Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-09-00-400-501 Procedures To Make Permanent Identification And Location Marks
Scope
To specify the procedure to make permanent marks on parts.
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
NONEConsumables, Materials and Expendables
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMat 07-050 VARNISH - PHENOLIC RESIN,CORROSION PREVENTIVE | LOCAL | CoMat 07-050 | ||
| CoMat 07-125 LACQUER | 0W199 | CoMat 07-125 |
Spares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
CAUTION
Procedure
Marks must be easily and accurately read with no aid to the eye.
Where there are unusual area or surface limitations, a maximum of 3.5X magnification is permitted to get the necessary readability.
Marks made on engine parts, assemblies, or weldments must be easily read and must not be easily removed.
The location of a mark must be where specified in the Service Bulletin or Engine Manual instructions.
Where reidentification or corrective marking is specified, removal of all or part of the old marking can be necessary. Use an approved marking method to put a wavy line, loop, flat oval, or X's through the initial mark to be removed.
If not specified in the Engine Manual or Service Bulletin, reidentification of parts, reapplication and/or relocation of part markings must be made adjacent to, or in a location almost the same as the initial mark.
Each character in a mark, unless specified differently, must be 0.050 in. to 0.160 in. (1.27 mm to 4.06 mm) in height. If necessary because of the dimensions or the shape of the part, characters not less than 0.028 in. (0.71 mm) in height and not more than 0.500 in. (12.7 mm) in height are permitted.
On external surfaces, apply the mark with ink and a stamp, then apply a full layer of CoMat 07-125 LACQUER on the mark. Refer to SPM TASK 70-09-01-400-501 for applicable inks.
On external surfaces, do the subsequent procedure:
If permitted by the repair instructions, use the vibration peen method to apply the mark.
Apply the mark with ink and a stamp, then apply a full layer of transparent CoMat 07-050 VARNISH - PHENOLIC RESIN,CORROSION PREVENTIVE on the mark. Refer to SPM TASK 70-09-01-400-501 for applicable inks.
On internal surfaces, do the applicable procedure in the subsequent list:
If none of the specified marking methods will show through the final surface treatment coating, then it is permitted to use the applicable procedure in the subsequent list to make the mark after you apply the surface treatment coating:
If the surface specified for a mark will get a plating, paint, hardcoat, anodized coating, or other surface treatment coating, it is necessary to apply the mark before you apply the coating. Use an approved permanent marking method that will show through the final surface treatment coating.
Electric arc scribing, especially hand arc scribing, in which characters are made by the action of an electric arc between the surface and an electrode (scriber), is unsatisfactory for jet engine parts and must not be used.
Acid etching, in which characters are formed by the action of an acid on the surface of a part, is not recommended. Acid etching can possibly cause corrosion.
Soapstone must not be used to mark engine parts.
Offset holes in mating parts can be identified with an X vibration peened adjacent to the offset hole (unless a different procedure is specified); but make sure that the condition or operation of the part does not change.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-300-001 General

CAUTION
DO NOT ELECTROLYTICALLY ETCH ANODIZED SURFACES.Refer to the procedure to electrolytically make identification and location marks in the SPM TASK 70-09-02-400-501.
Electrolytic etch.
Mechanical: the tool is mechanically operated. It has one or more tips which make one or more symbols at the same time.
NOTE
The vibration peen method can be used as an alternative to roll stamping or the drag impression procedure. This method can also be an alternative to the deep dot peen method used on turbine airfoils.
Symbols are made with the vibration of a radius-tipped conical tool as follows:
Vibration peen.
