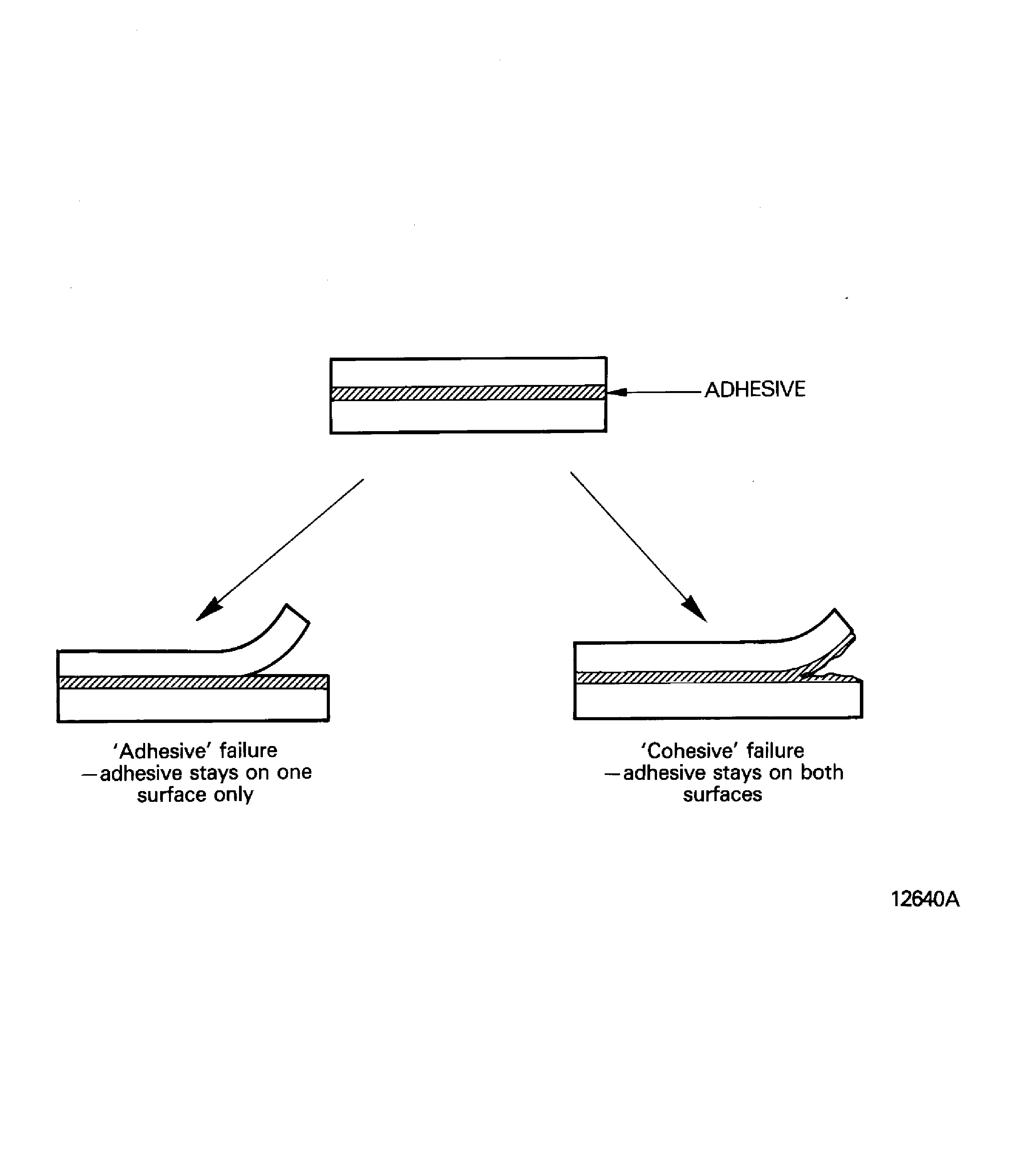
Figure: Unbond
Unbond
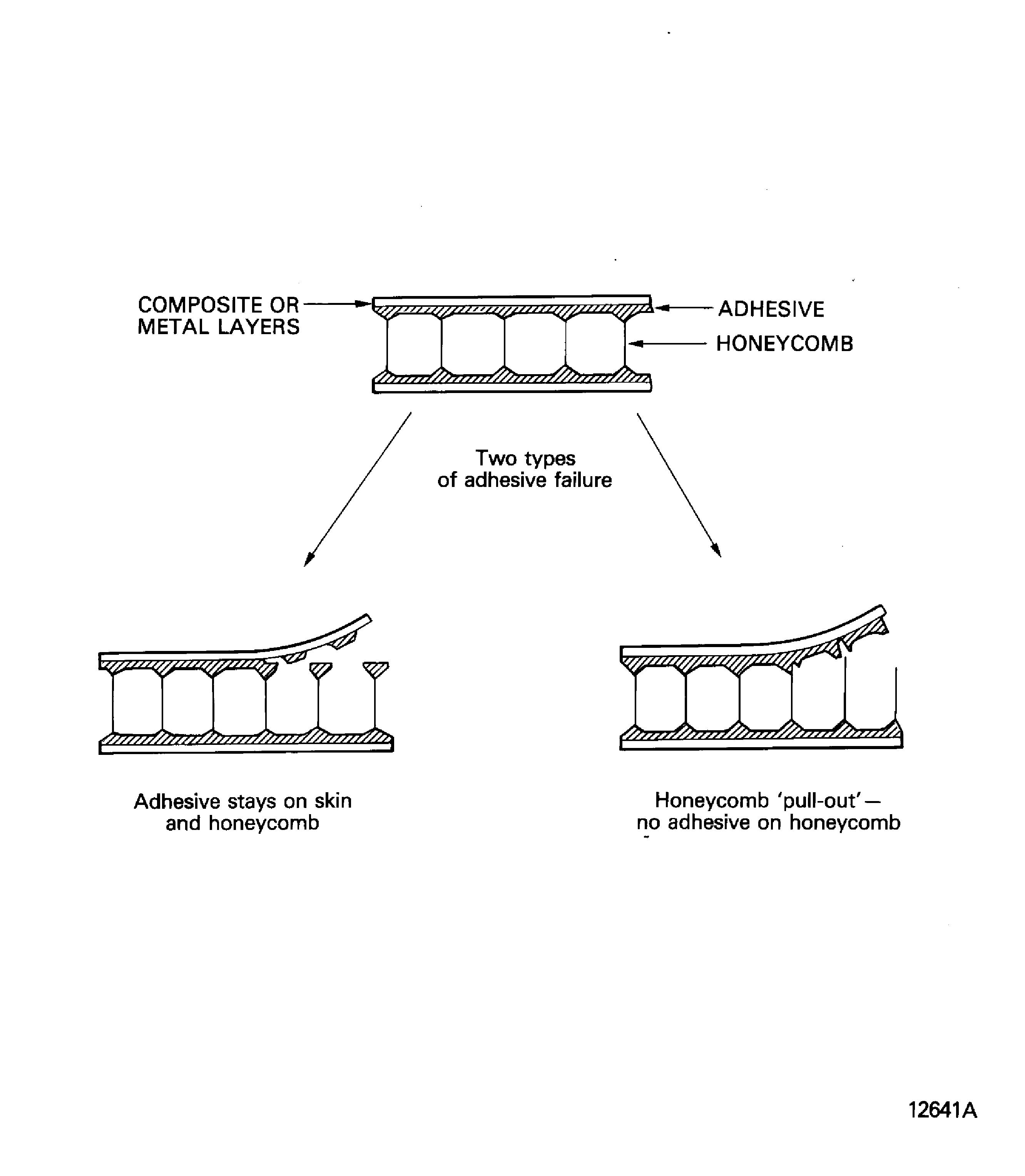
