Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-34-10-340-501 Flame spray coating - Nickel graphite
General
Abradable coating PWA 75-1 which is applied to airseal surfaces consists of flame sprayed nickel-coated graphite in the proportion of 75 percent nickel to 25 percent graphite.
NOTE
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powder flame spray gun | LOCAL | Powder flame spray gun | special 0.046 in. (1.168 mm) diameter nozzle | |
| Gas control unit | LOCAL | Gas control unit | To supply oxygen gas, hydrogen gas, acetylene gas, and argon gas with applicable regulators and flowmeters. | |
| Powder feeder | LOCAL | Powder feeder | Additional feeder to supply flame torch | |
| Flame spray equipment | LOCAL | Flame spray equipment |
Consumables, Materials and Expendables
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMat 03-010 ARGON GAS | 0B434 | CoMat 03-010 | ||
| CoMat 03-097 FLAME SPRAY POWDER | IAE15 | CoMat 03-097 | ||
| DELETED | LOCAL | DELETED | (Deleted CoMat 03-117 and CoMat 03-118) | |
| CoMat 03-138 HYDROGEN GAS (PROTECTIVE ATMOSPHERE) | 0B434 | CoMat 03-138 | ||
| CoMat 03-289 OXYGEN GAS | LOCAL | CoMat 03-289 | ||
| CoMat 03-347 ACETYLENE GAS | X222X | CoMat 03-347 | ||
| CoMat 05-019 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-019 | ||
| CoMat 05-020 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 05-020 | ||
| CoMat 05-021 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 44197 | CoMat 05-021 | ||
| CoMat 05-064 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-064 | ||
| CoMat 05-076 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-076 | ||
| CoMat 05-077 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-077 | ||
| CoMat 05-078 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-078 | ||
| CoMat 05-079 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-079 | ||
| CoMat 05-080 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-080 | ||
| CoMat 05-081 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-081 | ||
| CoMat 05-082 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE | 1E1X8 | CoMat 05-082 | ||
| CoMat 05-090 DIAMOND PASTE | 09410 | CoMat 05-090 |
Spares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
Procedure
