Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-11-47-110-501 Methods Of Testing Cleaning And Plating Solutions
General
This section includes instructions and precautions for doing wet chemical analysis of plating solutions.
Plating solution and the test procedure index gives applicable references to find the correct procedure to make an analysis of applicable solutions.
Instructions about sampling and procedures for correction to keep the operational limits are given to make complete use of testing procedures.
Use this information to keep solutions in operational limits to make sure you keep a high quality of workmanship, safety and efficiency.
Safety Precautions
Deleted.
Perchloric Acid (HClO4):
Perchloric acid of 60 percent strength can be boiled at approximately 388 °F (198 °C) but it cannot be too strongly emphasized that contact of boiling undiluted perchloric acid or hot vapor of the acid with organic matter, or even easily oxidized inorganic matter (such as, compounds of trivalent antimony) can lead to serious explosions.
If you find oxidizable substance, nitric acid must always be added and evaporated to fumes of the acid, as a precautionary measure before addition of perchloric acid. Rubber thumb stalls must not be used around fuming perchloric acid, and beakers must be handled with tongs. Perchloric acid evaporations must be done in a hood with good draft. Hoods in which a great deal of perchloric acid is fumed must be washed occasionally with water. Fumes can condense in hoods and form an explosive mixture with ammonia and nitric acid fumes.
Hydrofluoric Acid (HF):
Hydrofluoric acid burns and painful and dangerous infection and necrosis of bone tissue can occur. If hydrofluoric acid touches the skin, wash immediately with large quantities of water and soak the exposed part in a strong solution of borax.
Nitric Oxide (NO):
Nitric oxide vapors are cumulatively harmful to respiratory system; solution of metals in nitric acid must be made in a well ventilated hood.
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S):
Hydrogen sulfide is a dangerous poison, fatal if inhaled in sufficient concentrations. Operations involving hydrogen sulfide must be done under a hood.
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN):
Vapors of hydrogen cyanide are extremely dangerous, and can be fatal, if inhaled in sufficient quantities. All operations that can result in formation of this chemical must be done under a hood.
Bromine:
All operations involving use of bromine must be done under a hood.
Organic Solvents:
Organic solvents (such as acetone) are extremely flammable and must be kept well away from open flames, electrical sparks etc. Also, many organic solvents are extremely toxic; they must be used only in a well ventilated hood. Toluene is a solvent that falls into this category.
Mercury:
Mercury vapors are toxic. Mercury must be stored in well sealed containers. Each area where mercury is frequently used must be supplied with a spill pan.
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
NONEConsumables, Materials and Expendables
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMat 01-007 ETHYL ALCOHOL C2H5OH (DENATURED) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-007 | ||
| CoMat 01-008 SODIUM HYDROXIDE NaOH (CAUSTIC SODA), SOLID | LOCAL | CoMat 01-008 | ||
| CoMat 01-011 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-011 | ||
| CoMat 01-015 BORIC ACID H3BO3 | LOCAL | CoMat 01-015 | ||
| CoMat 01-022 SODIUM HYDROXIDE NaOH (SOLID) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-022 | ||
| CoMat 01-023 CHROMIUM TRIOXIDE CrO3(CHROM.ACID) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-023 | ||
| CoMat 01-025 NITRIC ACID HNO3, TECHNICAL GRADE | 5FCA4 | CoMat 01-025 | ||
| CoMat 01-030 SODIUM CARBONATE Na2CO3 | K0419 | CoMat 01-030 | ||
| CoMat 01-031 ACETONE (CH3)2CO | LOCAL | CoMat 01-031 | ||
| CoMat 01-037 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-037 | ||
| CoMat 01-043 SULFURIC ACID H2SO4 | LOCAL | CoMat 01-043 | ||
| CoMat 01-057 ACETIC ACID CH3COOH | LOCAL | CoMat 01-057 | ||
| CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN | LOCAL | CoMat 01-063 | ||
| CoMat 01-064 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-064 | ||
| CoMat 01-077 NICKEL CHLORIDE NiCl2+6H2O | LOCAL | CoMat 01-077 | ||
| CoMat 01-096 ELECTROLYTIC STRIPPINGSOLUTION | 02258 | CoMat 01-096 | ||
| CoMat 01-099 HYDROCHLORIC ACID | K6835 | CoMat 01-099 | ||
| CoMat 01-107 POTASSIUM CYANIDE KCN95% MIN | 70657 | CoMat 01-107 | ||
| CoMat 01-109 INDICATOR | U1185 | CoMat 01-109 | ||
| CoMat 01-129 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH | 0AM53 | CoMat 01-129 | ||
| CoMat 01-130 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE | K6835 | CoMat 01-130 | ||
| CoMat 01-132 HYDROFLUORIC ACID HF | LOCAL | CoMat 01-132 | ||
| CoMat 01-133 SILVER NITRATE CRYSTALS | LOCAL | CoMat 01-133 | ||
| CoMat 01-138 ALKALI CLEANER (HEAVYDUTY) | 94853 | CoMat 01-138 | ||
| CoMat 01-139 ALKALI CLEANER (HEAVYDUTY) | 71410 | CoMat 01-139 | ||
| CoMat 01-141 ALKALI DRAWING COMPOUNDREMOVER | 76071 | CoMat 01-141 | ||
| CoMat 01-143 ALKALI SMUT REMOVAL COMPOUND | 02258 | CoMat 01-143 | ||
| CoMat 01-176 ALKALI CLEANER (MEDIUMDUTY) | IE366 | CoMat 01-176 | ||
| CoMat 01-178 NICKEL STRIP SALT | 76071 | CoMat 01-178 | ||
| CoMat 01-179 NICKEL STRIP SALT | 0AM53 | CoMat 01-179 | ||
| CoMat 01-180 NICKEL STRIP SALT | 0AM53 | CoMat 01-180 | ||
| CoMat 01-181 NICKEL STRIP SALT | 0AM53 | CoMat 01-181 | ||
| CoMat 01-182 NICKEL STRIP SALT | 0AM53 | CoMat 01-182 | ||
| CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER | LOCAL | CoMat 01-201 | ||
| CoMat 01-217 ALKALI CLEANER (LIGHTDUTY) | IE366 | CoMat 01-217 | ||
| CoMat 01-218 ALKALI CLEANER | 02258 | CoMat 01-218 | ||
| CoMat 01-237 TRIS (HYDROXY METHYL)AMINO METHANE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-237 | ||
| CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-239 | ||
| CoMat 01-278 NICKEL STRIP ADDITIVE | 02258 | CoMat 01-278 | ||
| CoMat 01-281 ACTIVATED CARBON | IE366 | CoMat 01-281 | ||
| CoMat 01-282 ACTIVATED CARBON (GRANULAR) | 0AEA0 | CoMat 01-282 | ||
| CoMat 01-299 SYNTHETIC CLEANER | 94853 | CoMat 01-299 | ||
| CoMat 01-300 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) | 0GA37 | CoMat 01-300 | ||
| CoMat 01-301 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERALPURPOSE) | IAE64 | CoMat 01-301 | ||
| CoMat 01-302 ALKALI CLEANER PHOSPHATE-FREE | 02258 | CoMat 01-302 | ||
| CoMat 01-303 ALKALI CLEANER PHOSPHATE-FREE(HEAVY DUTY) | 02258 | CoMat 01-303 | ||
| CoMat 01-304 ALKALI CLEANER (LIGHTDUTY) | IE366 | CoMat 01-304 | ||
| CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED | LOCAL | CoMat 01-306 | ||
| CoMat 01-307 SODIUM CYANIDE (NaCN) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-307 | ||
| CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-308 | ||
| CoMat 01-310 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-310 | ||
| CoMat 01-311 CITRIC ACID | LOCAL | CoMat 01-311 | ||
| CoMat 01-314 SODIUM HYDROXIDE (NaOH), REAGENT GRADE (SOLID) | X222X | CoMat 01-314 | ||
| CoMat 01-319 SODIUM CHLORIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-319 | ||
| CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID | LOCAL | CoMat 01-320 | ||
| CoMat 01-321 POTASSIUM CHROMATE (CHLORIDEFREE) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-321 | ||
| CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-322 | ||
| CoMat 01-323 POTASSIUM ACID PHTHALATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-323 | ||
| CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID | LOCAL | CoMat 01-327 | ||
| CoMat 01-339 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-339 | ||
| CoMat 01-340 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-340 | ||
| CoMat 01-349 CADMIUM PLATE BRIGHTENER | 0RP46 | CoMat 01-349 | ||
| CoMat 01-350 ETHYLENE DIAMINETETRA-ACETIC ACID (EDTA) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-350 | ||
| CoMat 01-351 ZINC METAL | LOCAL | CoMat 01-351 | ||
| CoMat 01-352 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-352 | ||
| CoMat 01-353 FILTER PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 01-353 | ||
| CoMat 01-354 GUM ARABIC | LOCAL | CoMat 01-354 | ||
| CoMat 01-355 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-355 | ||
| CoMat 01-356 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-356 | ||
| CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-357 | ||
| CoMat 01-358 FERROUS SULFATE (FeSO4.7H2O) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-358 | ||
| CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3) | 0AM53 | CoMat 01-360 | ||
| CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-363 | ||
| CoMat 01-364 PHOSPHORIC ACID | LOCAL | CoMat 01-364 | ||
| CoMat 01-381 METHYL ALCOHOL | LOCAL | CoMat 01-381 | ||
| CoMat 01-382 SODIUM CARBONATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-382 | ||
| CoMat 01-383 SODIUM THIOSULFATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-383 | ||
| CoMat 01-384 POTASSIUM DICHROMATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-384 | ||
| CoMat 01-385 STARCH | LOCAL | CoMat 01-385 | ||
| CoMat 01-390 FERRIC AMMONIUM SULFATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-390 | ||
| CoMat 01-391 SODIUM THIOCYANATE (NaSCN) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-391 | ||
| CoMat 01-392 POTASSIUM CYANIDE (KCN) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-392 | ||
| CoMat 01-394 BARIUM CHLORIDE (BaCl2) | LOCAL | CoMat 01-394 | ||
| CoMat 01-395 BARIUM CHLORIDE - 2 HYDRATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-395 | ||
| CoMat 01-396 AMMONIUM BIFLUORIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-396 | ||
| CoMat 01-397 POTASSIUM PYROSULFATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-397 | ||
| CoMat 01-398 SODIUM OXALATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-398 | ||
| CoMat 01-399 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-399 | ||
| CoMat 01-400 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-400 | ||
| CoMat 01-401 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-401 | ||
| CoMat 01-402 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-402 | ||
| CoMat 01-403 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-403 | ||
| CoMat 01-404 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-404 | ||
| CoMat 01-405 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-405 | ||
| CoMat 01-406 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-406 | ||
| CoMat 01-407 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 01-407 | ||
| CoMat 01-410 ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL, REAGENT GRADE | 0AL61 | CoMat 01-410 | ||
| CoMat 01-414 AMMONIUM BIFLUORIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-414 | ||
| CoMat 01-415 SILVER CYANIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-415 | ||
| CoMat 01-416 NICKEL CARBONATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-416 | ||
| CoMat 01-423 FERROUS AMMONIUM SULFATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-423 | ||
| CoMat 01-424 AMMONIUM CHLORIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-424 | ||
| CoMat 01-425 CERIC SULFATE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-425 | ||
| CoMat 01-466 PHOSPHORIC ACID | LOCAL | CoMat 01-466 | ||
| CoMat 02-011 FILTER PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-011 | ||
| CoMat 02-021 MASKING WAX COMPOUND | 59460 | CoMat 02-021 | ||
| CoMat 02-136 CHROMATE CONVERSION SALT | IE366 | CoMat 02-136 | ||
| CoMat 02-137 WETTING AGENT | IE366 | CoMat 02-137 | ||
| CoMat 02-189 COMPRESSED PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-189 | ||
| CoMat 02-190 CHEMICAL TABLETS | LOCAL | CoMat 02-190 | ||
| CoMat 02-191 ALCOHOL | LOCAL | CoMat 02-191 | ||
| CoMat 02-203 FILTER PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-203 | ||
| CoMat 02-205 FILTER PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-205 | ||
| CoMat 02-206 INDICATOR PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-206 | ||
| CoMat 02-207 INDICATOR PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-207 | ||
| CoMat 02-208 FILTER PAPER TABLETS-ASHLESS | LOCAL | CoMat 02-208 | ||
| CoMat 02-210 FILTER PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 02-210 | ||
| CoMat 02-211 INDICATOR | LOCAL | CoMat 02-211 | ||
| CoMat 03-102 COPPER CYANIDE | 04883 | CoMat 03-102 | ||
| CoMat 03-103 POTASSIUM SILVER CYANIDE | 02258 | CoMat 03-103 | ||
| CoMat 03-104 POTASSIUM SILVER CYANIDE | 20816 | CoMat 03-104 | ||
| CoMat 03-105 POTASSIUM CARBONATE | LOCAL | CoMat 03-105 | ||
| CoMat 03-107 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE | 04883 | CoMat 03-107 | ||
| CoMat 03-108 SULFAMATE NICKEL PLATING SOLUTION | 76071 | CoMat 03-108 | ||
| CoMat 03-125 CHROMATE CONVERSION SALTS | IE366 | CoMat 03-125 | ||
| CoMat 03-128 WETTING AGENT | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-128 | ||
| CoMat 03-129 CHROMATE CONVERSION SALTS | 76071 | CoMat 03-129 | ||
| CoMat 03-130 SULFAMIC ACID | 0RMW8 | CoMat 03-130 | ||
| CoMat 03-131 SULFAMATE NICKEL REPLENISHING SOLUTION | 76071 | CoMat 03-131 | ||
| CoMat 05-152 SILICON CARBIDE PAPER | LOCAL | CoMat 05-152 | ||
| CoMat 07-055 STOP-OFF LACQUER | 0AM53 | CoMat 07-055 | ||
| CoMat 01-393 ACETONE | LOCAL | CoMat 01-393 | ||
| CoMat 03-338 HIGH SPEED CHROM. REPLENISHERSOL | IE225 | CoMat 03-338 |
Spares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Procedure
CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE has a specific gravity of 1.18.
CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) has a concentration of 48 percent.
CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID has a specific gravity of 1.42.
CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID has a specific gravity of 1.84.
CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED has a specific gravity of 0.90.
When acids and alkalis are specified by name or chemical formula only, it must be understood that reagents of the specific gravities or concentration that follow are intended.
Concentration of acids and alkalis.
Diluted acid and CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED, except when standardized, will be specified as a ratio, stating number of volumes of concentrated acid to be diluted with given number of volumes of water, as in the example that follows.
Hydrochloric acid (5-95) means 5 volumes of concentrated CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE (specific gravity 1.18) diluted with 95 volumes of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Concentrations of non-standardized solutions prepared by dissolving given weight of solid reagent in solvent will be specified in grams of reagent/volume of solution, and that it must be understood that CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER is the solvent unless otherwise specified. For example, KMnO4 (100 g/l) means 100 g of KMnO4 salt dissolved in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER to a volume of one liter.
NOTE
In testing solutions reference to water must be understood to mean CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.In case of certain reagents, concentration may be specified as a percentage weight, for example, H2O2 (30 percent) means a solution containing 30 g of H2O2 for every 100 g of solution. Other non-standardized solutions may be specified by name only and concentrations of such solutions will be governed by instructions for their preparation.
Non-standardized solutions.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-110-001 Concentrations of Reagents
Dissolve 10 g of CoMat 01-407 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-410 ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL, REAGENT GRADE.
Alpha-Naptholbenzein.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-356 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED).
Bromcresol green.
Dissolve 0.40 g of CoMat 01-310 INDICATOR in 50 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured).
Bromcresol purple.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-406 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured). (A commercially prepared indicator is available.).
Bromphenol blue.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-352 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured). (A commercially prepared indicator is available.).
Bromthymol blue.
Dissolve 1.00 g of CoMat 01-405 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID.
Diphenylamine.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-037 INDICATOR in 100 ml of hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and filter if necessary.
Methyl orange.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-404 INDICATOR in 100 ml of hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and filter, if necessary.
Methyl purple.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-064 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Filter if necessary.
Methyl red.
CoMat 01-403 INDICATOR is available commercially ready to use.
Ortho-Phenathroline-Ferrous sulphate.
Dissolve 1,00 g of CoMat 01-011 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured).
Phenolphthalein.
CoMat 01-402 INDICATOR is available commercially ready to use.
Sulfo-Orange.
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-401 INDICATOR in 20 ml of hot CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured). Dilute to 100 ml with CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured).
Thymol blue.
Dissolve 0.10 g CoMat 01-400 INDICATOR in 100 ml of 4-1 CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured).
Thymolphthalein.
Dissolve 0.50 g of CoMat 01-399 INDICATOR in 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 50 ml of CoMat 01-314 SODIUM HYDROXIDE (NaOH), REAGENT GRADE (SOLID) (15 percent) and dilute to 500 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water.
Titan yellow.
Dissolve 0.1 g of CoMat 01-356 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) ethyl alcohol (denatured).
Bromcresol green - Methyl red.
Indicators.
Weigh three samples of CoMat 01-323 POTASSIUM ACID PHTHALATE which has been dried at 210 to 220 deg F (99 to 104 deg C) for 90 to 120 minutes and which has an assay of 99.95 percent or better, according to the formula that follows:
Weight of potassium acid phthalate in grams = 8.5 x normality of hydroxide desired. Transfer each potassium acid phthalate sample to a clean 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask or 400 ml beaker.
Add 125 to 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dissolve the potassium acid phthalate salt.
Add 2 to 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution (Step A (11)) and titrate with hydroxide solution to a faint pink end-point that you can see continuously for 30 seconds minimum. Record titer.
For each flask or beaker, do the subsequent procedure:
Calculations:
N = (W x P)/(20.42 x V)
Where:
N = Normality of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
W = Weight of potassium acid phthalate.
P = Percent purity of the potassium acid phthalate.
V = Volume of hydroxide used.
Average the three values obtained.
Primary Standardization (standardization against potassium acid phthalate).
Pipette three 25 ml (or measure accurately by burette three 40 ml samples of standardized acid of similar normality to base into clean 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks.
Add 75 ml water and 2 to 3 drops phenolphthalein indicator.
Titrate with hydroxide solution to faint pink end-point that you can see continuously for 30 seconds minimum. Record titer.
For each flask, do the subsequent procedure:
Calculations:
N1 = (N2 x V2)/V1
Where:
N1 = Normality of hydroxide solution.
N2 = Normality of standardized acid.
V1 = Average volume of hydroxide solution used in the three titrations
V2 = Volume of standardized acid sample.
Average the three values obtained.
NOTE
Standardize the standard hydroxide solutions against potassium acid phthalate at least once every three months. These solutions may be used in an alternate method for standardization of acid solutions.Secondary Standardization (standardization against standardized acid solution).
Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide Solutions.
Primary standardization:
Weigh out accurately in to 400 ml beakers, three samples of CoMat 01-237 TRIS (HYDROXY METHYL)AMINO METHANE according to the formula that follows:
Weight of tris (hydroxy methyl) amino methane in grams = 5 x normality of acid desired.
Dissolve each sample in 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Add 5 to 6 drops of bromcresol green-methyl red and titrate to first appearance of faint rose color.
Calculations:
N = Normality of acid.
W = Weight of tris (hydroxy methyl) amino methane.
P = Percent purity of tris (hydroxy methyl) amino methane.
V = Volume of acid used.
N = WP/12.114V.
Average the three values obtained.
NOTE
Use previously standardized base solution.NOTE
Standardize the standard acid solutions against tris (hydroxy methyl) amino methane at least once every three months. These solutions may be used as an alternate method for standardization of base solutions.Secondary standardization:
Pipette three 25 ml (or measure accurately by burette three 40 ml) samples of the acid into clean 250 ml Erlenmeyer flasks.
Add 75 ml of water and 2 or 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator.
Titrate with standard base solution of approximately similar normality to faint pink end point which persists for at least 30 seconds. Record titer.
Calculations:
N1 = Normality of acid.
N2 = Normality of standardized base solution.
V1 = Volume of acid used.
V2 = Average volume of the standard base solution used in three titrations.
N1 = V2N2/V1.
Acid solutions.
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-19 sulfuric acid solution is 1 volume of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID diluted with 19 volumes of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.Standardization.
Weigh three samples of CoMat 01-398 SODIUM OXALATE dried at 210 to 220 deg F (99 to 104 deg C) for 90 to 120 minutes and having an assay of 99.95 percent or better according to the formula that follows:
Weight of sodium oxalate in grams = normality of potassium permanganate.
Dissolve in 250 ml of a 1-19 sulfuric acid solution.
Run a preliminary titration on one sample by heating to 130 to 140 deg F (54 to 60 deg C) and titrating to a permanent faint pink end point with potassium permanganate solution.
To the remaining solution of sodium oxalate, add from a burette about 95 percent of the potassium permanganate solution used in the paragraph above. Heat to 130 to 140 deg F (54 to 60 deg C) and continue titration to permanent faint pink end point. Record titer.
Calculations.
N = Normality of potassium permanganate.
V = Average volume of potassium permanganate (second and third titrations only).
P = Purity of sodium oxalate.
W = Weight of sodium oxalate.
N = WP/6.700V.
Potassium permanganate solution.
Primary standard potassium dichromate 0.1N.
Weigh accurately 4.9040 g of CoMat 01-384 POTASSIUM DICHROMATE dried at 300 to 350 deg F (149 to 177 deg C) for 60 to 90 minutes.
Dissolve in 200 to 300 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, transfer to flask, and dilute to 1 l.
NOTE
A starch solution can be purchased ready to use or make a paste of 1.0 g of CoMat 01-385 STARCH and a small quantity of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 150 ml of hot water and boil for 2 to 3 minutes.Standardization:
Pipette three 25 ml (or measure accurately by burette three 40 ml) samples of primary potassium dichromate solution into 500 ml glass-stoppered flasks.
Add 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, 2 to 3 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) and 10 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE hydrochloric acid.
Put the stopper in the flask, mix to dissolve iodide, and let it stand in a closed cabinet for 8 to 10 minutes.
Remove the stopper and add 150 to 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, rinsing the sides of the flask.
Titrate with sodium thiosulfate, mix constantly until reddish brown changes to yellow green.
Add 4 to 6 ml of starch solution and continue titrating until the color changes sharply from blue to light green. Add thiosulfate dropwise as end point nears.
Record titers and average.
Calculations.
N = Normality of sodium thiosulfate.
V = Volume of sodium thiosulfate.
W = Normality of potassium dichromate.
P = Volume of potassium dichromate.
N = WP/V.
Sodium thiosulfate solutions.
Standardization.
Weigh three 0.1 g samples of CoMat 01-319 SODIUM CHLORIDE which has been dried at 203 to 239 deg F (95 to 115 deg C) for two hours and which has an assay of 99.8 percent or better.
Dissolve in 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water.
Add 2 to 3 drops of 10 percent CoMat 01-321 POTASSIUM CHROMATE (CHLORIDEFREE) solution.
Titrate with silver nitrate solution until the first permanent reddish tint appears.
Record titer.
Calculations.
M = Molarity of silver nitrate solution.
W = Weight of sodium chloride.
P = Purity of sodium chloride.
V = Volume of silver nitrate.
M = WP/5.845V.
Average the three values obtained.
Silver nitrate solutions.
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution is 1 volume of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE hydrochloric acid diluted with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water.Weigh accurately 3.269 g of CoMat 01-351 ZINC METAL into a 1000 ml volumetric flask. Add 50 ml of a 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution to dissolve the zinc and dilute to the mark with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Mix well. Save for future EDTA standardization.