Figure: Unbond (Adhesive failure)
Unbond (Adhesive failure)
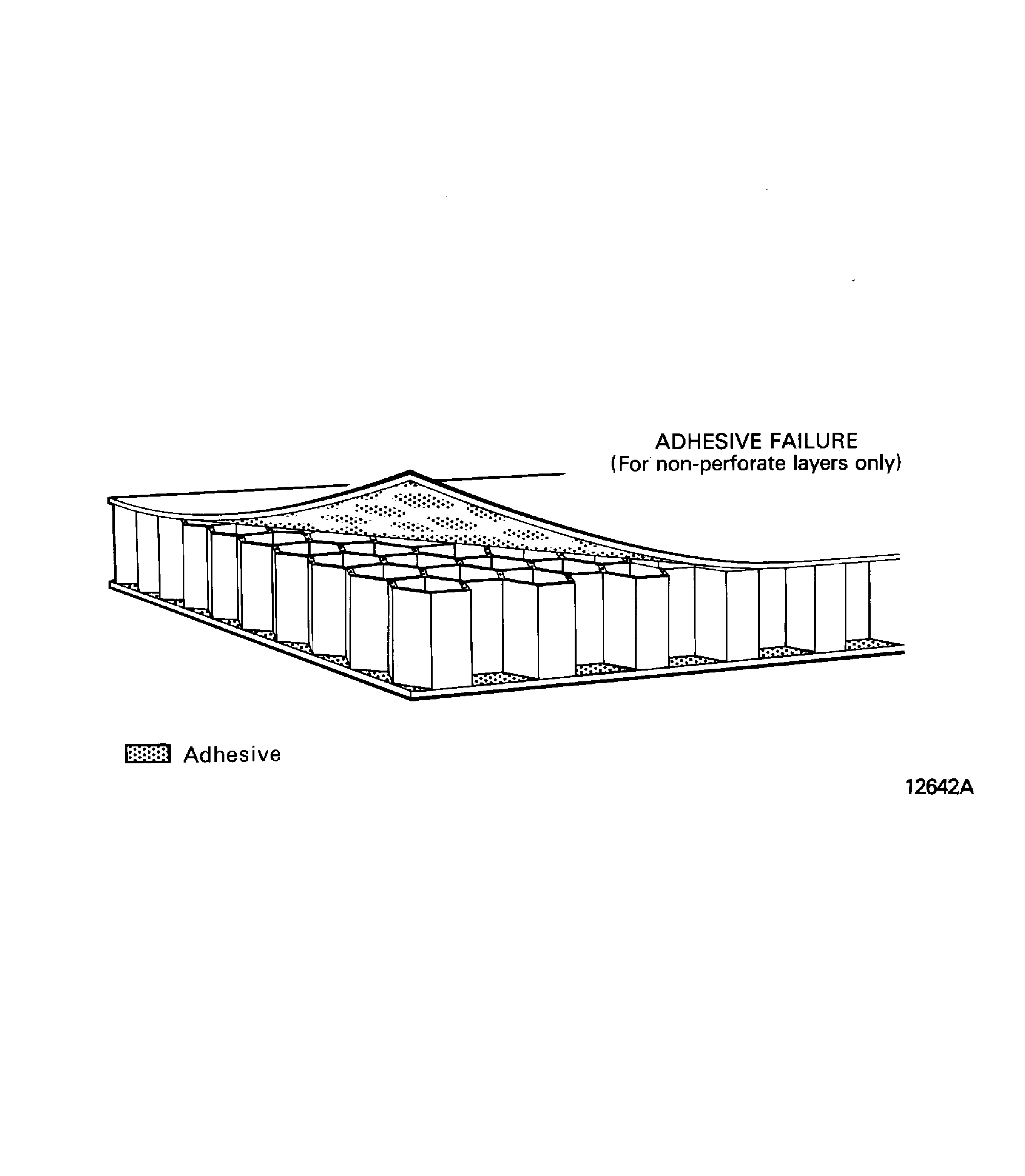