Apply CoMat 03-097 FLAME SPRAY POWDER to an additional thickness of 0.040 in. (1.016 mm), unless otherwise specified to produce the PWA 75-1 coating.
NOTE
For sequence of repair operations, masking and surface preparation, refer to SPM TASK 70-34-03-340-501.Application.
SUBTASK 70-34-10-340-001 Apply the Plasma Coating
Pre-grind and polish mount using CoMat 05-082 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-081 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-080 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-079 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-021 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-078 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-020 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-077 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-019 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE, CoMat 05-076 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE and CoMat 05-064 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE or equivalent. Grind cross-section directionally from coating into base metal.
Polish using CoMat 05-090 DIAMOND PASTE on cellulose cotton cloth or equivalent.
Examine the unetched coating at the specified magnifications for the conditions in the applicable metallographic examination limits below.
Metallurgical mounting procedure.
Conditions shown in Figure up through 15 percent of total micro distance are satisfactory.
Conditions shown in Figure over 15 percent through 25 percent of total micro distance must be re-evaluated.
Conditions shown in Figure more than 25 percent of total micro distance must be rejected.
Bond at coating interface at 500X magnification.
NOTE
Specimens must be given a metallographic polish before the inspection that follows.PWA 75-1 Metallographic Examination Limits, On Surfaces Other Than Blade Roots.
SUBTASK 70-34-10-220-001 Quality Control and Acceptance Standards
Cut specimen approximately 0.75 in. to 1.00 in. (19.05 mm to 25.4 mm) long and full width using a band saw with HSS 10-14 teeth/inch blade at approximately 30 SFPM feeding by hand. Refer to Figure.
Specimen preparation.
SUBTASK 70-34-10-280-001 Thermal Shock Test for Adhesion (PWA 75-1 coating)