Pipette a 25 ml aliquot of standard CoMat 01-351 ZINC METAL (0.05M) into a 250 ml beaker. Add concentrated CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED, drop by drop, until a white precipitate appears and remains for a few seconds. Then add 5 ml of CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED ammonium hydroxide in excess and 50 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water. Add a pinch of CoMat 01-109 INDICATOR. Titrate with EDTA solution to a purple end point.
Calculations.
M = Molarity of EDTA solution.
V = Volume of EDTA (ml) used in titration.
M = 1.25/V.
Standardization of 0.1M EDTA.
Standardized solutions (Assay of chemical must be considered in weight of salt used for standard solutions). When the given make-up for a standard solution becomes impractical or inconvenient, such solution may be made in any convenient multiple or sub-multiple.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-001 Make-up Solutions in Standard Use
Volume measurements must be maintained in accordance with values listed below, unless otherwise specified. When pipettes and burettes or volumetric flasks are specified, or when procedure indicates use of such equipment by means of descriptive terms such as TITRATE, no tolerances in measurement will be permitted outside of those inherent in measuring devices.
When dissolving samples in acids, larger additions of acids, other acids or CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER than specified may be used if difficulty arises in dissolving chips.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-002 Accuracy of Volumetric Measurement
Before you start to weigh, be sure that the balance is properly adjusted. If necessary, turn the leveling screws at the base of the case until the spirit level on the back of the pillar shows balance is level. Note whether knife-edges are in correct positions with respect to bearings, and whether the pointer rests at zero point on the scale. Check the chain to be sure that it is tight around the drum or in column.
With the balance case closed, release the pan rests. The pointer must come to rest two divisions to the left of center. If it does not, increase or decrease the weight of the right hand pan by the chain adjusting knob hanging from the circular vernier. Then correct the zero setting by adjusting the screw on the upper right side of the balance case.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-003 Procedure and Accuracy of Weighing
When data is necessary for the calculations of results of analyses, this data must be recorded in a work log book. For example, when a chemical procedure calls for a titration to be done, it must be understood to mean that initial and final titration readings will be recorded. Logbook specimen weight entries must be recorded to four decimal places unless otherwise specified. Weight can be recorded to one or two places if the places that follow are zeros.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-005 Recording of Results
Analysis of solutions has been predicated on use of chemicals of known purity meeting these standards. Chemicals of equivalent standards will give equivalent results. If chemicals of known lower standards are used, there may have to be an equivalent adjustment in calculations. A special danger is that contamination in chemicals of lower standards can introduce errors in results.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-006 Primary Standards
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-1 nitric acid solution is 1 volume of CoMat 01-025 NITRIC ACID HNO3, TECHNICAL GRADE nitric acid diluted with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water.Put fully in a 1-1 nitric acid solution.
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-1 ethyl alcohol (denatured) solution is 1 volume of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) diluted with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.Flush in a 1-1 ethyl alcohol (denatured) solution.
For nickel plate, boil the electrode in CoMat 01-025 NITRIC ACID HNO3, TECHNICAL GRADE before you do Step (a).
Electrodes.
Place 1 or 2 scoops of CoMat 01-397 POTASSIUM PYROSULFATE or CoMat 01-182 NICKEL STRIP SALT in the crucible or dish and fuse gently over an oxidizing flame.
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution is 1 volume of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE diluted with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.Wash in boiling CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER or in boiling 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution.
Polish dull surfaces with 75 to 100 grit sea-sand made moist with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and applied with fingers or a soft cloth.
Crucibles and Dishes.
Cleaning.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-007 Platinum Ware
Polyethylene and polypropylene are generally interchangeable. These materials must be used wherever high concentrations of CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) are present. They must not be used where hot oxidizing acids (such as CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID) are involved. Polyethylene may be safely used at temperatures up to 175 deg F (79 deg C) and polypropylene up to 275 deg F (135 deg C). Beakers can be used over a steam bath, in a sand bath or heated by electrical jackets.
Teflon ware is also resistant to CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) but has the added feature of resisting hot oxidizing acids. Also, Teflon can be safely heated to 600 deg F (316 deg C) and is better for use where large volumes of solutions must be evaporated. Teflon beakers can be heated by all methods for polyethylene or polypropylene, and can also be set on wire gauze in contact with medium temperature hot plates.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-008 Use of Polyethylene, Polypropylene and Teflon Ware
A sufficiently long 0.5000in. (12.70 mm) diameter open tube, which is chemically inactive to the solution, must be flushed in the solution to be tested. The tube in a vertical position must then be put fully into the solution in several locations, closed at the upper end and removed. Each time the solution in the tube must be moved to a container which has been flushed in the solution and which can be sealed and identified.
Sampling procedures.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-009 Sampling of Solutions
NOTE
Depending on the amount of use each solution gets, the frequency can be increased or decreased based on experience. In any event, samples must be analyzed often enough to be sure that there is adequate control.The critical property or concentration of each solution that must be controlled is given along with the suggested frequency with which each must be checked.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-011 Plating Solutions Index, Refer to SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-035
Test Method P-1 is given in Step.
Test Method P-4 is given in Step.
Test Method P-6 is given in Step.
Test Method P-8 is given in Step.
Test Method P-9 is given in Step.
Test Method P-14 is given in Step.
Test Method P-17 is given in Step.
Test Method P-18 is given in Step.
Test Method P-22 is given in Step.
Test Method P-30 is given in Step.
Test Method P-33 is given in Step.
Test Method P-36 is given in Step.
Test Method P-55 is given in Step.
Test Method P-59 is given in Step.
Test Method P-60 is given in Step.
Test Method P-66 is given in Step.
Test Method P-79 is given in Step.
Test Method P-82 is given in Step.
Test Method P-90 is given in Step.
Test Method P-91 is given in Step.
Test Method P-100 is given in Step.
Below is the index of solution test method numbers (refer to Step) and their SUBTASK numbers.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-170-012 Test Method Index
Dissolve 40.0 g of CoMat 01-314 SODIUM HYDROXIDE (NaOH), REAGENT GRADE (SOLID) in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Dilute to 1000 ml with water.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(1).
Sodium hydroxide (1.ON).
Dissolve 1.0 g of CoMat 01-011 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED).
Indicator.
Solutions.
10.00 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE.
5.00 ml of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID.
5.00 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID.
2.00 ml of CoMat 01-364 PHOSPHORIC ACID or CoMat 01-466 PHOSPHORIC ACID.
Pipette a sample into a 250 ml flask as follows.
Add 75 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 2 to 3 drops of indicator solution.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-013 Test Method P-1, Acid Solutions
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-394 BARIUM CHLORIDE (BaCl2) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Barium chloride (10 percent).
Add 43.0 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 500 ml of water. Cool and dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric acid (0.5N).
Solutions.
Pipette a 10.0 ml specimen into a 250 ml beaker, dilute with 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, and heat to 110 to 140 deg F (43 to 60 deg C).
Add 50 ml of hot distilled or deionized water and a few drops of methyl orange indicator. Refer to Step, Step A.(7)(a).
Add 1/2 - 1 tablet of CoMat 02-189 COMPRESSED PAPER.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-014 Test Method P-4, Carbonates in Cyanide Plating Solutions
Add 28.0 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Sulfuric acid (1.ON).
Add 43.0 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric acid (0.5N).
Add 8.5 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, and dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER .
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric acid (0.1N).
Phenolphthalein indicator solution, refer to Step, Step 5.A.(11).
Bromcresol green - Methyl red indicator solution, refer to Step, Step 5.A.(16).
Add 1.7 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER in a 2000 ml volumetric flask. Dilute to volume.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step Step 5.B.(2)(b).
Hydrochloric acid (0.01N).
Solutions.
Put the salts in plastic volumetric flasks, each containing 300 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Heat to 195 to 205 deg F (91 to 96 deg C) to dissolve the salts. Cool at room temperature and dilute to 500 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Mix well.
NOTE
This test specimen is used in Step C.(1)(d) and Step D.(1) that follows:Pipette a 10 ml test specimen of the lowest concentration and add phenolphthalein indicator solution and titrate with CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID solution (1.ON) to a colorless endpoint and monitor the titer. Adjust the test specimen size or acid normality, as necessary, to give a titer of 10 ml minimum.
Pipette three test specimens of each concentration, size as given in Step (c), and add 25 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 2 to 8 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution and titrate to the colorless end point, refer to Step, Step 5.A.(11). Record titers.
Calculate the factors for each test specimen as follows:
a = concentration of cleaner necessary in oz/gal.
b = ml standard acid.
c = normality of standard acid.
Factor = a/bc.
Average the nine results. This is the factor to be used in Step E.(1).
For dry or solid cleaners.
Add the above parts to 1000 ml plastic volumetric flasks which contain 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool to room temperature, if necessary, and mix well. Fill to 1000 ml with water and mix well.
Pipette a 10 ml test specimen of the lowest concentration (for CoMat 01-300 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE), use a 50 ml specimen). Do as in Step C.(1)(c), to find the test specimen size to use in Steps C.(2)(e) and D.(1). For CoMat 01-300 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) specimens, use 0.1N hydrochloric acid solution and bromcresol green - methyl red indicator solution.
Pipette three test specimens of each concentration and add 25 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 2 to 8 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution and titrate to the colorless end point. For concentrations of 2.5 percent or less, use a pH meter to find the end point of 8.2. Record titers. For CoMat 01-300 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) specimens, add 5 to 10 drops of bromcresol green - methyl red indicator solution and titrate with O.1N hydrochloric acid solutions to a straw orange end point. Record titer.
For cleaners supplied as liquids.
Make up of cleaner factor.
Pipette the test specimen as given in Step C.(1)(c) or C.(2)(d) into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 25 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 2 to 8 drops of phenolphthalein indicator solution.
Procedure to give the concentration.
Use a 5 ml specimen size for CoMat 01-008 SODIUM HYDROXIDE NaOH (CAUSTIC SODA), SOLID.
Use a 20 ml specimen size for CoMat 01-301 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERALPURPOSE).
Use a 25 ml specimen size for CoMat 01-299 SYNTHETIC CLEANER.
Use a 50 ml specimen size for CoMat 01-300 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE).
Liquid alkalis.
Specimen size for regular analysis.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-015 Test Method P-6, Alkali Cleaning Solution
Dissolve 16.9890 g of CoMat 01-133 SILVER NITRATE CRYSTALS, previously dried for 1 to 2 hours at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C), in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml. Store in a dark container.
Silver nitrate (0.1N).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Potassium iodide (10 percent).
Add 28 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID slowly to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER in a large beaker. Add 53 g of CoMat 01-425 CERIC SULFATE and stir until dissolved. Dilute to 1000 ml with distilled or deionized water, mix thoroughly, and transfer to a glass-stoppered bottle. It may be standardized at once.
Standardize against freshly standardized 0.1N ferrous ammonium sulfate. Refer to Step 4. Pipette 25 ml ferrous ammonium sulfate solution into a 500 ml flask that contains 100 ml cold sulfuric acid (1-4). Add 1 to 2 drops of CoMat 01-403 INDICATOR, O-phenanthroline indicator and titrate with ceric sulfate solution (refer to Step (3)) until the color changes from reddish to colorless or greenish.
Normality Ceric sulfate =
(N Ferrous ammonium sulfate x 25)/ml ceric sulfate
Standardization.
Ceric sulfate (0.1N).
Standardize against standard 0.1N potassium dichromate (refer to Step 5.). Pipette 25 ml ferrous ammonium sulfate solution into a 500 ml flask that contains 100 ml of sulfuric acid H2SO4 (1-4). Add 10 ml CoMat 01-364 PHOSPHORIC ACID H3PO4 (85 percent) and 1 to 2 drops of diphenylamine indicator. Refer to Step (7). Titrate to a purple end point with standard 0.1N potassium dichromate solution (refer to Step (5)).