Figure: Unbond (Cohesive failure)
Unbond (Cohesive failure)
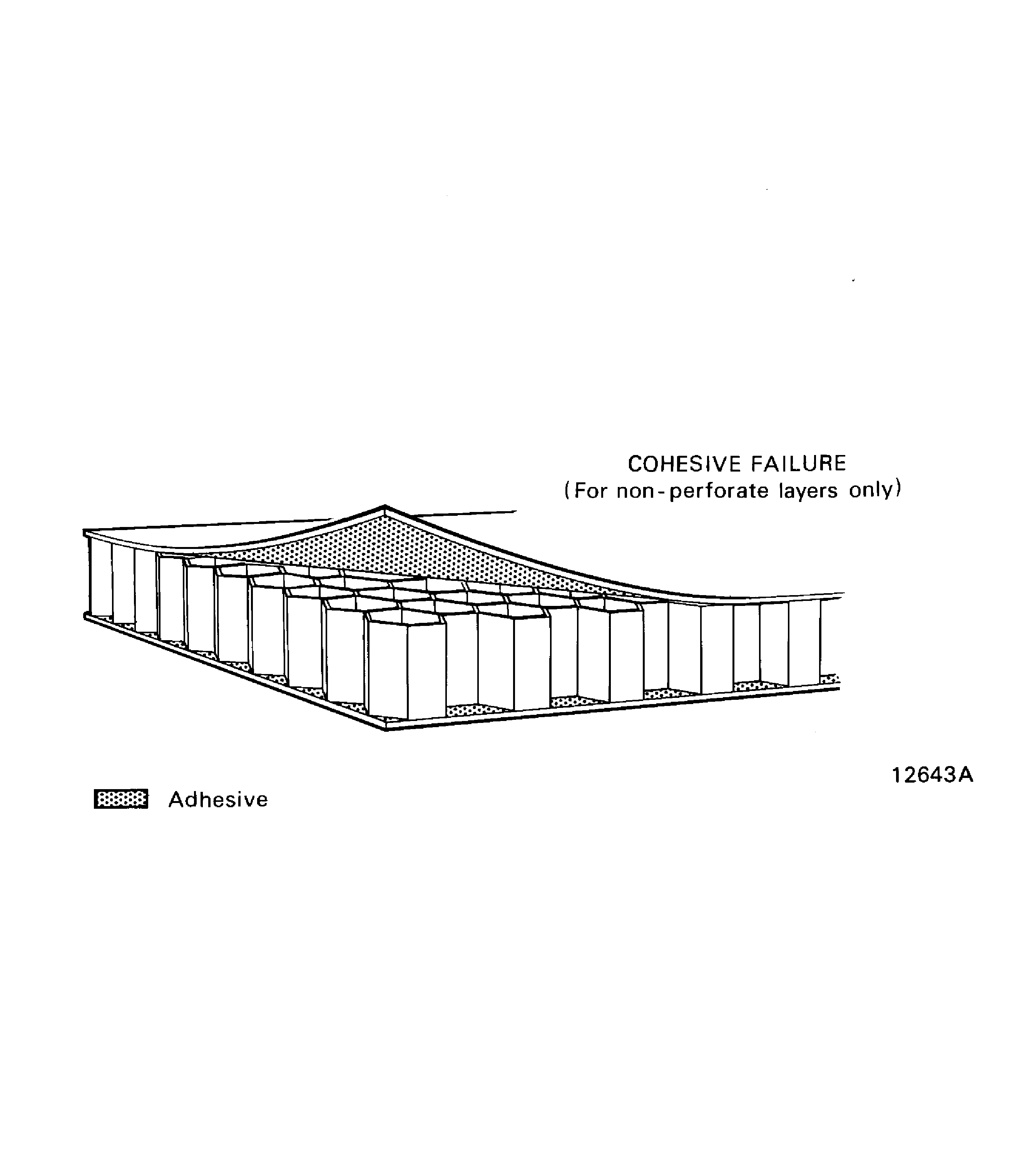
Figure: Delaminated