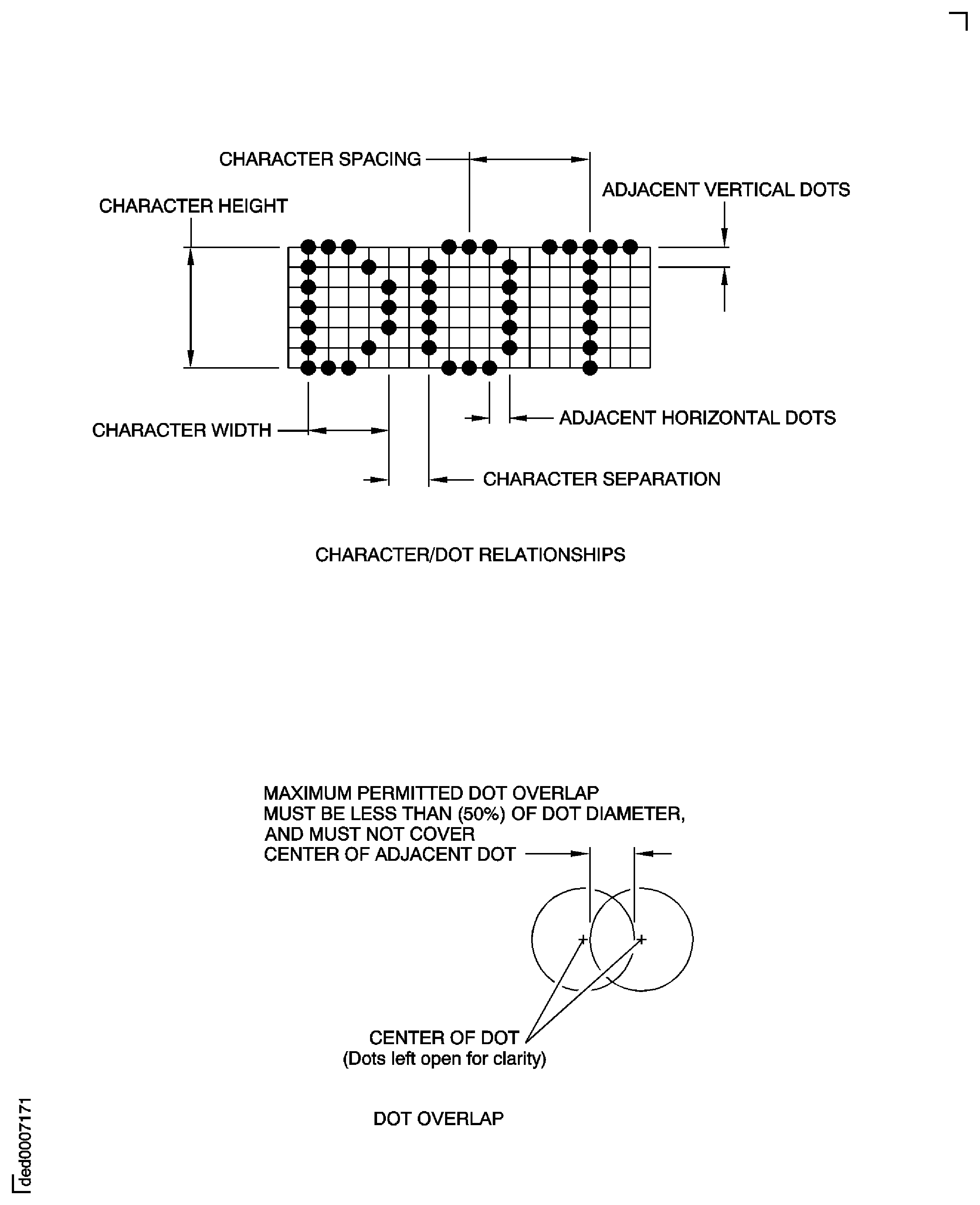
See Character/Dot Relationships in Figure.
Character height/width relationship:
The dot placement distance between two adjacent dots in the vertical direction must be equal to (Height/6) plus or minus 5 percent and in the horizontal direction equal to (Width/4) plus or minus 5 percent. See Character/Dot Relationships in Figure.
Character separation must be a minimum of one dot between adjacent characters. See Character/Dot Relationships in Figure.
The adjacent dot overlap must be less than 50 percent, so the center of the adjacent dot is visible. See Dot Overlap in Figure.
The characters are made by a pattern of dots laid out in a 5 x 7 (width x height) matrix. See Figure.
