Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-32-01-320-501 Machine Reaming
General
Taper bolt holes can be reamed by hand or by machine. It is recommended that, unless specified differently, the holes are reamed by machine.
The reamers must always have a Morse taper shank and a driving tang, when used to ream with a radial arm drilling machine. When it is necessary to ream by hand, adapters (Or drawings of the adapters) can be supplied by International Aero Engines AG.
The Repair Scheme instructions must always be read together with these instructions. Each hole must be fully reamed through the parallel, rough and finish stages, before the subsequent holes are started; but this does not apply to split-taper reaming (Refer to Step).
New component installation.
When a new component is installed, the mating face of the new part must have a good bedding surface with that of the remaining part. To make sure of this, a satisfactory "blue-bed" check (As specified in the related Repair Scheme) must be done between the new and remaining parts.
Split-taper reaming.
Materials with the same cutting properties can be satisfactorily reamed to give a continuous tapered hole, in one operation only.
Materials with different cutting properties must always be finish reamed separately to get a continuous tapered hole. This procedure is known as split-taper reaming.
The different material properties can be referred to as "softer" and "harder". The "harder" materials try to be resistant to the reaming operations which causes undersize holes to be made. The "softer" materials do not resist the reaming operation and hence it is necessary to finish ream the two materials when they are apart.
Run-out and concentricity checks.
Always make accurate run-out and concentricity checks before and after all reaming operations, as specified in the usual procedures.
If the run-out and concentricity limits are not satisfactory, disassemble the parts and make the bedding better, to agree with the specified limits.
Blueing gage.
Use an approved blueing gage to examine the quality of the tapered holes.
Clean the holes to remove all oil and unwanted materials, with compressed air and solvent , refer to the SPM TASK 70-11-26-300-503.
Put the gage into the hole and hit it lightly to make sure it is correctly installed.
Remove the gage and apply a thin layer of a suitable marking compound to the gage.
Put the gage into the hole again and turn it. Remove the gage and clean it to remove the marking compound.
Put the clean gage into the hole again and push it, to make sure it is correctly installed. Do not turn the gage in the hole. Remove the gage straight from the hole.
Examine the marks on the gage. The two holes must be aligned, must have no fluting and must show a bedding area, as specified in the related Repair Scheme.
A visual check for scores must also be made, because they will possibly not show when the blueing gage is used.
When new parts are installed, it is possible that the taper will not be complete after reaming. If this occurs, more metal must be removed by reaming until the necessary bedding area is satisfactory.
NOTE
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
NONEConsumables, Materials and Expendables
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMat 10-001 CUTTING OIL | 0AM53 | CoMat 10-001 |
Spares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
Procedure
The usual type of external grinding machine, with an offset bed to make the necessary taper, can be used; to grind the maximum oversize bolts to the necessary taper. Examine the offset of the machine with a taper setting mandrel. The mandrel will also be used to offset the machine to grind the reamers again.
The dimensions to which each bolt must be machined, is controlled by the tapered hole; which must be correct and with the necessary draw. Also, the angle of the taper must be examined with a taper bolt gage. A zero indication must be available when the bolt is installed in the gage to examine the taper.
SUBTASK 70-32-01-320-001 Taper Bolts
Clean all the parts, the fixtures and the bolts, with dry compressed air and solvent , refer to the SPM TASK 70-11-26-300-503 to remove all dust and other unwanted material.
Preparation.
NOTE
If the reamer is not correctly set, it will rub against the internal wall of the guide bush. This can only be felt with practice. To correct the defect, loosen the spindle head and set the reamer again. If this procedure does not correct the defect, examine the position of the bush plate again.Set the spindle speed to between 80 and 150 rpm, as specified for the hole diameter and material to be reamed.
Open the valve to control the flow of CoMat 10-001 CUTTING OIL.
Parallel reaming.
NOTE
To make sure of a good quality finish, always use CoMat 10-001 CUTTING OIL. Frequently remove the reamer from the hole, to apply the oil.Use a spindle speed of approximately 45 rpm to hand feed the reamer in steps of 0.025 in. (0.64 mm). Lift the tool between each step to help remove the unwanted material from the hole.
Clean the reamed hole with a bottle brush that is soaked in solvent , refer to the SPM TASK 70-11-26-300-503.
Rough taper reaming.
Use CoMat 10-001 CUTTING OIL, then hand feed the reamer into the hole until the cutting starts.
Do Step again, until the reamer is 0.015 in. (0.38 mm) vertically above the stop.
Turn the reamer by hand and examine the bolt draw in the hole. Use a bolt of the correct dimensions, as specified in Step.
Finish taper reaming.
Hand ream the hole in the "softer" of the two materials, to give the correct draw between the bolt head and the component (Refer to Step).