Delaminated
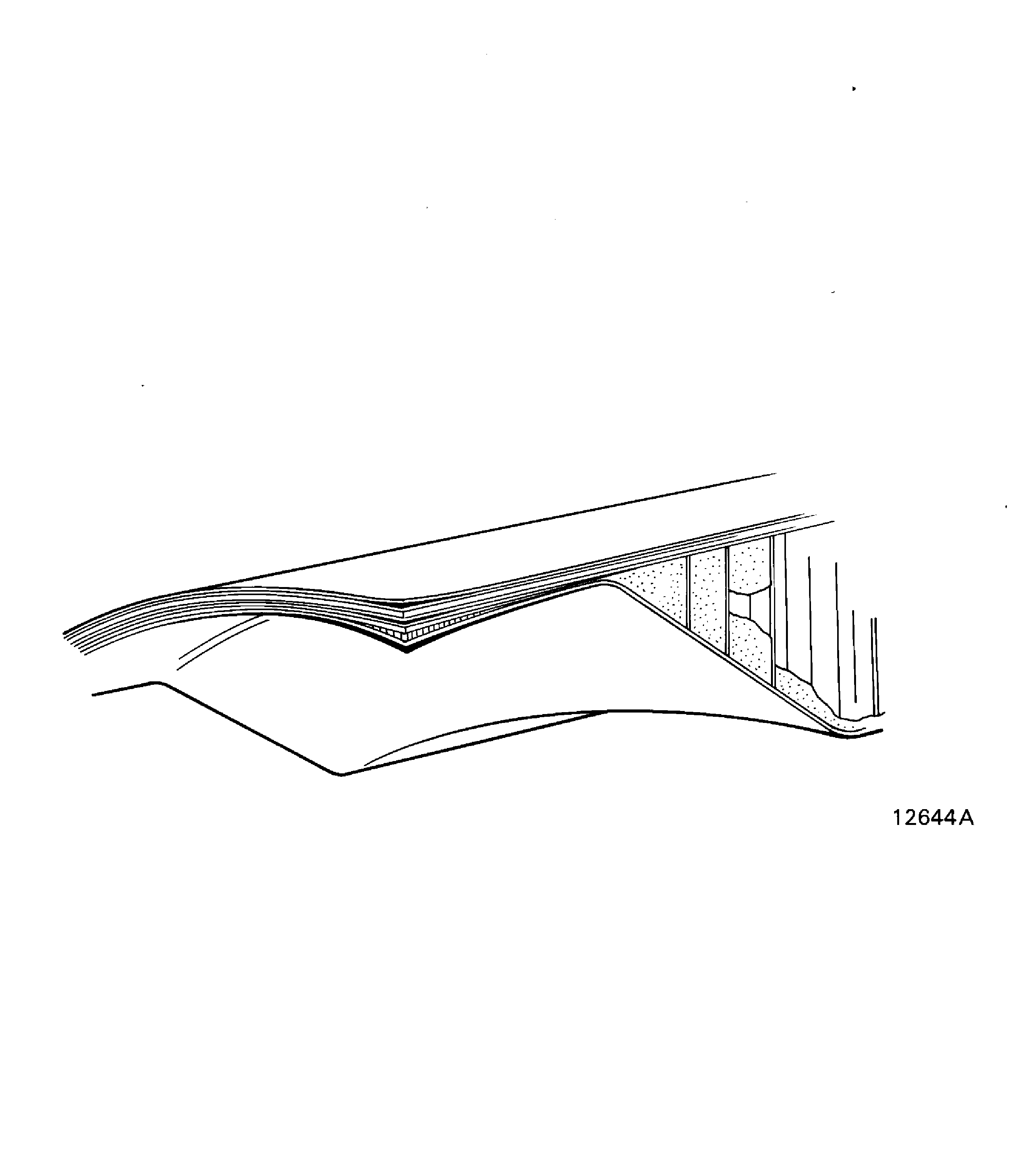
Figure: Cracked/Split
Cracked/Split