Normality Ferrous ammonium sulfate =
(ml potassium dichromate x 0.1)/25
Standardization.
Ferrous ammonium sulfate (0.1N). Add 30 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID (H2SO4) slowly to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 39.5 g of CoMat 01-423 FERROUS AMMONIUM SULFATE Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, stir until dissolved, and dilute to 1000 ml with distilled or deionized water. Filter before the standardization.
Dry 5g pure CoMat 01-384 POTASSIUM DICHROMATE K2Cr207 at 225 to 230 deg F (107 to 110 deg C) for no less than two hours. Weigh 4.9035g of dried salt, transfer to 600 ml beaker, dissolve in 400 ml warm CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml.
Standard potassium dichromate.
CoMat 01-403 INDICATOR. Purchase ready to use.
Dissolve 1.00 g of CoMat 01-405 INDICATOR (C6H5)2NH in 100 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID H2SO4.
Diphenylamine indicator.
EDTA (0.1M) Comat CoMat 01-350 ETHYLENE DIAMINETETRA-ACETIC ACID (EDTA). Purchase ready to use. Store in a plastic container.
Dissolve 70 g of CoMat 01-424 AMMONIUM CHLORIDE NH4C1 in 570 ml CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED NH40H. Dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Store in a plastic container.
Buffer solution (pH10).
Murexide indicator CoMat 02-190 CHEMICAL TABLETS. Purchase in tablet form.
Solutions.
Under a hood, add 10 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID and 15 ml of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID HNO3. Cover with a raised cover glass.
Metallic Copper.
Add 1 tablet of CoMat 02-190 CHEMICAL TABLETS Murexide indicator. Shake to dissolve.
Titrate with CoMat 01-350 ETHYLENE DIAMINETETRA-ACETIC ACID (EDTA) to a permanent blue-violet end point.
Copper (EDTA) Alternate Method.
Add 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 5 ml of potassium iodide solution (10 percent). Refer to Step B.(2).
Free Sodium Cyanide.
Pipette duplicate 1 ml specimens into 500 ml flasks. Add 75 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 25 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID.
Remove from hot plate and cool to room temperature. Add 1 to 2 drops of CoMat 01-403 INDICATOR and titrate with 0.1N ceric sulfate solution (refer to Step B.(3) until the color changes from orange or pale rose to colorless. Add ceric sulfate solution dropwise as only a few drops are necessary.

CAUTION
THE SOLUTION SUPERHEATS.NOTE
If while boiling, the solution changes from yellow to colorless, pipette an additional 25 ml of ceric sulfate solution into the flask.Pipette 25 ml of ceric sulfate solution into the flask and add water until the solution level is about 1 to 1 1/2in. from the bottom of the flask. Boil gently for 30 to 60 minutes.
Remove from hot plate and cool to room temperature. Add CoMat 01-403 INDICATOR and titrate with 0.1N ferrous ammonium sulfate solution (refer to Step B.(4)) until the color changes from yellow thru colorless to the orange or pale rose end point.
Rochelle Salt or Rocheltex.
Hydroxide. Refer to Test Method P-9 in Step.
Carbonate. Refer to Test Method P-4 in Step.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-016 Test Method P-8, Copper Plating Solution (Cyanide Type)
Add 43.0 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE HCl to 500 ml of water and dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Mix well.
Standardization - Acid solution refer to Step Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric Acid (0.5N).
Lamotte Sulfo - Orange Indicator CoMat 02-211 INDICATOR. Purchase ready to use.
Solutions.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-017 Test Method P-9, Hydroxides in Cyanide Solutions
Soak 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER with CoMat 01-390 FERRIC AMMONIUM SULFATE. Add CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID (free of nitrous acid by heating) until the solution is clear and a pale yellow color.
Ferric ammonium sulfate.
Dissolve 8.1 g of CoMat 01-391 SODIUM THIOCYANATE (NaSCN) in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml. Pipette 25 ml of silver nitrate solution (0.1M) into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask. Add 5 ml of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID, 1 ml of ferric ammonium sulfate solution and 50 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Titrate with sodium thiocyanate solution until a permanent reddish brown tinge appears in the solution which is being shaken.
Molarity of NaSCN = 25 x Molarity of AgNO3/ml NaSCN.
Sodium thiocyanate (0.1M).
Dissolve in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER 17.0 g of CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3) dried before for 1 to 2 hours at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C) and dilute to 1000 ml. Keep in a dark container.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(5).
Silver nitrate (0.1M).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 1.0 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE. Keep in a dark container.
Potassium iodide solution.
Add 43.0 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric acid (0.5N).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-394 BARIUM CHLORIDE (BaCl2) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water.
Barium chloride (10 percent).
NOTE
In this test method, sodium thiocyanate solution may be written as NaSCN; silver nitrate solution as AgNO3 and hydrochloric acid solution as HCl.Solutions.
Under a hood, add 20 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID and 15 ml of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID.
Decrease the temperature and add 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER slowly and cautiously.
Metallic silver (Volumetric, alternate procedure).
Add 150 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, 4 to 6 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE and 9 to 11 g of CoMat 01-392 POTASSIUM CYANIDE (KCN).
Plate at 1.8 to 2.2 amps on weighed platinum electrodes until all silver is removed from the solution. To find out if all the silver has been plated out of the solution, increase the level of solution with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and check for more deposits of silver on the cathode.
With the current on, remove the cathode and flush with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Clean the cathode in baths one after the other, of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, 1-1 alcohol and alcohol. Supply ignition and burn off the alcohol.
Metallic silver (electrolytic).
Pipette a 5 ml sample into a 250 ml flask, add 100 ml of (CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 2 ml of potassium iodide solution (10 percent).
Free potassium cyanide.
Pipette three 10 ml specimens into 250 ml flasks. Number the specimens 1, 2 and 3. Also label and pipette a 10 ml CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER blank and add 3 to 5 drops of hydrochloric acid solution (0.5N) to the blank.
NOTE
Unless the indicator volumes are equal, the color produced will not be the same.Add 10 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 7 to 9 drops of CoMat 01-402 INDICATOR to each flask.
Potassium hydroxide.
Pipette a 10 ml sample into a 250 ml beaker, dilute with 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and heat to 110 to 140 deg F (43 to 60 deg C).
Permit the precipitate to go to the bottom of the beaker. Filter the liquid through CoMat 02-210 FILTER PAPER and add a few drops of barium chloride solution (10 percent) to the first portion of filtrate to find if precipitation is complete.
Clean with hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and move the filter paper and precipitate to the beaker in which precipitation was initially done.
Add 50 ml of hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and a few drops of methyl orange indicator solution.
Potassium carbonate.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-018 Test Method P-14, Silver Plating Solutions (Cyanide-type)
Dissolve 49.0 g of CoMat 01-307 SODIUM CYANIDE (NaCN) in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml.
Standardization.
Pipette 10 ml of sodium cyanide solution into a 250 ml Erelenmeyer flask, add 50 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 10 to 15 drops of potassium iodide solution (10 percent).
Titrate with silver nitrate solution (0.1M) to a faint permanent turbidity.
Molarity of NaCN soln. = ml AgNO3 soln. x molarity of AgNO3 x 0.2.
Sodium cyanide (1.0M).
Dissolve 16.9890 g of CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3), dried for 1 to 2 hours at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C), in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml. Store in a dark bottle.
Standardize silver nitrate solutions. Refer to Step, Step B.(5).
Silver nitrate (0.1M).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 1.0 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE. Store in a dark bottle.
Potassium iodide (10 percent).
Weigh out 37.2 g of CoMat 01-350 ETHYLENE DIAMINETETRA-ACETIC ACID (EDTA) pure dihydrate salt and 6.0 g of CoMat 01-314 SODIUM HYDROXIDE (NaOH), REAGENT GRADE (SOLID). Dissolve in a final volume of 1 l of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Standardization of 0.1M ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid.
Weigh accurately 3.269 g of CoMat 01-351 ZINC METAL into a 1000 ml volumetric flask. Add 50 ml of 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution to dissolve the zinc and dilute to mark with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Mix well. Save for future EDTA standardization.
Pipette a 25 ml aliquot of standard zinc (0.05M) into a 250 ml beaker. Add concentrated CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED, drop by drop, until a white precipitate appears and stays for a few seconds. Then add 5 ml of CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED in excess of 50 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add a pinch of CoMat 01-109 INDICATOR. Titrate with EDTA solution to a purple end point.
Molarity of EDTA = 1.25/ml of EDTA.
Ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid, Sodium salt (EDTA) (0.1M).
Dissolve 200 g of CoMat 01-311 CITRIC ACID in a cooled mixture of 900 ml CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 100 ml of CoMat 01-043 SULFURIC ACID H2SO4.
Citric acid.
Murexide indicator. Purchased CoMat 02-190 CHEMICAL TABLETS (0.4 mg).
Solutions.
Pipette 5.00 ml of plating solution into a 250 ml flask. Add 25 ml of citric acid, 50 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED dropwise until the solution just turns a clear blue.
Add from a burette 2.00 ml of silver nitrate solution (0.1M). If the solution becomes turbid add CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED dropwise until the solution turns clear again. Add 10 to 15 drops of potassium iodide solution (10 percent).
Nickel (Procedure A).
Add 50 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, 10 ml of citric acid solution and from a burette 15 ml of CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED .
Add 1 CoMat 02-190 CHEMICAL TABLETS and mix to dissolve.
Nickel (Procedure B).
Pipette a 2 ml sample into a 250 ml beaker, add 75 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and mix.
Add 10 ml of CoMat 01-306 AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE (NH4OH),CONCENTRATED and two CoMat 02-190 CHEMICAL TABLETS.
Nickel (Alternative Non-cyanide for Solution Codes 30 and 55).
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-019 Test Method P-17, Nickel Plate Solution
Dissolve 16.9890 g of CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3) dried for 1 to 2 hours at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C), and dilute to 1000 ml. Keep in a dark container.
Standardize, Silver nitrate solutions, refer to Step, Step 5.B.(5).
Silver nitrate (0.1M).
Potassium iodide (10 percent). Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 1.0 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE. Keep in a dark container.
Solutions.
Pipette a 10 ml sample into a 250 ml flask. Add 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 5 ml of potassium iodide solution.
Free Sodium cyanide or Potassium cyanide.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-020 Test Method P-18, Free Cyanide in Process Solutions
Purchase ready to use or make a paste of 1.0 g CoMat 01-385 STARCH and a small quantity of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 150 ml of hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and boil for 2 to 3 minutes.
Starch solution.
Dissolve 25 g of CoMat 01-383 SODIUM THIOSULFATE in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 0.1 g of CoMat 01-382 SODIUM CARBONATE for each liter of solution and permit it to stand for one week before standardization.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(4).
Sodium thiosulfate (0.1N).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-394 BARIUM CHLORIDE (BaCl2) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Barium chloride (10 percent).
Special sulfate solution A purchased ready to use, or dilute 420 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Sulfate solution A.
Special sulfate solution B purchased ready to use, or dissolve 300 g of CoMat 01-395 BARIUM CHLORIDE - 2 HYDRATE in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Sulfate solution B.
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 1.0 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE. Store in a dark bottle.
Potassium iodide solution (10 percent).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-396 AMMONIUM BIFLUORIDE in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Store in a plastic container.
Ammonium bifluoride solution (10 percent).
Solutions.
Pipette a 10 ml test specimen into a 250 ml volumetric flask and dilute with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Add 10 ml of ammonium bifluride solution, 50 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 25 ml of potassium iodide solution.
Add 10 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID (1-1) and titrate immediately with standard sodium thiosulfate solution to a light yellow green color.
Chromic acid.
Add 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, 25 ml of potassium iodide solution and 10 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID (1-1). Mix.
pH of solution. Refer to Test Procedure P-82, Step.