This tester has a traverse table with stops to hold the test block during the test. The traverse table must have a motor drive that can move the table in the traverse direction at approximately 1 foot/minute (0.3 m/minute), and the range of travel must be more than 0.75 in. (19 mm).
This tester also has a weight holder that applies a total load (the weight of the weight holder plus the weight of the added weight(s)) of 8.5 lbs (3.9 kg) to the cutter. The cutter is a nominal 120 degrees edge angle, 0.215 in. (5.46 mm) outer diameter, tungsten carbide wheel with an inner diameter of 0.090 in. - 0.095 in. (2.29 mm - 2.41 mm) in a wheel insert with a tungsten carbide axle, or a nominal 120 degrees edge angle, 0.215 in. (5.46 mm) outer diameter, quick change tungsten carbide wheel unit. The scratch hardness tester keeps the rolling axis of the tungsten carbide cutter wheel parallel to the plane of the traverse table, and perpendicular to the traverse direction of the traverse table.
The tungsten carbide cutter wheels, axles, wheel inserts, and quick change tungsten carbide wheel units are available from:
The Fletcher - Terry Company, LLC
65 SPRING LANE
FARMINGTON CT 06032
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Scratch hardness tester may be fabricated locally to the design shown in Figure.
Scratch hardness tester.
Using sufficient coolant to prevent work hardening rough polish the coated side with CoMat 05-082 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE through CoMat 05-064 WATERPROOF SILICON CARBIDE to a thickness of 0.040 in. to 0.050 in. (1.016 mm to 1.270 mm) coating.
Specimen preparation.
Calibrate the scratch hardness tester, refer to subparagraph (b) above and Figure.
Traverse the specimen to make a scratch approximately 0.75 in. (19.05 mm) long in circumferential direction. Refer to Figure.
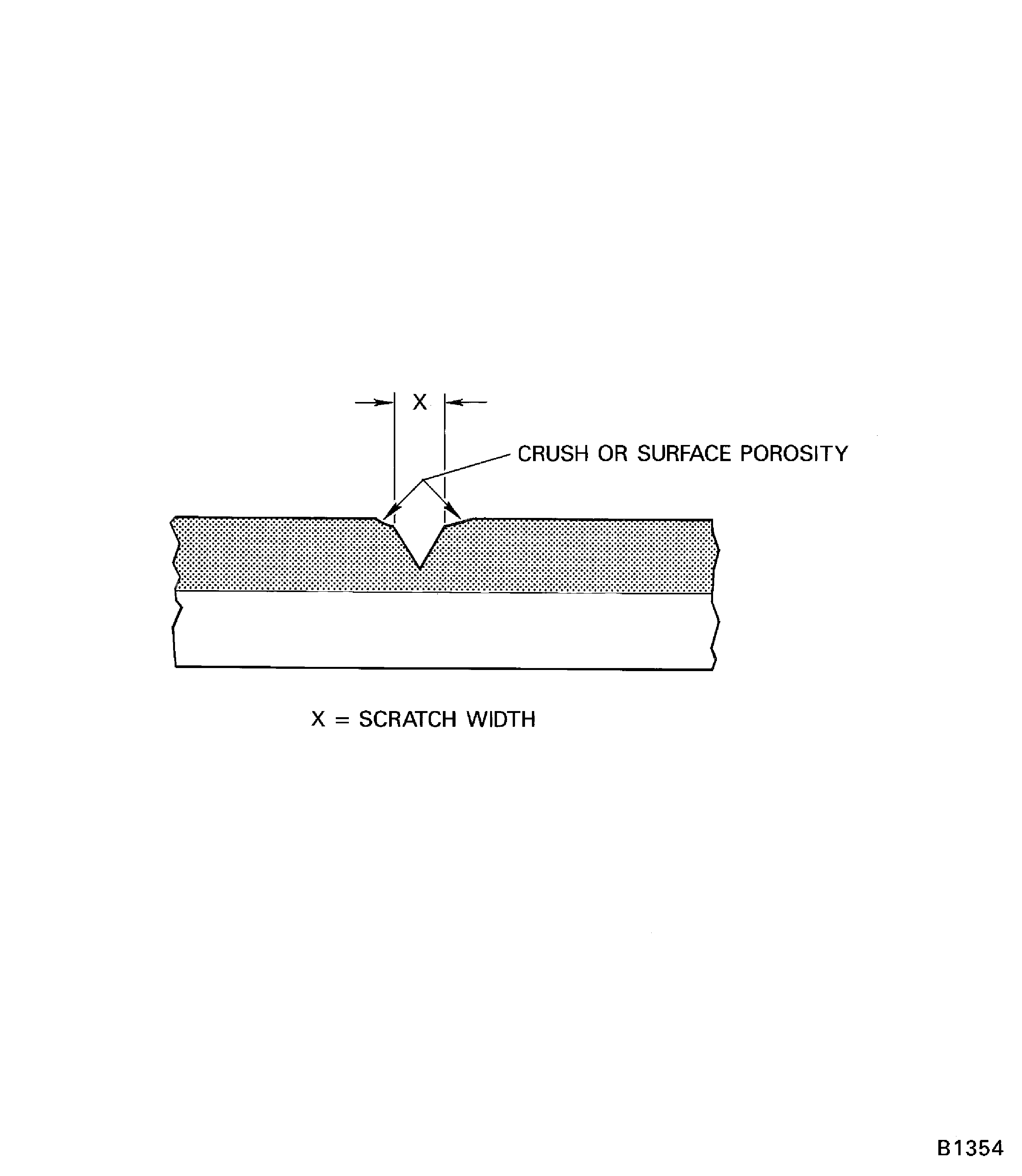
Measure width (x) of scratch to nearest 0.002 in. (0.051 mm) in several places with Brinell microscope, refer to Figure. Do not include area of crush, surface porosity, or area within 2.5 scratch widths of any specimen containing vertical supports.
Hardness testing procedure.
SUBTASK 70-34-10-280-002 Scratch Hardness Test
Figure: Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)
Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)