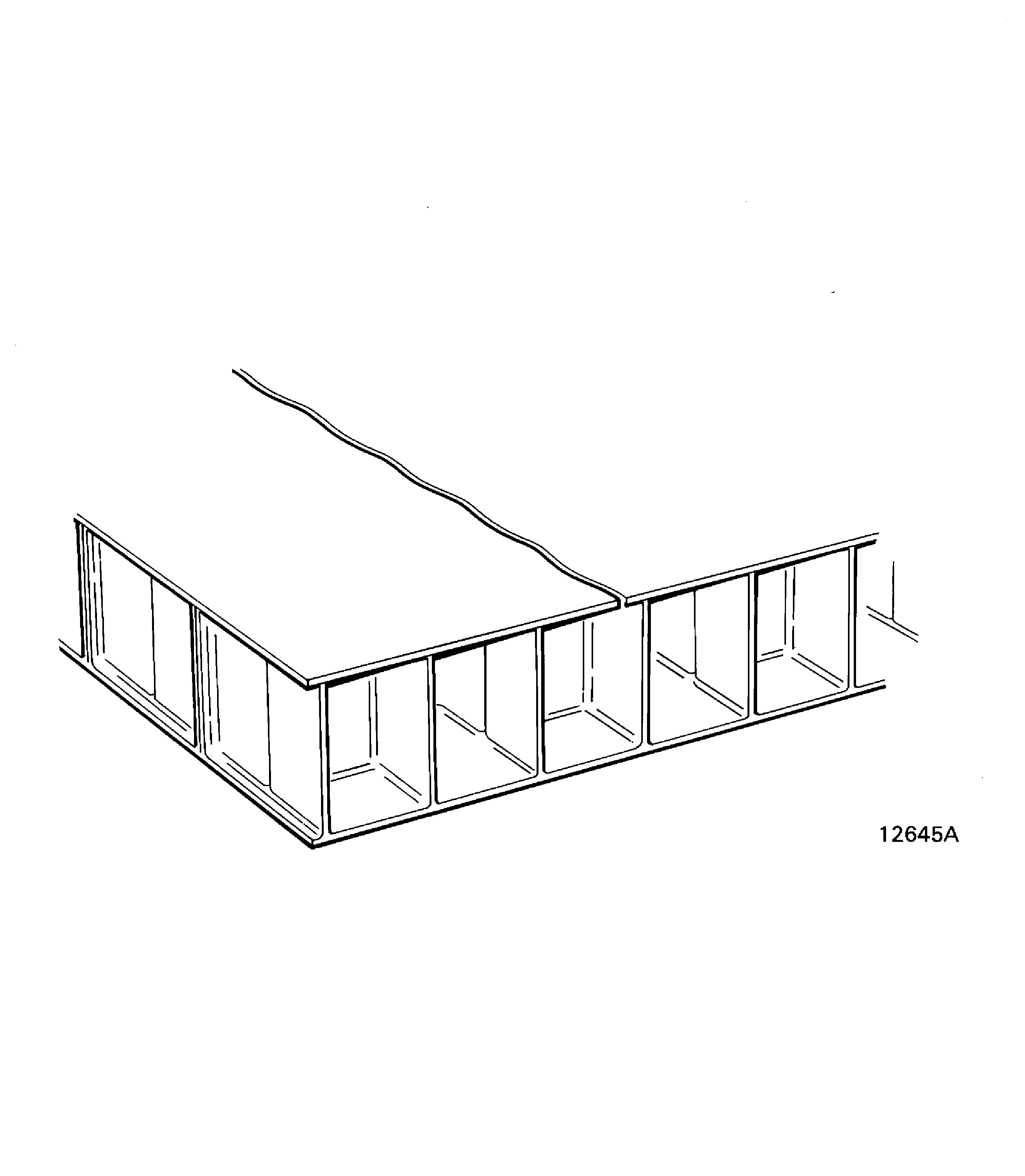
Figure: Fretted
Fretted
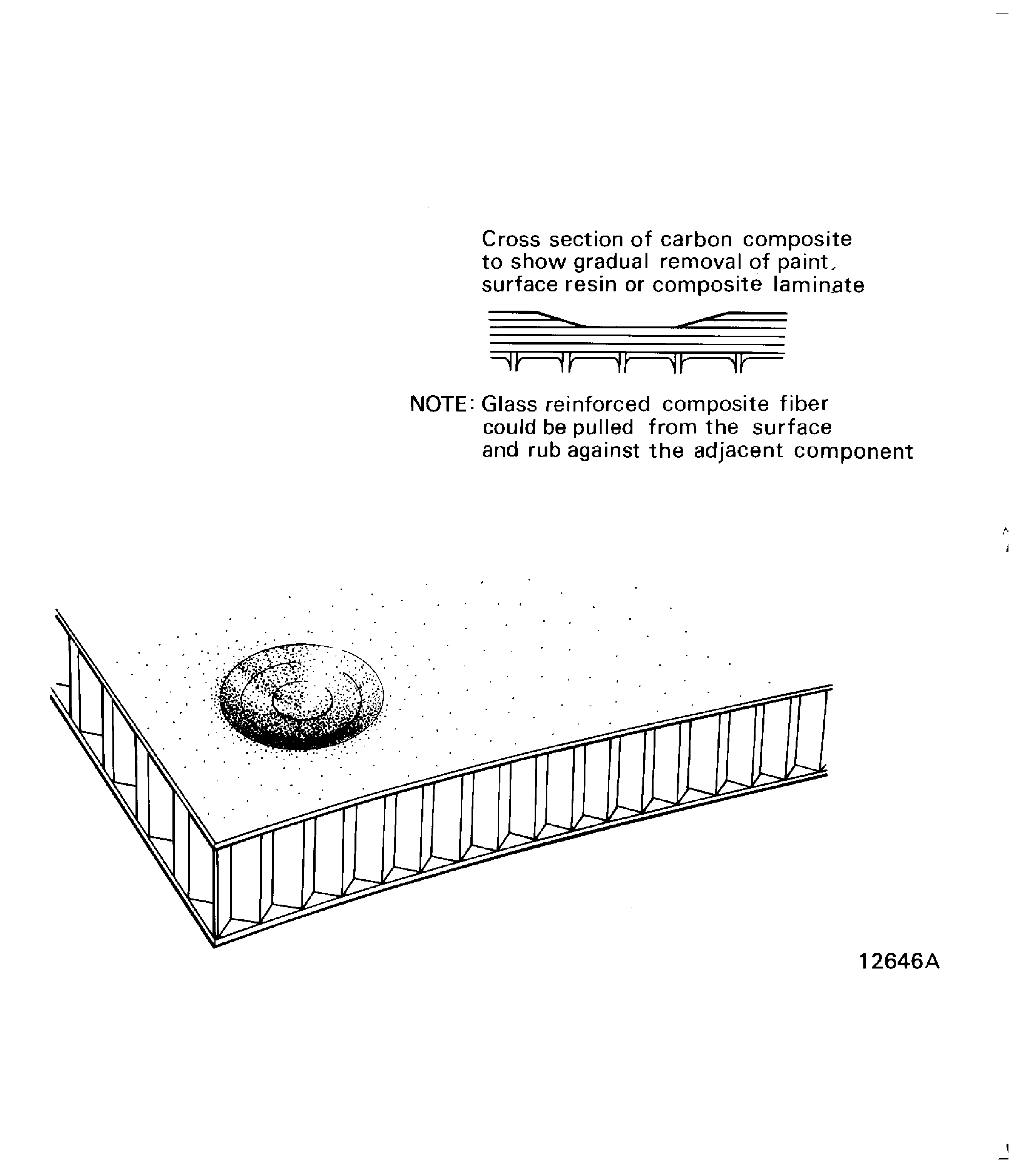