NOTE
For solutions which have a concentration of sulfate resulting in readings off the scale, a smaller specimen can be used in Step (c), and the final reading, Step (j) minus Step (f) can be multiplied by 20 divided by the volume.Record the reading of the level. Subtract blank (f) for the corrected reading.
Sulfates (a modification of the Kocour Procedure).
Pipette a 5 ml sample into a 400 ml beaker and add 175 to 250 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Add 10 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE, 10 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) and 10 ml of CoMat 01-057 ACETIC ACID CH3COOH.
Filter on CoMat 02-011 FILTER PAPER, washing paper and precipitate well unit the filtrate is not acid.
Sulfates (Optional Procedure).
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-021 Test Method P-22, Chromium Plating Solution and Anodize Touch-Up Solution (CoMat 02-136 Chromate Conversion Salt or CoMat 03-125 Chromate Conversion Salt)
Silver nitrate (0.1N). Dissolve 16.9890 g of CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3), dried before for 1 to 2 hours at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C), in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml. Store in a dark container.
Potassium iodide (10 percent). Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1000 ml. Add 1,0 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE. Store in a dark bottle.
Solutions.
Make up to 150 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Add 5 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE and 10 g of CoMat 01-392 POTASSIUM CYANIDE (KCN). Mix to dissolve.
Plate at 1.8 to 2.2 amps on weighed platinum electrode until all silver is removed from the solution. To find out if all the silver is removed, increase the level of the solution with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and check for more deposition of silver on cathode.
With current on, remove the cathode, flush fully with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Dip the cathode in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER distilled or deionized water; then dip in alcohol. Ignite and burn off the alcohol.
Metallic silver.
Pipette a 5 ml sample into a 250 ml flask, add 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 2 ml of potassium iodide solution (10 percent).
Free potassium cyanide.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-022 Test Method P-30, Silver Strike Solution
To 2000 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, add slowly and cautiously 700 ml of concentrated CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID and dilute to 3500 ml; mix well. This can be measured in a large graduate as the solution must be standardlized against CoMat 01-237 TRIS (HYDROXY METHYL)AMINO METHANE.
Standardization. Nitric acid solutions. (Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2)).
Primary standard Nitric acid solutions (approximately 3N, 200 ml/liter).
To a 1000 ml Nalgene volumetric flask which contains approximately 300 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, add 400 ml of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID and 29.6 ml of CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) (or 20 ml of CoMat 01-132 HYDROFLUORIC ACID HF, 70 percent). Dilute to 1 l with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and mix well. Store in a plastic bottle.
NOTE
AR HF is an Analytical Reagent Grade hydrofluoric acid (48 to 51 percent).Optional synthetic standard Solution Code 50 (40 percent (that is, 400 ml/l) CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID), 2 percent (that is, 20 ml of CoMat 01-132 HYDROFLUORIC ACID HF /1 = 29 ml AR/l) CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) by volume.
NOTE
AR HF is an Analytical Reagent Trade hydrofluoric acid (48 to 51 percent).Optional synthetic standard solution (15 percent (that is, 150 ml/l) CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID), 0.5 percent (that is, 5 ml of CoMat 01-132 HYDROFLUORIC ACID HF/l = 7.3 ml AR/l) CoMat 01-357 HYDROFLUORIC ACID (HF) by volume.
Add 2600 ml (or 65 percent of the final volume) of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER to a 5 l Pyrex jar. With constant agitation, add very slowly 1000 ml (or 250 ml/l) of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID. Add 740 g (or 185 g/l) of CoMat 01-358 FERROUS SULFATE (FeSO4.7H2O), agitate to dissolve and cool in cold water. Filter the solution through CoMat 01-353 FILTER PAPER, using a Buchner funnel. Dilute with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER to 4 l.
Standardization of the ferrous sulfate solution. Refer to Steps C.(1)(a) thru (g) for nitric acid content. Use a 2.0 ml specimen of primary standard nitric acid from Step B.(1)(a) in the place of the unknown process solution in Step C.(1)(c). Do again until 3 results are obtained.
N = (NA x VA)/VF.
where:
N = Normality of ferrous sulfate.
NA = Normality of acid.
VA = Volume of acid.
VF = Volume of ferrous sulfate - 0.2.
Ferrous sulfate factor = N (ferrous sulfate) x 5.
Ferrous sulfate solution (0.3N).
NOTE
You can use a graduate or marked bottle because the solution is standardized against a primary standard.Dissolve 660 g of CoMat 01-314 SODIUM HYDROXIDE (NaOH), REAGENT GRADE (SOLID) in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 8 l.
Standardize against primary standard nitric acid. (Refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2)). Use 30.0 ml portions of nitric acid solution and sufficient bromthymol blue indicator solution to produce a deep orange color.
Sodium hydroxide (approximately 2N, 82.5 g/l).
Dissolve 0.10 g of CoMat 01-352 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED).
Bromthymol blue indicator solution to use:
Solutions.
Add 80 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID to a 200 ml or 300 ml plastic beaker and a flat circular magnetic stirring bar if a magnetic stirrer is to be used.
Pipette a 2.0 ml specimen of the solution with the NALGENE pipette and a rubber bulb or auto pipette. Slowly deliver the specimen below the surface of the CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID. Be sure that the pipette tip stays below the surface of the sulfuric acid until the titration is completed.
During the delivery of the specimen, when the magnetic stirrer is not used, stir the acid solution by the constant movement of the tip of the pipette along the sides of the beaker. Keep in contact with the bottom of the beaker.
When the magnetic stirrer is used, keep a maximum agitation without splashing acid or exceeding spinner compliance speed. Movement of the pipette is not necessary.
NOTE
Temperature must not exceed 120 deg F (49 deg C) during titration. Standards and test specimens must be titrated in the same manner.Add ferrous sulfate solution (0.3N) in a fine stream to the mixture near the outer wall until the yellow color that first forms takes on a faint brown tinge. Keep a constant movement at all times in an applicable manner.
Nitric acid content.
NOTE
For Solution Code 33, a 5.0 ml specimen may be used.Pipette a 10.0 ml specimen into a 400 ml plastic beaker. Add 175 to 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
NOTE
The indicator will not change to clear blue when selected solution has been in use. The yellow color will change to green and then gradually change to a solid opaque blue.Iron contamination will mask the end point, but the color may be seen at an angle through the edge of the solution. Stopping the agitation to permit the settling of brown precipitate after each sodium hydroxide addition also helps.Titrate with a 2N of sodium hydroxide solution with the use of strong agitation until traces of bluish color appears. Then slowly continue titration dropwise until the blue color continues at least one minute after the last drop has been added.
Ammonium bifluoride or Hydrofluoric acid content.
Summary of method: Specimens are aliquoted from various tanks. The solution is aspirated into a nitrous oxide flame where the specimen is dissociated into atoms. Absorbance of the unknowns is compared to known standards. The concentration of titanium, in g/l, is then determined either instrumentally or manually.
Standard preparation: Volumetrically pipette these various quantities of 1000 ug/ml titanium stock solution into a separate 100 ml volumetric flask and bring to volume with water and shake vigorously:
For flask 1 the standard concentration of 0 ug/ml equivalent to 0.0 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 0.0.
For flask 2 the standard concentration of 20 ug/ml equivalent to 2.0 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 2.0.
For flask 3 the standard concentration of 50 ug/ml equivalent to 5.0 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 5.0.
For flask 4 the standard concentration of 100 ug/ml equivalent to 10.0 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 10.0.
For flask 5 the standard concentration of 125 ug/ml equivalent to 12.5 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 12.5.
For flask 6 the standard concentration of 150 ug/ml equivalent to 15.0 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 15.0.
For flask 7 the standard concentration of 200 ug/ml equivalent to 20.0 g/l for each ml of 1000 ug/ml Ti stock solution is 20.0.
NOTE
Instrument is calibrated to read the final answer in g/l only for 10 to 1000 (or 1 to 100) dilution. If a different solution is used, do the alternate step that follows.Determination of titanium content: Set the instrument parameters as follows and make adjustments as necessary to maximize absorbance:
Wavelength: 365.3 nm.
Alternate wavelength: 320.0 nm.
Slit opening: 0.2 nm.
Operational mode: Abs AA-BG.
Flame gases: Nitrous oxide and acetylene.
Burner head: Nitrous oxide.
Burner orientation: Normal.
With the absorbance maximized, aspirate the 15.0 g/l standard.
Switch operational mode (signal) to CONC (concentration).
Enter 15.0 on the keyboard - (display reads 15.0, keyboard light on). Press key S1 once - (display reads 15.0, S1 light on). If so equipped, magnetic cards can be used to complete this step.
Press key S1 once.
Aspirate the standards and record the concentration in grams/liter (g/l).
Aspirate the diluted test specimen from step (c) and record Ti concentration in g/l.
Alternate step: Aspirate standards and specimens and record the readings. Maintain operational mode (signal) on ABS (absorbance). Absorbance reading must not exceed 0.466 units.
Plot the standards curve on rectangular coordinates (concentration versus absorbance) or calculate a least square curve. This curve must be treated as linear only within the range established by the standards.
Titanium content in hydrofluoric-nitric acid process solutions: Wet chemical tests - Atomic absorption.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-023 Test Method P-33, Nitric Acid, Ammonium Bifluoride or Hydrofluoric Acid Solution
Weigh 42.47 g of CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3) dried at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C) for 1 to 2 hours, into a 1 l volumetric flask, dissolve in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and make up to volume. Store in an amber or dark glass container.
Standardize - silver nitrate solutions, refer to Step, Step 5.B.(5).
Silver nitrate (0.25M).
Add 14 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and dilute to 1 l in a volumeter flask with water.
Standardize, refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Sulfuric acid (0.5N).
Dissolve 50 g of CoMat 01-354 GUM ARABIC in 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Gum arabic solution (10 percent).
Dissolve 5.0 g of CoMat 01-064 INDICATOR (acid type formula C15H15N3O2 Formula weight 269.3) in 500 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED).
Methyl red indicator solution.
Dissolve 1.0 g of CoMat 01-011 INDICATOR in 1 l of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED).
Phenolphthalein indicator solution.
Solutions.
Add 10 ml of gum arabic solution (10 percent) and 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Sodium cyanide (free).
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-024 Test Method P-36, Alkali Smut Removal Solution (Solution Code 47)
Add 28.0 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, cool and dilute to 1000 ml.
Standardize - acid solutions, refer to Step, Step 5.B.(2).
Sulfuric acid (1.0N).
Add slowly 400 ml of CoMat 01-320 SULFURIC ACID to 400 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER with constant agitation.
Sulfuric acid (1-1).
Dissolve 100 g of CoMat 01-308 POTASSIUM IODIDE (KI) in 1 l of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and add 1.0 g of CoMat 01-322 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE. Store in a dark container.
Potassium iodide solution (10 percent).
Purchase ready to use, or make a paste of 1.0 g of CoMat 01-385 STARCH with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 150 ml of hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and boil for 2 to 3 minutes. Store in a dark container.
Starch solution.
Dissolve 25.0 g of CoMat 01-383 SODIUM THIOSULFATE in 1 l of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Add 0.1 g of CoMat 01-382 SODIUM CARBONATE for each liter of solution and let it stand for one week.
Standardize - sodium thiosulfate, refer to Step, Step 5.B.(4).
Sodium thiosulfate (0.1N).
Solutions.
Add 5 ml of CoMat 01-381 METHYL ALCOHOL or 30 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) to a 400 ml beaker. Pipette a 5 ml sample of the solution into the beaker and agitate until completely brown.
NOTE
Use CoMat 02-206 INDICATOR PAPER or CoMat 02-207 INDICATOR PAPER for pH determination.Add 75 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and one half a 3.85 cm ashless CoMat 02-208 FILTER PAPER TABLETS-ASHLESS or CoMat 02-189 COMPRESSED PAPER; then filter through a folded CoMat 02-205 FILTER PAPER into a 800 ml beaker. Wash well with hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER until the pH of the filtrate, on discharge from the funnel, is below pH 8.