Figure: Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)
Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)

Figure: Excessive porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)
Excessive porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)

Figure: Diagram showing porosity criteria for PWA 75-1 coating adjacent to chamfers
Diagram showing porosity criteria for PWA 75-1 coating adjacent to chamfers
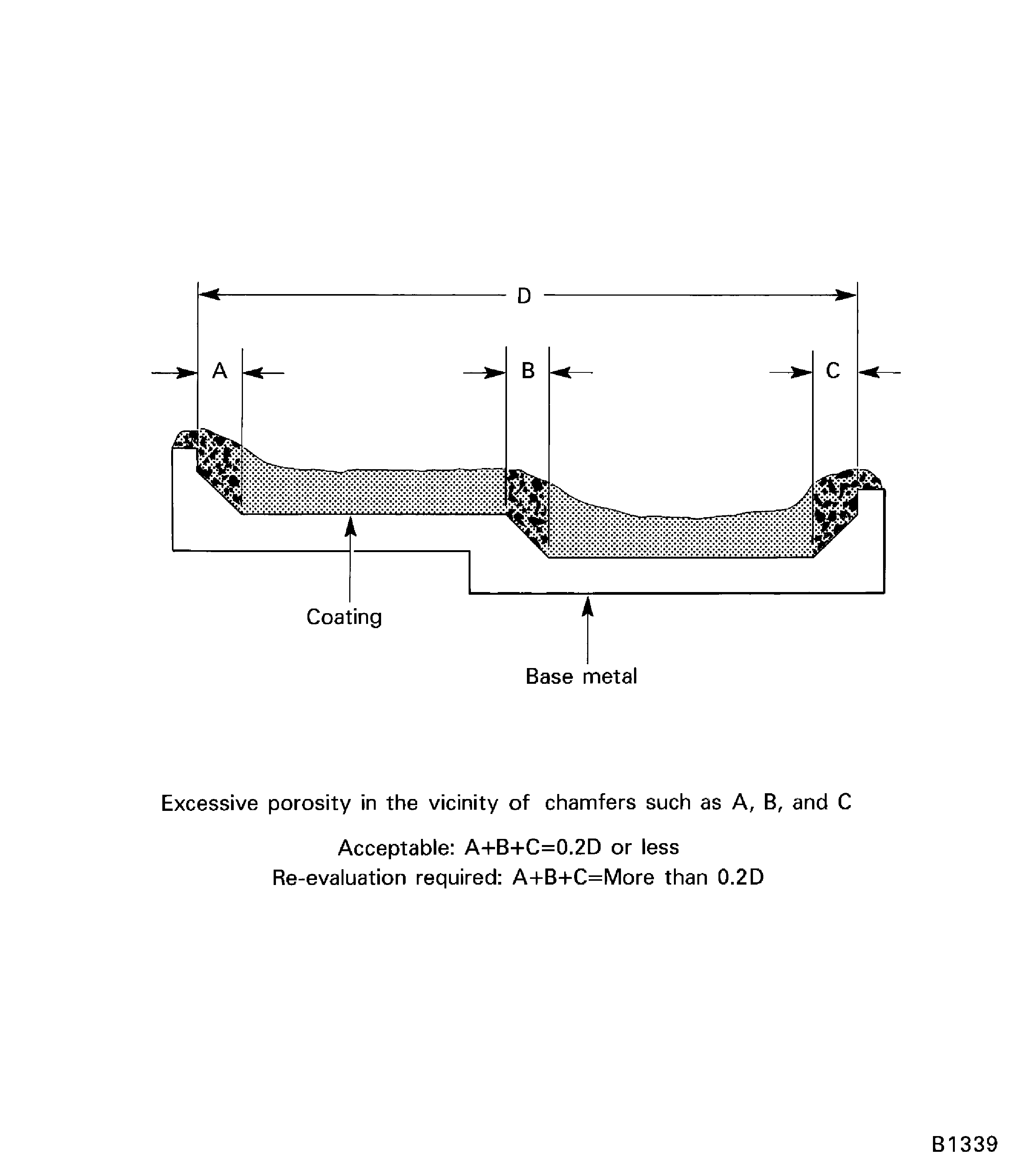
Figure: Inadequate porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)
Inadequate porosity in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)

Figure: Dispersal of nickel/graphite constituents in PWA 75-1 coating
Dispersal of nickel/graphite constituents in PWA 75-1 coating

Figure: Satisfactory dispersal of nickel/graphite constituents in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)
Satisfactory dispersal of nickel/graphite constituents in PWA 75-1 coating (100X)

Figure: Unsatisfactory dispersal of nickel/graphite constituents in PWA 75-1 coating (100X) insufficient graphite
Unsatisfactory dispersal of nickel/graphite constituents in PWA 75-1 coating (100X) insufficient graphite

Figure: Unsatisfactory bond at coating interface in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)
Unsatisfactory bond at coating interface in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)

Figure: Satisfactory oxides in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)
Satisfactory oxides in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)