Figure: Eroded and Cavities
Eroded and Cavities
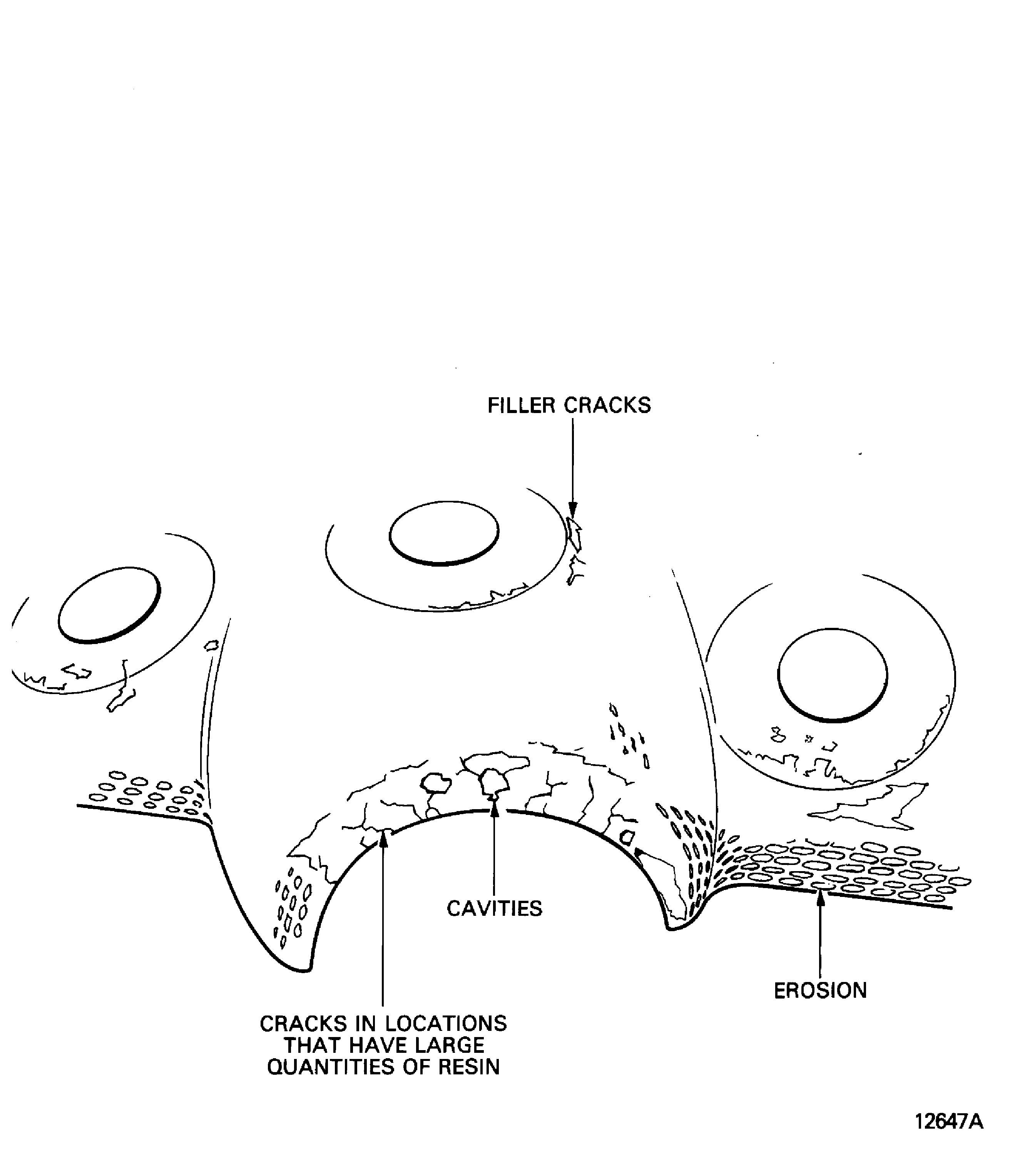
Figure: Impact damage
Impact damage