Add 2 to 3 drops of phenolphthalein solution to the filtrate (Refer to Step Step 5.A.(11) and titrate quickly to the colorless end point with a 1.0N sulfuric acid solution.
Alkalinity.
Pipette a 25 ml sample into a 250 ml volumetric flask and dilute to the mark with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Pipette a 10 ml aliquot specimen and transfer to a 250 ml beaker. Add 50 to 60 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Potassium permanganate.
Procedure.
Add 2 to 3 drops of Methyl Orange indicator solution and continue to titrate to a faint pink end point (Refer to Step Step 5.A.(7)).
Procedure A.
Sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-025 Test Method P-55, Caustic Soda or Potassium Permanganate
Add 43 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and dilute to 1 l with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER .
Standardize - acid solutions, refer to Step Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric acid (0.5N).
Dissolve 1.0 g of CoMat 01-394 BARIUM CHLORIDE (BaCl2) in 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Barium chloride (10 percent).
Dissolve 1.0 g of CoMat 01-011 INDICATOR in 100 ml of CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED).
Phenolphthalein indicator solution.
Solutions.
Dissolve with less than 400 ml of warm 120 to 130 deg F (49 to 54 deg C) CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER which has been previously boiled and cooled.
Filter dissolved salts through folded CoMat 02-203 FILTER PAPER into a 1 l volumetric flask. Wash insoluble residue with warm CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Do this until the filtrate dropping from the funnel has a pH of 8 or less with CoMat 02-206 INDICATOR PAPER.
Filter again into another volumetric flask large enough to hold the solution and washings (1 l or 2 l). Wash again with cold (boiled and cooled) CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER until the filtrate is again below pH 8. Dilute to volume.
Solution of sample.
Add 50 ml of boiled and cooled CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 20 ml of the barium chloride solution (10 percent). Stir and let it settle for 5 minutes.
Sodium hydroxide.
Add 50 ml of boiled and cooled CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Sodium carbonate.
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-026 Test Method P-59, Descaling Salt Bath
Add 334 ml of CoMat 01-349 CADMIUM PLATE BRIGHTENER to a 500 ml volumetric flask, add CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER to volume. Increment 1 ml = 1 quart for every 100 gal of solution being tested when used with a 267 ml Hull cell.
Additive stock solution.
CoMat 01-138 ALKALI CLEANER (HEAVYDUTY) or CoMat 01-139 ALKALI CLEANER (HEAVYDUTY) made to a concentration of 16 oz/gal.
Alkaline cleaner.
Solutions.
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution is 1 volume of CoMat hydrochloric acid diluted with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.After cleaning the cadmium anode in a 1-1 CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE, and rinsing, position the anode in the Hull cell.
NOTE
The make-up of a 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution is 1 volume of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE diluted with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.Remove zinc from steel panels by putting them fully into a 1-1 hydrochloric acid solution and wiping the smut from the surface using a clean gauze cloth.
Rinse in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and check for water breaks.
Remove the plated panel from the apparatus, then flush with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dry by dipping in CoMat 01-239 ETHYL-ALCOHOL (DENATURED) or CoMat 01-393 ACETONE and allow to stand until dry.
Read the current density range from the furnished chart, refer to Fig Figure.
Cadmium (for Brightener).
Put fully in alkaline solution and anodically clean for 10 to 15 seconds. Remove and flush in hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Refer to Step C.(2) for the make-up of the alkaline cleaner solution.
Place the panel in 35 percent hydrochloric acid solution and agitate for 5 to 10 seconds. Remove and flush in cold CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Remove the panel from the solution. Rinse in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, dip in CoMat 01-393 ACETONE, and allow to dry.
NOTE
To find the effectivness of CoMat 01-281 ACTIVATED CARBON or CoMat 01-282 ACTIVATED CARBON (GRANULAR) to be used in purification, 1 oz/gal of solution must be used and tested. Additional increments of activated carbon must be made until a panel is satisfactory to the requirements of Solution Code 30. You can use this finding to recommend the quantity of carbon to be used for purification of the production tank solution.Read the current density range from the furnished chart, refer to Figure, and record the results.
Nickel strike (Current Density).
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-027 Test Method P-60, Hull Cell Testing
NOTE
This equipment (or use a unit with equivalent features and safeguards) is available from the sources that follow:Industrial Instruments, Inc.
446 Winterhaven Drive,
Newport News,
VA 23606-2533 USA
www.industrialinstruments.com
Tel: +1-757-930-0856
Fax: +1-757-930-3119
Kameras Instruments
10715 Clermont Avenue,
PO Box 100
Garrett Park, MD 20896 USA
Tel: +1-301-946-3210
Gearless Contractometer (refer to the manufacturer's instructions for its use).
Rack with nickel anodes for supporting contractometer. Refer to Figure.
Apparatus.
Measurement of helix. Refer to Fig Figure.
Degrease the helix. Refer to the SPM TASK 70-11-03-300-503.
Flush in running CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. If the helix shows visual water breaks when removed from the water, do the cycle again.
Dry with reagent grade alcohol or CoMat 01-393 ACETONE.
Preparation of the helix.
Mount a prepared unplated helix onto the spindle of the instrument. The helix should be flush with the shoulder of the upper support mount A, refer to Figure, and even with the end of the lower support mount B.
Remove cover from the instrument dial; then use the bubble gage to level the instrument. The instrument can be set in an anode cage which has been leveled before. Refer to Fig Figure.
Put the screw threaded end of the pulley arm into hole C, refer to Fig Figure. The pulley arm must be on the same plane as the dial face.
NOTE
Constant determination must be done again after every 12 uses.Calculation of the constant of helix (K).
K = (in x lb)/degree = ((wt) (a(in)) (0.002205 lb/gm))/W in deg.
where.
a = distance between the pulley and supporting arm (refer to Step D.(9)).
wt = calibration weight (refer to Step D.(6)).
W = degrees of deflection from calibration (refer to Step D.(15)).
Determine of helix constant.
Calculation of plating current.
AMPS = (45 (3.1416) (dh) (L))/144.
where.
45 = ASF (amperes/square foot).
3.1416 = pi or the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
144 = Conversion factor (square inches/square foot).
dh = outside diameter of helix (refer to Step B.(6)).
L = height of helix (refer to Step B.(4)).
NOTE
A 20 to 30 percent hydrochloric acid solution has 20 to 30 volumes of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE hydrochloric acid for every 100 volumes of solution.Put fully into a 20 to 30 percent hydrochloric acid solution for 30 to 60 seconds.
Flush in running CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Check for water breaks. Do Steps (a) thru (d) again until the helix shows no water breaks.
Flush in running cold CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and then in hot CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Dry in an oven at 202 to 222 deg F (94 to 106 deg C), or dip in CoMat 01-031 ACETONE (CH3)2CO or CoMat 01-007 ETHYL ALCOHOL C2H5OH (DENATURED) and air dry.

CAUTION
DO NOT DO STEPS (I) AND (J) IF THE HELIX USED HAS A PERMANENT TEFLON MASKING.Apply a mask or maskant to the helix with a thin even film of CoMat 02-021 MASKING WAX COMPOUND by putting fully into hot wax at approximately 200 °F (93 °C) until the helix is up to temperature, or mask the inside diameter of the helix with an even layer of CoMat 07-055 STOP-OFF LACQUER. Equivalent materials can be used. After application of wax, keep helix in constant rolling motion while cooling between absorbent towels to apply wax evenly over the inner surface.
Helix preparation.
NOTE
A 20 to 70 percent hydrochloric acid solution has 20 to 30 volumes of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE for every 100 volumes of solution.Put fully into a 20 to 70 percent hydrochloric acid solution for 30 to 60 seconds.
Flush fully in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Check for water breaks. Do Steps (b) to (e) again if necessary.
Mounting and Cleaning Helix.
Use nonconductive supports to place arms of the fixture over the solution to be tested; then adjust the arms so that the solution will fully cover the helix. Mount the apparatus into the fixture that contains the nickel anodes. Refer to Figure. The solution must not be agitated too much. Let the helix and other components adjust to the solution temperature.
Connect the positive lead to the nickel anodes and the negative lead to the steel clamp of the helix contractometer. Refer to Figure.
The test must be run at a serviceable current. The test time is 12 minutes at the current A, as calculated in Step E for the helix. When helix deflections show very high stress values, the test can be run for 20 minutes, or some other between time, but the minimum final calculated plate thickness must be 0.00037 in.
At the end of determination, disconnect the apparatus and remove from the plating solution. Flush in cold CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER; then flush in warm CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and blow dry.
In preparation for next analysis, strip the nickel from the helix by putting fully in 1-1 nitric acid solution (that is, 1 volume of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID mixed with 1 volume of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER) at 160 to 180 deg F (71 to 82 deg C). Flush fully. The chemically clean surface can now be processed through nickel strike as in Step F(1)(c) thru F(1)(g).
Plating procedure.
Testing procedure.
Calculate the deposit thickness (Dt) as follows:
Deposit thickness (Dt) = (Bf-Bi)/(145.84) (3.1416) (dh) (L).
where.
(Bf-Bi) is in grams (refer to Steps F.(3)(m) and F.(1)(h)).
145.84 is the conversion factor of density of nickel 8.9 g/cu cm to 145.84 g/cu in.
3.1416 = pi or the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
dh = outside diameter (refer to Step B.(6)).
L = length of plated area (refer to Step B.(4)).
.
Stress calculation by formula.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-028 Test Method P-66, Contractometer Determination of Nickel Plate Stress in Nickel Plate Solution (Solution Code 55)
Sodium hydroxide standardization, refer to Step Step 5.B.(1)(b).
Sodium hydroxide (1.ON).
Solutions.
Add 75 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 8 to 12 drops of Bromcresol green indicator solution, refer to Step Step 5.A.(2).
Dry acid salt concentration.
Procedure.
Dissolve in 75 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 100 ml.
Derivation of factor.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-029 Test Method P-79, Acid Salt Solution
Flush the electrodes and put fully in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER when not in use.
Solution examination.
Procedure.
Wash the electrodes with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and wipe with absorbent tissue or fully flush it.
Remove the electrodes from the buffer solution, flush with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, wipe with paper tissue or fully flush.
Instrument and installation adjustment, assemble to manufacturers instructions.
Flush the electrodes and put fully in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER when not in use.
Solution examination.
Alternate procedure.
Calculations.
(1) Gallons of acid to add =.
vol. of acid used (ml)x(ATC)x(.05)/vol. of tank specimen (ml).
(2) Gallons of base to add =.
vol. of base used (ml)x(ATC)x(.05)/vol. of tank specimen (ml).
(3) Pounds base to add =.
vol. of base used x(0.417)x(ATC)/vol. of tank specimen (ml).
Where ATC = actual tank capacity in gallons.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-030 Test Method P-82, pH Determination
Polishing material: CoMat 05-152 SILICON CARBIDE PAPER.
Apparatus.
CoMat 01-096 ELECTROLYTIC STRIPPINGSOLUTION - control solution: To 300 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, add 100 ml of Solution A and 100 ml of Solution B. Dilute to 500 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Add 250 ml of concentrated CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 200 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Dilute to 500 ml with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Deoxidizing solution: 30 to 50 percent hydrochloric acid.
CoMat 01-278 NICKEL STRIP ADDITIVE. Pipette 25 ml of purchased additive to a 100 ml volumetric flask. Dilute to volume with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Solutions.
Polish two copper strips with CoMat 05-152 SILICON CARBIDE PAPER.
Dip the copper strips in alkaline cleaner. Remove and flush fully in warm CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Dip the copper strips in acid solution. Remove and flush fully in cold CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Pour 50 ml of room temperature CoMat 01-096 ELECTROLYTIC STRIPPINGSOLUTION into a 100 ml beaker and 50 ml of test solution into another 100 ml beaker.