If it is necessary that the characters be readable by an automated Optical Character Reader, the characters must agree with the subsequent requirements:
Character Description.
Dot Peen.
Methods used to make permanent marks.
NOTE
Electrolytic etch is sometimes used as a temporary method. It is not the same as electric arc scribing.Unless specified differently, the depth of the marks must agree with the specified limits in Table:
Table 2. Marking Method
Minimum Depth
Maximum Depth
Electrolytic Etch, Shallow
(See Note 1)
0.0003 in. (0.008 mm)
Electrolytic Etch, Deep
0.0005 in. (0.013 mm)
0.002 in. (0.05 mm)
Metal Stamp, Hammer
(See Note 1)
0.010 in. (0.25 mm)
Metal Stamp, Press and Roll
(See Note 1)
0.006 in. (0.2 mm) (See Note 2)
Metal Stamp, Roll
(See Note 1)
0.006 in. (0.2 mm) (See Note 3)
Vibration Peen, Manual or Mechanical
(See Note 1)
0.006 in. (0.2 mm)
Engrave, Manual or Mechanical
(See Note 1)
0.006 in. (0.2 mm) (See Note 4)
Brand
(See Note 1)
0.010 in. (0.25 mm)
Drag Impression
(See Note 1)
0.006 in. (0.2 mm) (See Note 4)
Blast
(See Note 1)
0.0003 in. (0.008 mm)
Laser Engrave, Shallow
(See Note 1)
0.0004 in. (0.01 mm) (See Note 5)
Laser Engrave, Intermediate
(See Note 1)
0.003 in. (0.08 mm)
Laser Engrave, Deep
(See Note 1)
0.005 in. (0.1 mm) (See Note 4)
Dot Peen, Shallow
0.0002 in. (0.005 mm)
0.0007 in. (0.02 mm)
Dot Peen, Intermediate
(See Note 1)
0.0015 in. (0.038 mm)
Dot Peen, Deep
(See Note 1)
0.003 in. (0.08 mm) (See Note 6)
NOTE
1: The minimum permitted marking depth is the minimum depth that is sufficient for the marking to be easily and accurately readable with no magnification during the usual service life of the part.NOTE
2: Maximum depth of 0.015 in. (0.38 mm) is permitted on the sides of main shaft bearing rings.NOTE
3: Maximum depth of 0.010 in. (0.25 mm) is permitted if metal stamp hammer is also an approved marking method.NOTE
4: Unless specified differently, maximum permitted marking depth on titanium or titanium alloy parts in locations other than the bottom surface of blade roots is 0.003 in. (0.08 mm).NOTE
5: Maximum depth of 0.003 in. (0.08 mm) is permitted for anti-friction roller bearings and cages.NOTE
6: Unless specified differently, maximum depth of 0.005 in. (0.1 mm) is permitted on static parts where the marked surface will subsequently get a coating layer, the cross-sectional material thickness is more than 0.030 in. (0.76 mm), and the material hardness is not more than HRC 45.
Depth of marks.
NOTE
For detailed information on shallow and deep electrolytic etch, refer to SPM TASK 70-09-02-400-501.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-400-001 Procedures to Make Permanent Marks
A beehive symbol on a part shows that the part had a repair for plating, plasma spray, epoxy adhesion, or flame spraying at manufacture. Application of a beehive symbol on components after repair is not necessary. The beehive symbol and equivalent procedures are shown on Figure. When it is possible, you will find the symbol adjacent to the part number and the repaired area on the part.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-400-005 Beehive Symbols
This SUBTASK is deleted. Refer to the SPM TASK 70-09-01-400-501.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-400-002 Procedures to Make a Temporary Mark
This SUBTASK is deleted. Refer to the SPM TASK 70-09-02-400-501.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-400-003 Equipment Used to Make a Mark Electrochemically
This SUBTASK is deleted. Refer to the SPM TASK 70-09-02-400-501.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-400-004 Procedure to Make a Mark Electrochemically
This SUBTASK is deleted. Refer to the SPM TASK 70-09-02-400-501, SUBTASK 70-09-02-400-002.