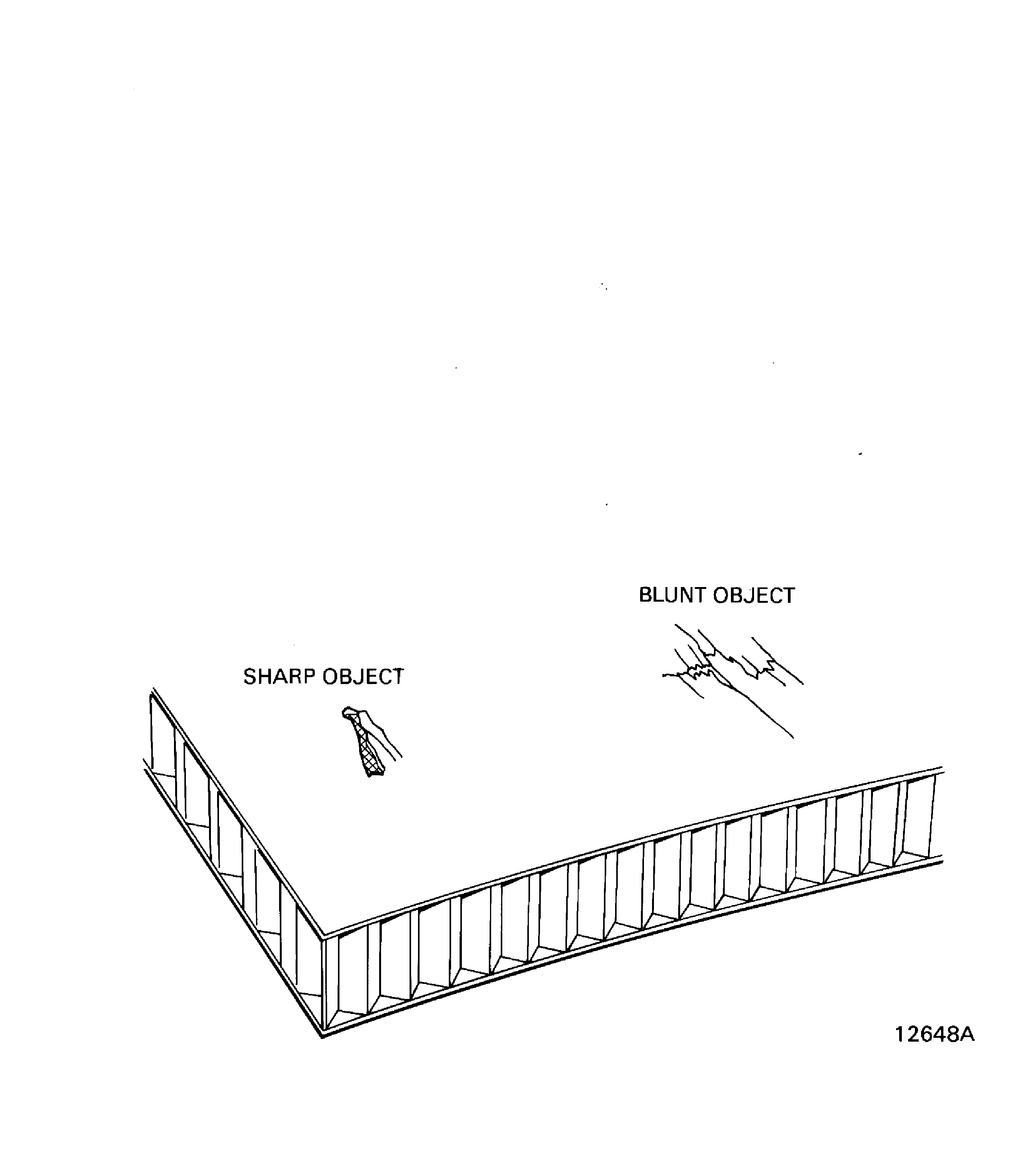
Figure: Torn fibers
Torn fibers
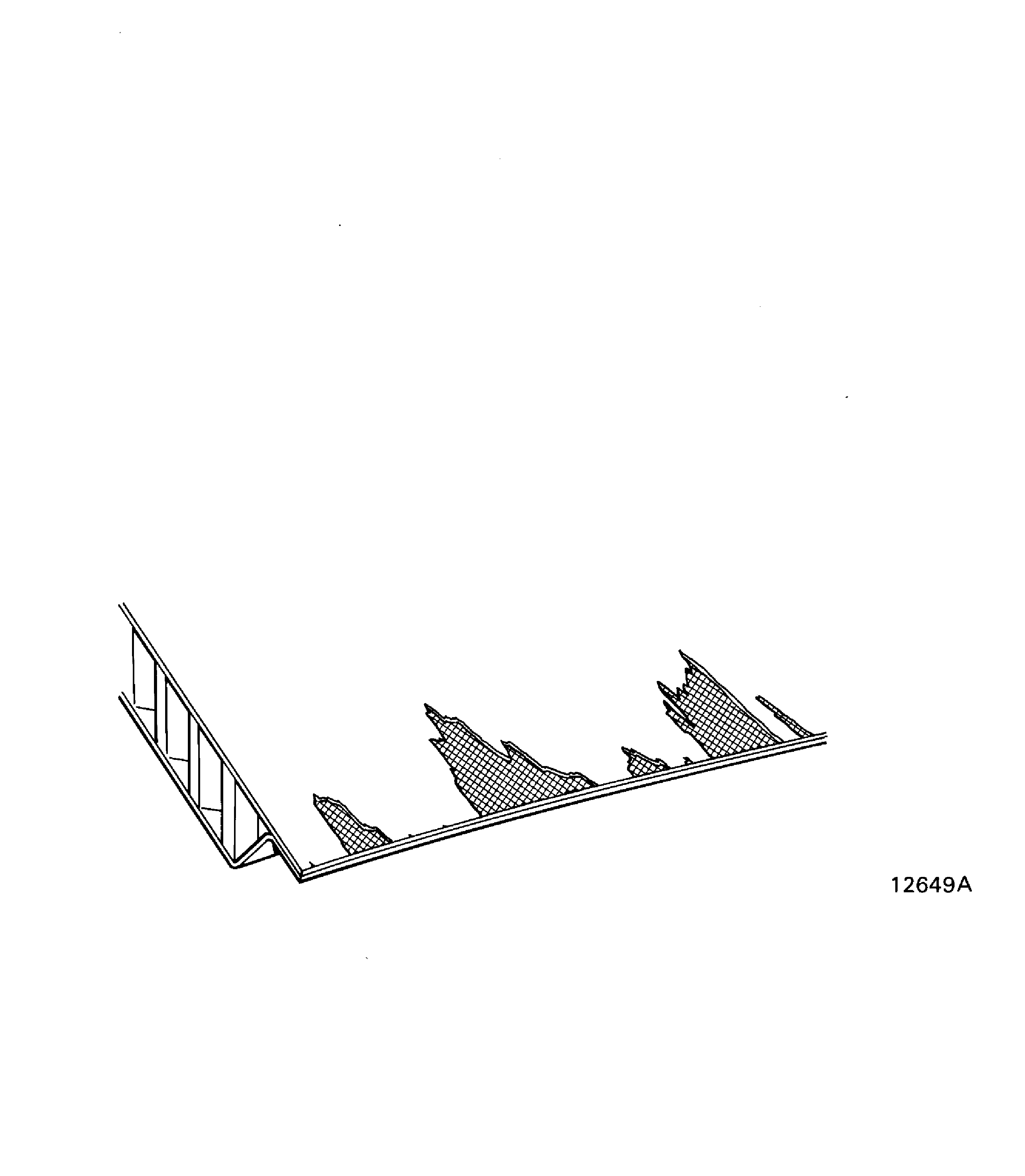