Remove and flush the copper strips in clean running CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and air dry.
Add 1.0 ml of CoMat 01-278 NICKEL STRIP ADDITIVE and do Steps (1) to (7) again.
If brown film still does not match film from control do Step (a) again with further 1.0 ml additions of CoMat 01-278 NICKEL STRIP ADDITIVE until brown film matches that from control.
If film from test solution is lighter than film from control, deletion of CoMat 01-278 NICKEL STRIP ADDITIVE is indicated and the test should be continued as follows:
Procedure.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-031 Test Method P-90, Inhibitor Replenishment for Solution Code 57
Add 43.0 ml of CoMat 01-363 HYDROCHLORIC ACID (HCl),REAGENT GRADE to 500 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1 l with CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Mix well.
Standardize, refer to Step Step 5.B.(2).
Hydrochloric acid (0.5N).
CoMat 01-355 INDICATOR. Purchase ready to use.
Solutions.
Pipette 5 ml of filtrate into a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask, add approximately 50 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 1 ml of CoMat 01-355 INDICATOR.
Titrate with the 0.5N hydrochloric acid solution against a white background (0.5 tablet of CoMat 02-189 COMPRESSED PAPER) .
Procedure.
NOTE
To increase the value of CoMat 01-096 ELECTROLYTIC STRIPPINGSOLUTION, add 2 parts of Solution B to 1 part Solution A.Calculations.
Percent strip = HCl solution titer x N of HCl solution x 1.133.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-032 Test Method P-91, Analysis of Nickel Strip Solution
Silver indicating electrode and Reference electrode - (Fischer Catalogue No.13-639-122 and 09-313-216 respectively).
or.
Silver sulfide ion-selective electrode and Double-junction reference electrode - (Orion Catalogue No.941600 and 900200 respectively. Fill inner and outer chambers with No.900002 solution).
Apparatus.
Dissolve 16.9890 g of CoMat 01-360 SILVER NITRATE (AgNO3), dried before for 1 to 2 hours at 205 to 215 deg F (96 to 102 deg C), in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and dilute to 1 l. Store in a dark bottle.
Standardize, refer to Step Steps 5.B.(5).
Silver nitrate (0.1M).
Dissolve 10.0 g of CoMat 01-321 POTASSIUM CHROMATE (CHLORIDEFREE) in 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Potassium chromate (10 percent).
Dissolve 4.0 g of CoMat 01-314 SODIUM HYDROXIDE (NaOH), REAGENT GRADE (SOLID) in CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Cool and dilute to 1 l.
Standardize, refer to Step Step 5.B.(1).
Sodium hydroxide (0.1M).
To 50 to 60 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER, slowly and cautiously add 10 ml of CoMat 01-327 NITRIC ACID and dilute to 100 ml.
Nitric acid (10 percent).
Solutions.
Pipette 10 ml of plating solution into a 250 ml flask. Add 50 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 10 to 15 drops of the potassium chromate solution (10 percent).
Chlorides (Nickel plating solution).
Pipette 10 ml of plating solution (20 ml of CoMat 03-108 SULFAMATE NICKEL PLATING SOLUTION) into a 250 ml beaker.
Add 150 to 175 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER and 5 ml of the nitric acid solution (10 percent).
Chloride (Alternate Procedure - Potentiometer).
Chloride (Potentiometric procedure for CoMat 03-131 SULFAMATE NICKEL REPLENISHING SOLUTION) .
Pipette a 2 ml test specimen of the solution into a 250 ml flask and add 50 to 100 ml of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER.
Neutralize the solution with sodium hydroxide solution (0.1M), refer to Step B(5), to a yellow end point, use methyl orange as an indicator, refer to Step Step 5.A.(7).
Chloride (as hydrochloric acid) for Nickel strike solution (Solution Code 30).
Add CoMat 02-191 ALCOHOL to make a thick paste.
Add 15 to 25 drops of CoMat 01-310 INDICATOR and 1 tablet of CoMat 02-189 COMPRESSED PAPER.
Boric acid.
Procedure.
oz/gal CoMat 01-015 BORIC ACID H3BO3 boric acid = titer x M NaOH solution x 1.652.
Calculations.
In these calculations, AgNO3 means silver nitrate, HCl means hydrochloric acid, NaOH means sodium hydroxide, and Ni means Nickel.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-033 Test Method P-100, Chlorides and Boric Acid in Nickel Plate Solutions
Pounds of CoMat 01-414 AMMONIUM BIFLUORIDE to be added =.
oz/gal ammonium bifluoride necessary x tank capacity/16
Acid solutions.
Pounds of CoMat 01-023 CHROMIUM TRIOXIDE CrO3(CHROM.ACID) to be added =.
oz/gal chromium trioxide necessary x tank capacity/16
Chromic acid solutions.
Pounds of CoMat 01-023 CHROMIUM TRIOXIDE CrO3(CHROM.ACID) to be added =.
oz/gal chromium trioxide necessary x tank capacity/16
Milliliters of CoMat 01-043 SULFURIC ACID H2SO4 to be added =.
oz/gal sulfuric acid necessary x tank capacity x 15
Chromium plating solution.
Pounds of CoMat 03-129 CHROMATE CONVERSION SALTS to be added =.
oz/gal chromate conversion salt necessary x tank capacity/16
Gallons of CoMat 01-099 HYDROCHLORIC ACID to be added =.
fl oz of hydrochloric acid necessary x tank capacity/128
To decrease pH = add CoMat 01-099 HYDROCHLORIC ACID hydrochloric acid by increments, after CoMat 01-099 HYDROCHLORIC ACID hydrochloric acid analysis.
Pounds of CoMat 03-129 CHROMATE CONVERSION SALTS to be added =.
oz/gal chromate conversion salt necessary x tank capacity/16
Milliliters of CoMat 01-025 NITRIC ACID HNO3, TECHNICAL GRADE to be added = ml of CoMat 01-025 NITRIC ACID HNO3, TECHNICAL GRADE necessary x tank capacity.
Chromate conversion solution immersion.
Pounds of CoMat 01-300 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE), CoMat 01-339 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) or CoMat 01-340 ALKALI CLEANER (GENERAL PURPOSE) to be added =.
oz/gal alkali cleaner necessary x tank capacity/16
Cleaners or Caustic soda.
Pounds of CoMat 03-102 COPPER CYANIDE to be added =.
oz/gal Cu metal necessary x tank capacity x 0.0875
Pounds of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN to be added =.
(oz/gal NaCN needed x tank capacity/16)+(lbs of CuCN to be added x 1.1)
Pounds of CoMat 01-107 POTASSIUM CYANIDE KCN95% MIN to be added =.
oz/gal KCN necessary x tank capacity + (lbs CuCN to be added x 1.6)/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN to be added.
oz/gal sodium cyanide necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-107 POTASSIUM CYANIDE KCN95% MIN to be added =.
oz/gal potassium cyanide necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-030 SODIUM CARBONATE Na2CO3 to be added =.
oz/gal sodium carbonate necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 03-105 POTASSIUM CARBONATE to be added =.
oz/gal potassium carbonate necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-022 SODIUM HYDROXIDE NaOH (SOLID) to be added =.
oz/gal sodium hydroxide necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-129 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH KOH, or CoMat 01-130 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH, or CoMat 03-107 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH to be added =.
oz/gal potassium hydroxide necessary x tank capacity/16
Copper plate and strike solutions (cyanide).
Pounds of CoMat 01-143 ALKALI SMUT REMOVAL COMPOUND to be added =.
oz/gal activator necessary x tank capacity x 1.5/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN =.
(oz/gal NaCN needed x tank capacity/16)-(lbs alkali smut remover added x 0.33)
Pounds of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN to be added =.
oz/gal NaCN (free) necessary x tank capacity/16
Alkali smut removers.
Pounds of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN to be added =.
oz/gal sodium cyanide necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-022 SODIUM HYDROXIDE NaOH (SOLID) to be added =.
oz/gal sodium hydroxide x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-107 POTASSIUM CYANIDE KCN95% MIN to be added =.
oz/gal potassium cyanide necessary x tank capacity/16
Neutralizer (Caustic-cyanide).
Pounds of CoMat 01-077 NICKEL CHLORIDE NiCl2+6H2O to be added = oz/gal nickel metal necessary x tank capacity x 0.25.
Milliliters of CoMat 01-099 HYDROCHLORIC ACID to be added =.
ml of hydrochloric acid/gal x tank capacity
Gallons of CoMat 01-099 HYDROCHLORIC ACID to be added =.
(ml of hydrochloric acid needed/gal) x tank capacity/3785
Nickel strike solution.
Pounds of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN to be added =.
oz/gal sodium cyanide necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 01-178 NICKEL STRIP SALT, or CoMat 01-179 NICKEL STRIP SALT, or CoMat 01-180 NICKEL STRIP SALT, or CoMat 01-181 NICKEL STRIP SALT or CoMat 01-182 NICKEL STRIP SALT = 0.5 the quantity of CoMat 01-063 SODIUM CYANIDE NaCN.
Nickel strip solution.
Gallons of CoMat 03-131 SULFAMATE NICKEL REPLENISHING SOLUTION to be added =.
oz/gal nickel metal necessary x tank capacity/20
Pounds of CoMat 01-077 NICKEL CHLORIDE NiCl2+6H2O to be added = oz/gal chloride necessary x tank capacity x 0.21.
Pounds of CoMat 01-015 BORIC ACID H3BO3 to be added =.
oz/gal boric acid necessary x tank capacity/16
To adjust the pH. Add CoMat 01-416 NICKEL CARBONATE, solution code 51, or CoMat 03-130 SULFAMIC ACID.
Nickel plate (sulfamate).
Pounds of CoMat 01-415 SILVER CYANIDE to be added =.
oz/gal silver metal necessary x tank capacity x 0.078
Pounds of CoMat 01-107 POTASSIUM CYANIDE KCN95% MIN to be added =.
(oz/gal KCN x tank capacity/16) + lbs AgCN to be added x 0.5
Pounds of CoMat 01-129 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH (KOH), CoMat 01-130 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH or CoMat 03-107 POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE KOH to be added =.
oz/gal potassium hydroxide necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 03-105 POTASSIUM CARBONATE to be added =.
oz/gal potassium carbonate necessary x tank capacity/16
Pounds of CoMat 03-103 POTASSIUM SILVER CYANIDE or CoMat 03-104 POTASSIUM SILVER CYANIDE to be added =.
oz/gal silver metal necessary x tank capacity x 0.115
Pounds of CoMat 01-107 POTASSIUM CYANIDE KCN95% MIN =.
oz/gal potassium cyanide necessary x tank capacity/16
Silver plate and strike solutions.
Use the formulae that follow as aids to calculate necessary quantities necessary to replenish, or keep, solutions within specified operating limits.
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-034 Replenishing of Plating Solutions
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-035 Solution Index
SOLN. CODE No.