SUBTASK 70-09-00-400-006 Specification Table for Electrolytic Marking.
Figure: Beehive Symbols
Beehive Symbols
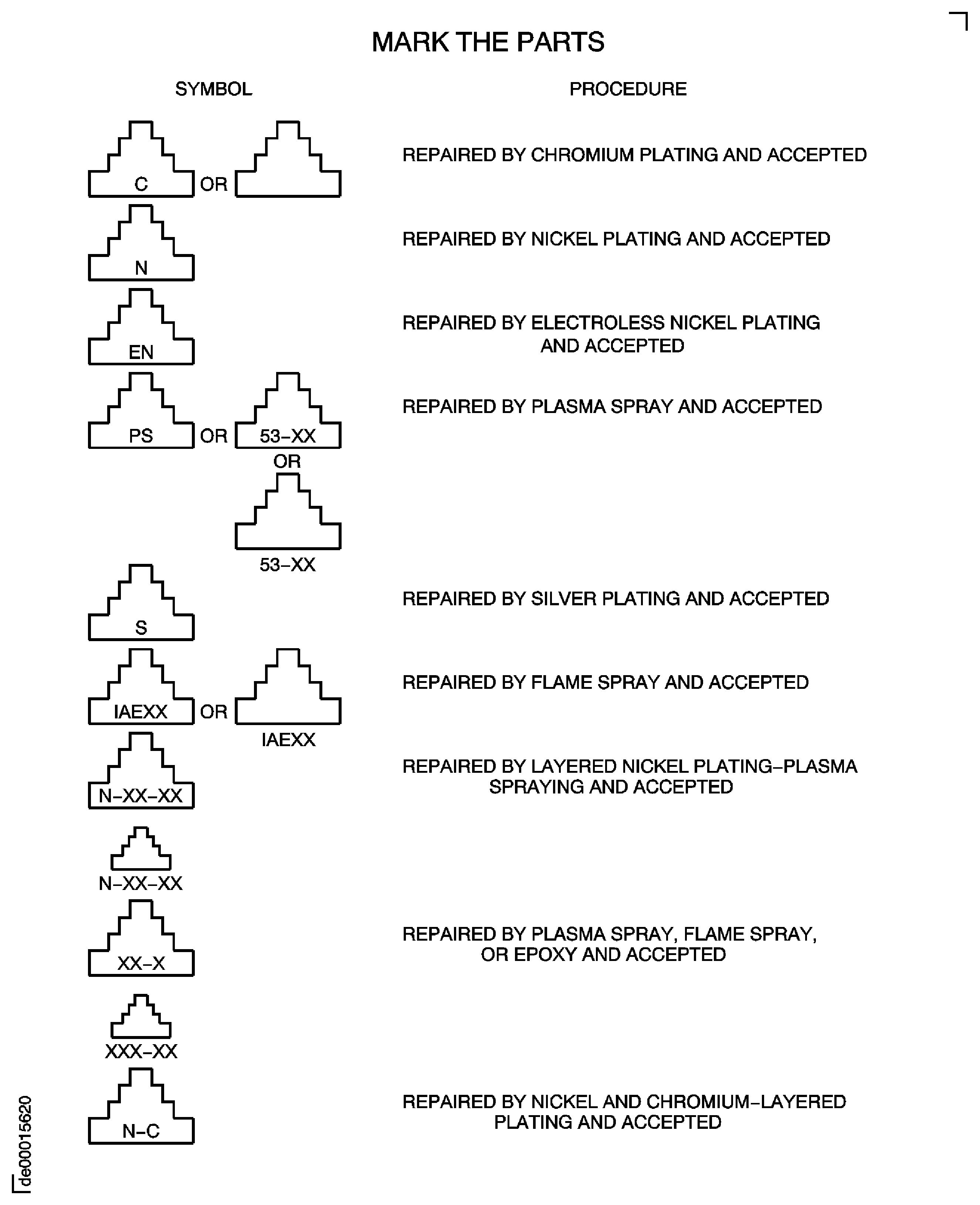
Figure: Dot Peen Character Height/Width Relationships