Figure: Blistered
Blistered
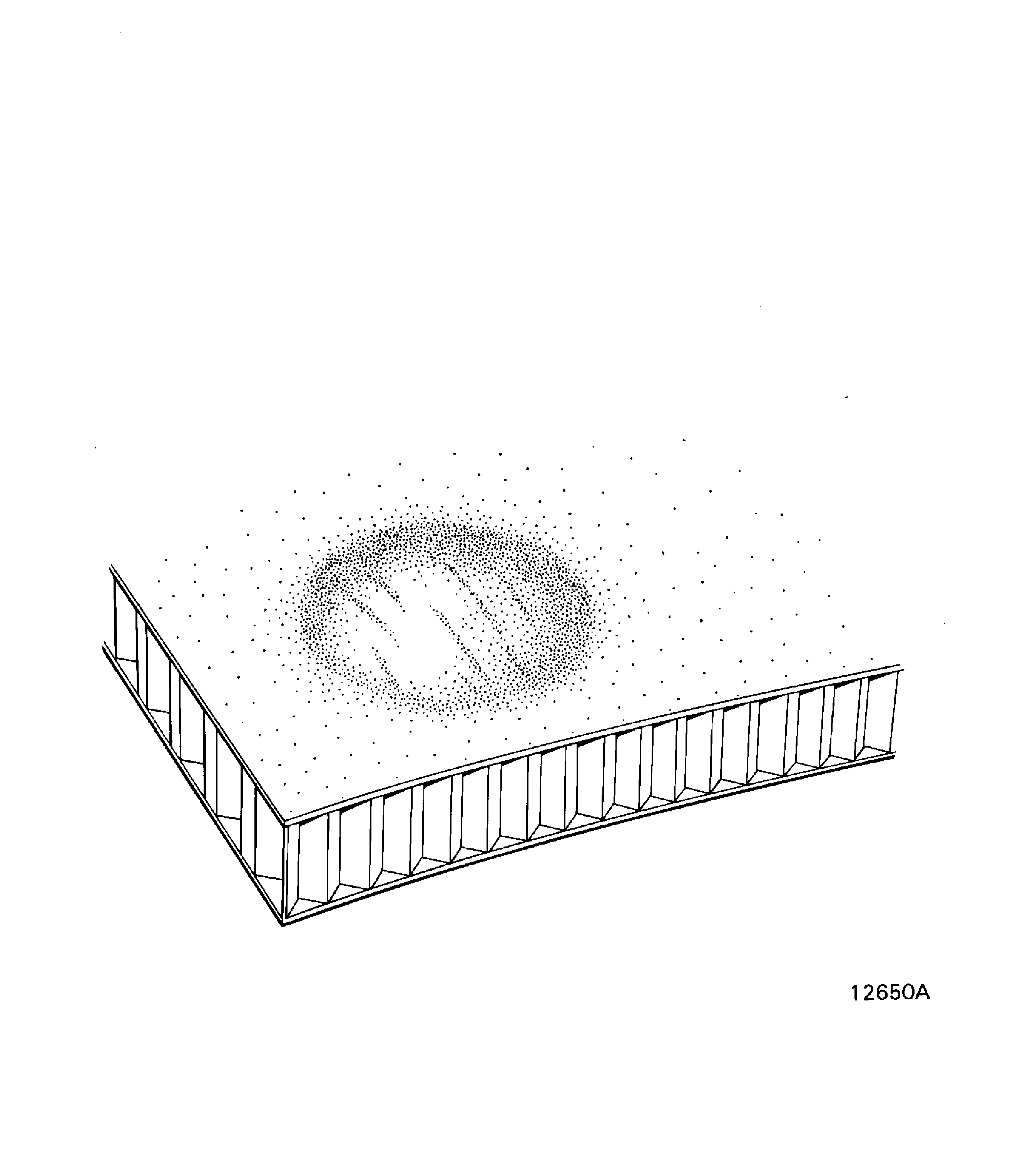
Figure: Scorched
Scorched