Figure: Satisfactory oxides in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)
Satisfactory oxides in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)
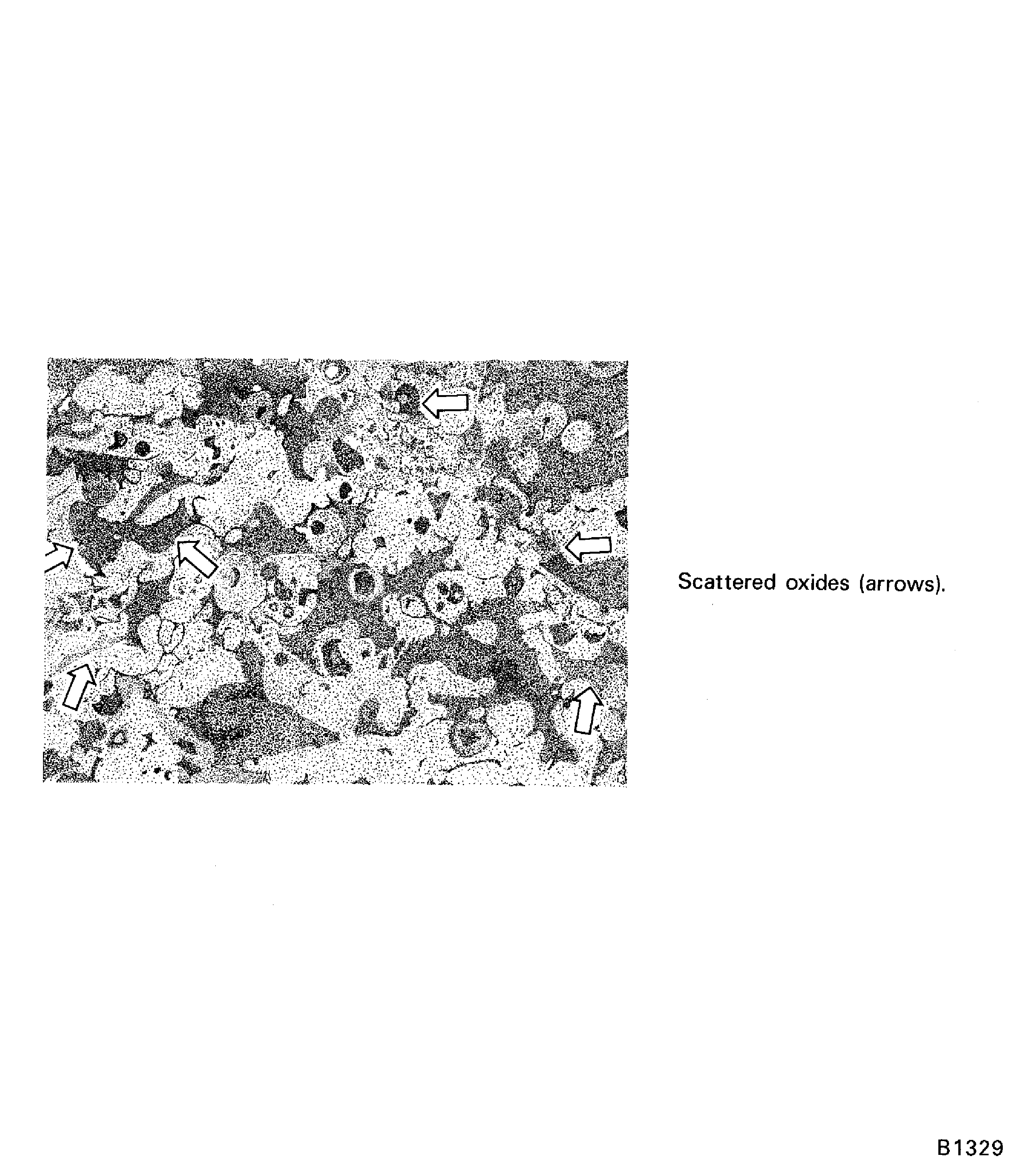
Figure: Unsatisfactory oxides in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)
Unsatisfactory oxides in PWA 75-1 coating (500X)

Figure: Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)
Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)
Figure: Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)
Satisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)

Figure: Unsatisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)
Unsatisfactory porosity in PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)

Figure: Interface condition of PWA 75-1 on blade roots (100X)
Interface condition of PWA 75-1 on blade roots (100X)