NAME
PROPERTY OR CONSTITUENT
MINIMUM FREQUENCY
TEST METHOD
1
Caustic- Potassium Permanganate Descaling Solution
Sodium Hydroxide
Potassium Permanganate
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
P-55
2
Deleted
3
Deleted
4
Alkali Cleaner (General Purpose)
Total Alkalinity
Every 2 months
P-6
27
Hydrochloric Acid Solution 30%
Hydrochloric Acid
Monthly
P-1
28
Nitric Acid Solution 55%
Nitric Acid
Every 3 months
P-1
29
Sulfuric Acid Solution 20%
Sulfuric Acid
Monthly
P-1
30
Nickel Strike Solution
Nickel Metal
Chloride
Contaminants
Monthly
Monthly
Every 2 months
P-17
P-100
p-60
31
Sulfuric Acid Solution 40%
Sulfuric Acid
Every 3 months
P-1
32
Titanium Etching Solution
Nitric Acid
Hydrofluoric Acid
Monthly
Monthly
P-33
P-33
33
Nitric- Hydrofluoric Acid Solution
Nitric Acid
Hydrofluoric Acid
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
P-33
P-33
34
Sulfuric Acid Solution 10%
Sulfuric Acid
Monthly
P-1
35
Sodium Hydroxide Solution 3%
Sodium Hydroxide
Every 3 months
P-6
36
Hydrochloric Acid Solution 65%
Hydrochloric Acid
Every 3 months
P-1
37
Sulfuric- Hydrofluoric Acid Solution 30%
Sulfuric Acid
Monthly
P-1
38
Molten Salt Bath
Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium Carbonate
Every 12 months
Every 12 months
P-59
39
Alkali Cleaner
Total Alkalinity
Every 3 months
P-6
40
Chromium Plating Solution
Chromic Acid
Sulfate
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
P-22
41
Chromium Strip Solution
Total Alkalinity
Monthly
P-6
42
Chromium Plating solution
Chromic Acid
Sulfate
Monthly
Monthly
P-22
P-22
43
Self-Regulating Chromium Plating Solution
Chromic Acid
Sulfate
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
P-22
44
Nitric Acid Solution 20%
Nitric Acid
Every 2 weeks
P-1
46
Acid Salt Solution
Dry Acid Salt
Every 6 months
P-79
47
Alkali Cleaner Solution (Medium duty)
Total Alkalinity
Monthly
P-6
48
Alkali Smut Remover Solution
Activator
Free Sodium Cyanide
Monthly
Monthly
P-36
P-36
49
Alkali Cleaner Solution (Heavy duty)
Total Alkalinity
Every 2 months
P-6
50
Descaling Solution
Hydrofluoric Acid
Nitric Acid
Titanium
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
Monthly
P-33
P-33
P-33
51
Sodium Hydroxide Solution 11%
Total Alkalinity
Monthly
P-6
52
Silver Strike Solution
Silver Metal
Free Potassium Cyanide
Monthly
Monthly
P-30
P-30
53
Silver Plate Solution
Silver Metal
Free Potassium Cyanide
Potassium Carbonate
Potassium Hydroxide
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
P-14
P-14
P-14
P-14
54
Nickel Strip Solution (Cyanide)
Free Sodium Cyanide
Every 2 weeks
P-18
55
Soft Nickel Plating Solution (Sulfamate)
Nickel Metal
Boric Acid
Chloride
pH
Stress
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
Weekly
Every 4 months
P-17
P-100
P-100
P-82
P-66
56
Multiple Strip Solution (Cyanide)
Free Sodium Cyanide
Monthly
P-18
57
Nickel Strip Solution (noncyanide)(For silver or copper alloy brazed parts)
Inhibitor Replenisher
Nickel Strip Solution
Monthly
Weekly
P-90
P-91
58
Alkali Cleaner
Alkalinity
Monthly
**
60
Nickel Strip Solution (Cyanide)
Free Sodium Cyanide
Every 2 weeks
P-18
61
Nickel Strip Solution (Noncyanide)(For silver or copper alloy brazed parts)
Part II
As required
**
62
Descaling Solution
Nitric Acid
Addition Agent
Titanium Metal
**
**
63
Descaling Solution
Nitric Acid
Addition Agent
Titanium Metal
**
**
64
Descaling Solution
Nitric Acid
Addition Agent
Titanium Metal
**
**
65
Gold-Nickel Braze Strip Solution
Nitric Acid
Part B
Monthly
Monthly
**
**
66
Nickel Strike Solution
Nickel Metal
Boric Acid
Hydrochloric Acid
pH
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
Every 2 months
Weekly
P-17 Proc. A
P-100
*
P-82
67
Stripping Solution
Solution A
Compound B
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
**
**
68
Nickel Strip Solution (Noncyanide) (For silver or copper brazed parts)
Solution A
Compound B
Regulator
As required
As required
As required
**
**
**
75
Alkali Cleaner (General purpose, low foam)
Total Alkalinity
**
82
Hydrochloric Acid Solution 100%
Hydrochloric Acid
Weekly
P-1
84
Copper Sulfate Strike Solution
Metallic Copper
Free NaCN
Rochelle Salt or Rocheltex
Hydroxide
Carbonate
Weekly
Weekly
Weekly
Weekly
Weekly
P-8
P-8
P-8
P-9
P-4
85
Deleted
86
Electroless Nickel Plating Solution
Nickel Metal
pH
***
***
**
**
87
Electroless Nickel Plating Solution
Nickel Metal
pH
Solution A
Solution B
***
***
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
**
88
Chromic Acid Solution
Chromic Acid
Monthly
P-22
89
High Speed Chromium Plating Solution
Chromic Acid
Sulfate
Monthly
Monthly
Monthly
P-22
P-22
P-22
136
Deleted
137
Electrolytic Cleaner Solution (Without Phosphate and Cyanide)
Alkalinity
Monthly
**
138
Chromium Plating Solution
Chromic Acid
Sulfate
Monthly
Monthly
P-22
P-22
150
Hydrofluoric - Nitric Acid Solution
Hydrofluoric Acid
Nitric Acid
Titanium
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
P-33
P-33
P-33
151
Nitric - Hydrofluoric Acid Solution
Nitric Acid
Hydrofluoric Acid
Every 2 weeks
Every 2 weeks
P-33
P-33
153
Deleted
154
Electrolytic Cleaner Solution (Cyanide-Type Phosphate-Free)
Alkalinity
Monthly
**
155
Electroless Nickel Plating Solution
Nickel Metal
pH
***
***
**
**
156
Alkali Smut Removal Solution
Alkaline Material
Sodium Cyanide
Monthly
Monthly
P-36
P-36
170
Sulfuric Acid Solution - 30 percent
Sulfuric Acid
Three Months
P-1
* TASK 70-33-27-330-501 SUBTASK 70-33-27-180-037 (Solution Code 66)
** Refer to Manufacturer's Instructions
*** Before and during operation
NOTE
For a cross reference list of IAE solution code numbers to equivalent Party Company designations, see TASK 70-11-58-110-501, SUBTASK 70-11-58-110-501.pH meter.
Apparatus
Dissolve 40.0 g of CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER. Dilute to 1000 ml with water.
Let the solution become cool, then add sufficient CoMat 01-201 DISTILLED, DEIONIZED, DEMINERALIZED, OR REVERSE OSMOSIS (RO) WATER to increase the solution volume to 1000 ml.
Standardize the solution. Refer to Sodium Hydroxide and Potassium Hydroxide Solutions in Step
Sodium hydroxide
Solutions.
Pipette 25.00 ml of anodizing solution into a 250 ml beaker and dilute to approximately 100 ml with water,
With continuous stirring, titrate with NaOH (1.0N) to a pH of 3.2 on the pH meter, and record the burette reading as X. Continue to titrate the sample to a pH of 4.8, and record the burette reading as Y. Near each end point, add the NaOH solution cautiously, as small quantities of the NaOH solution will cause a large increase in pH.
Free Chromic Acid (CrO3) and Total Hexavalent Chromium.
Procedure
Oz/gal free chromic acid (CrO3) = X x (N of NaOH) x 0.53 where X = NaOH burette reading in ml at pH of 3.2, and N = normality of NaOH solution
Oz/gal total hexavalent chromium = Y x (N of NaOH) x 0.53 where Y = NaOH burette reading in ml at pH of 4.8, and N = normality of NaOH solution
Percent free chromic acid (CrO3) = X x (N of NaOH) x 0.4 where X = NaOH burette reading in ml at pH of 3.2, and N = normality of NaOH solution
Percent total hexavalent chromium = Y x (N of NaOH) x 0.4 where Y = NaOH burette reading in ml at pH of 4.8, and N = normality of NaOH solution
Calculations
SUBTASK 70-11-47-180-036 Chromic Acid Solution Free Chromic Acid Titration (Test Method P-2)
Figure: Solution Index Fig 70-11-47-990-001
Solution Index Fig 70-11-47-990-001

Figure: Hull cell standard chart
Hull cell standard chart
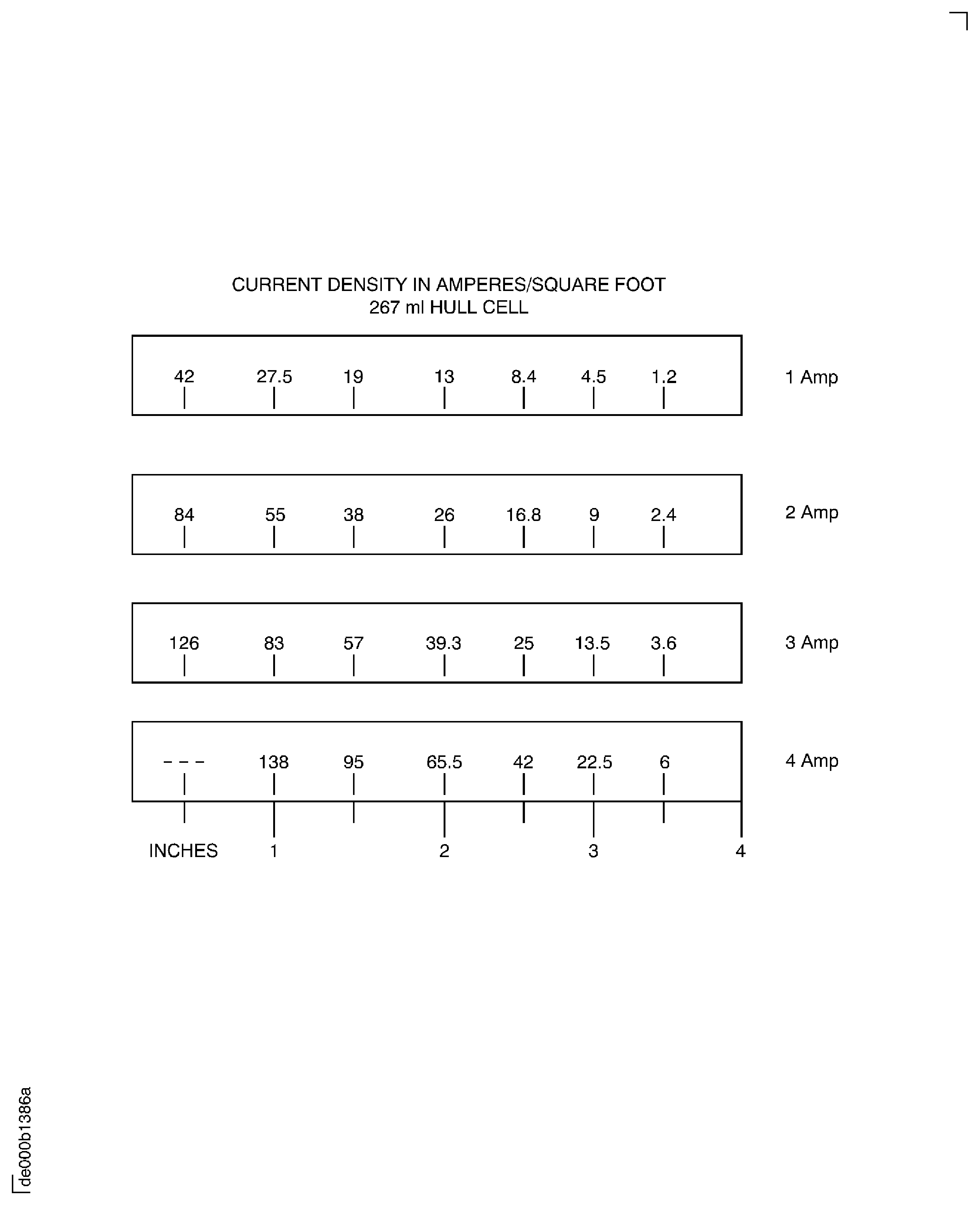
Figure: Measure the helix
Measure the helix
Figure: Contractometer calibration
Contractometer calibration
Figure: Contractometer equipment
Contractometer equipment
Figure: Titanium calculations
Titanium calculations