Slowly and continuously machine ream the agreed hole in the "harder" material, as specified in step F. Make sure you get the same draw, 0.002 in. (0.05 mm) with the same bolt, as that between the bolt and the "softer" part (Refer to Step).
NOTE
The procedures that follow are for the split-taper reaming of two components together; when one component is made of "softer" material and the other component is made of "harder" material. Refer to General.Split-taper reaming.
SUBTASK 70-32-01-320-002 Reaming
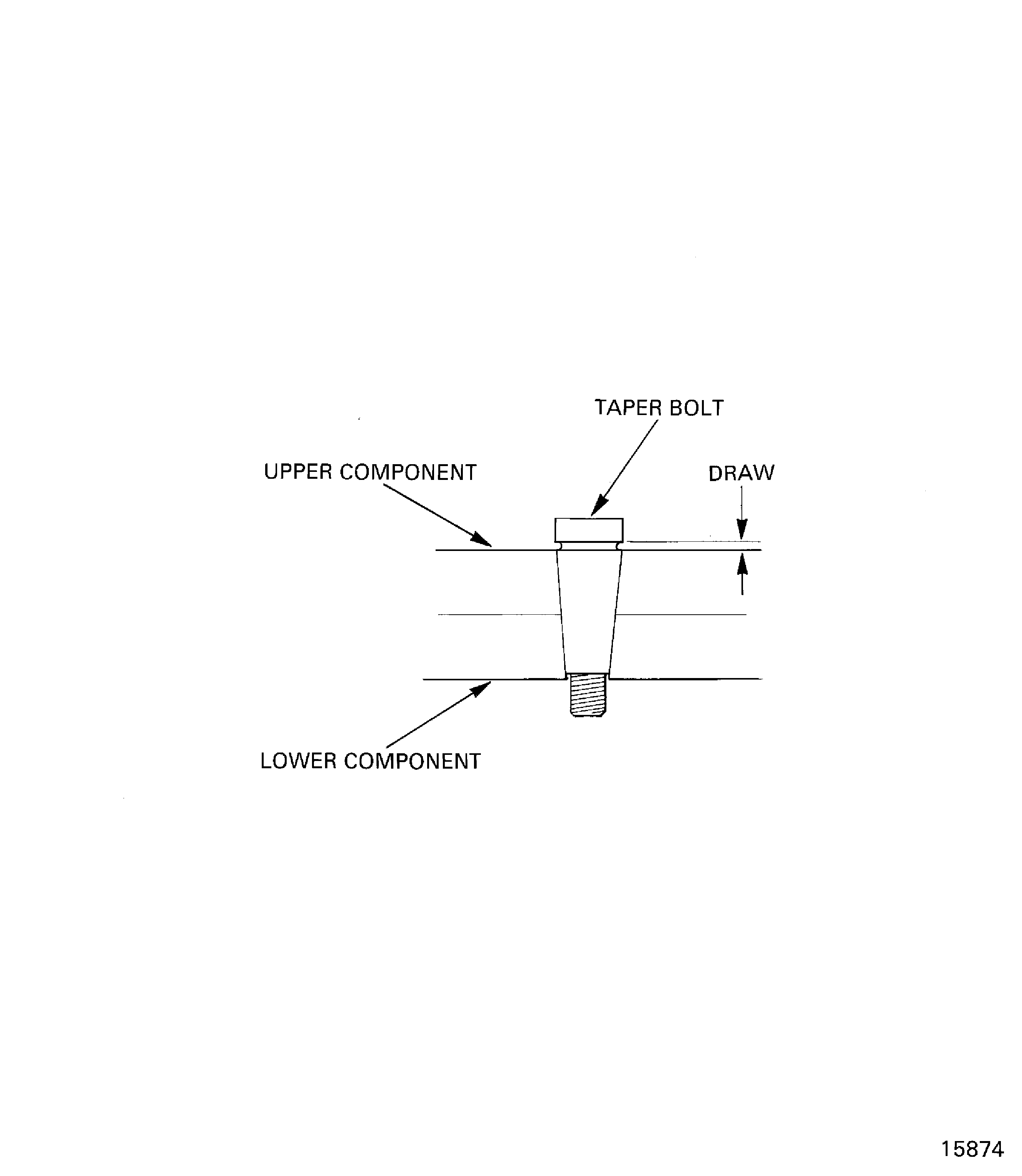
To get the specified conditions, taper bolt holes must always be reamed to give the correct bolt draw. This is the distance between the mating face of the bolt head and the assembly (Refer to Figure).
Clean the hole with a brush soaked in solvent , refer to the SPM TASK 70-11-26-300-503 and compressed air.
The procedure to examine the bolt draw is as follows.
SUBTASK 70-32-01-320-003 Examine the Bolt Draw
Figure: Examine the bolt draw
Examine the bolt draw