Dot Peen Character Height/Width Relationships
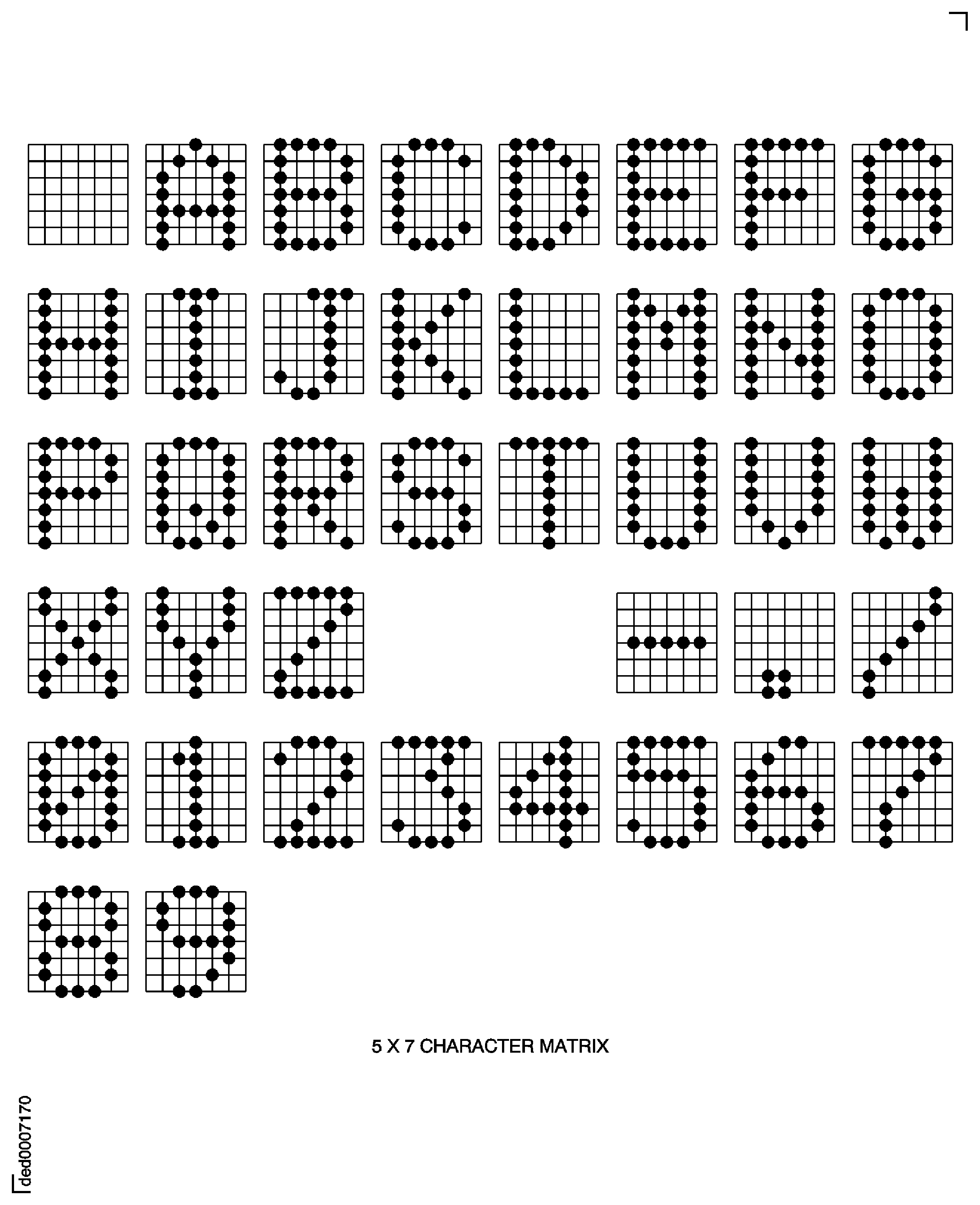
Figure: Dot Peen Character Height/Width Relationships
Dot Peen Character Height/Width Relationships