Figure: Interface condition of PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)
Interface condition of PWA 75-1 coating on blade roots (100X)
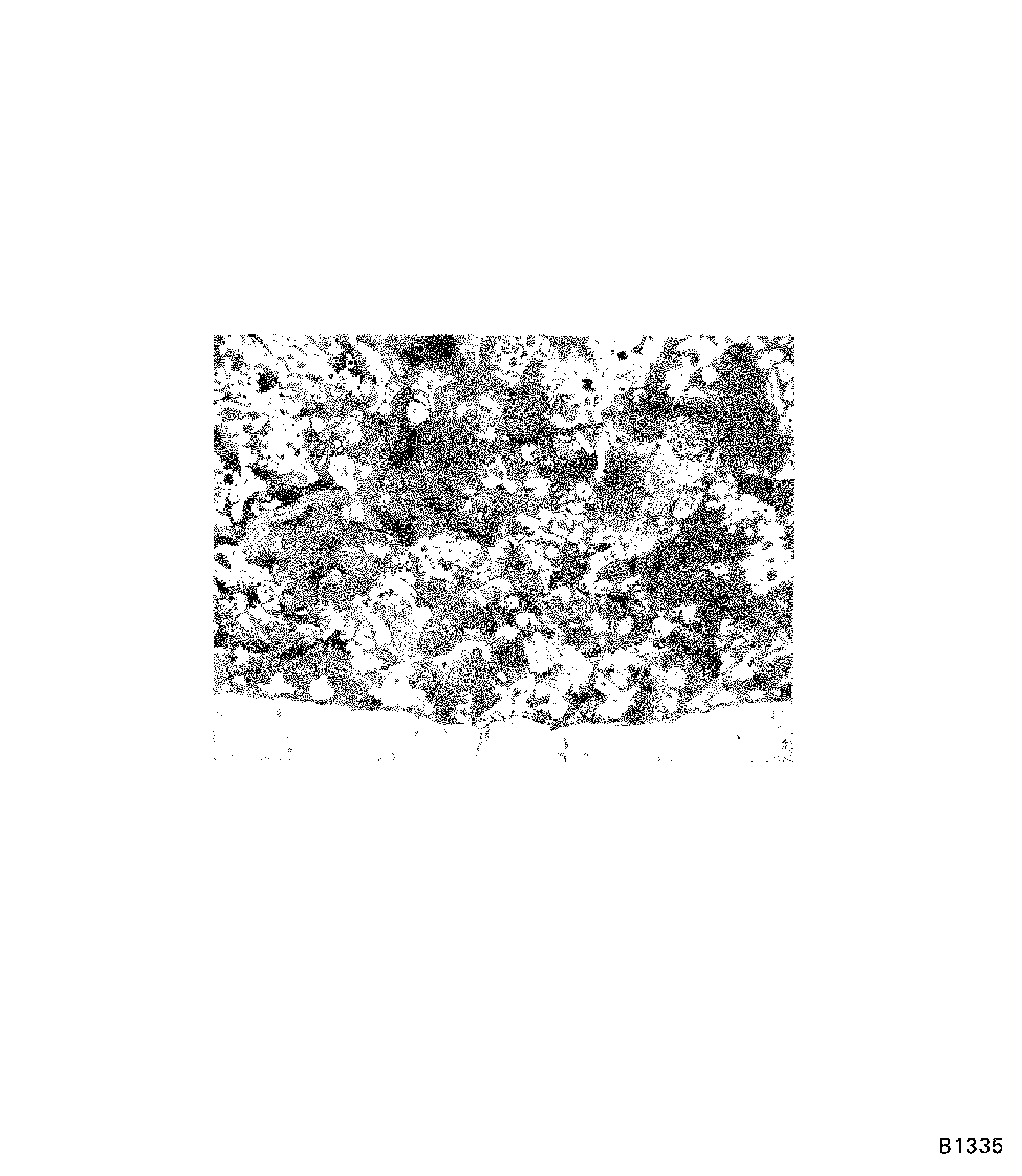
Figure: Band saw set-up
Band saw set-up
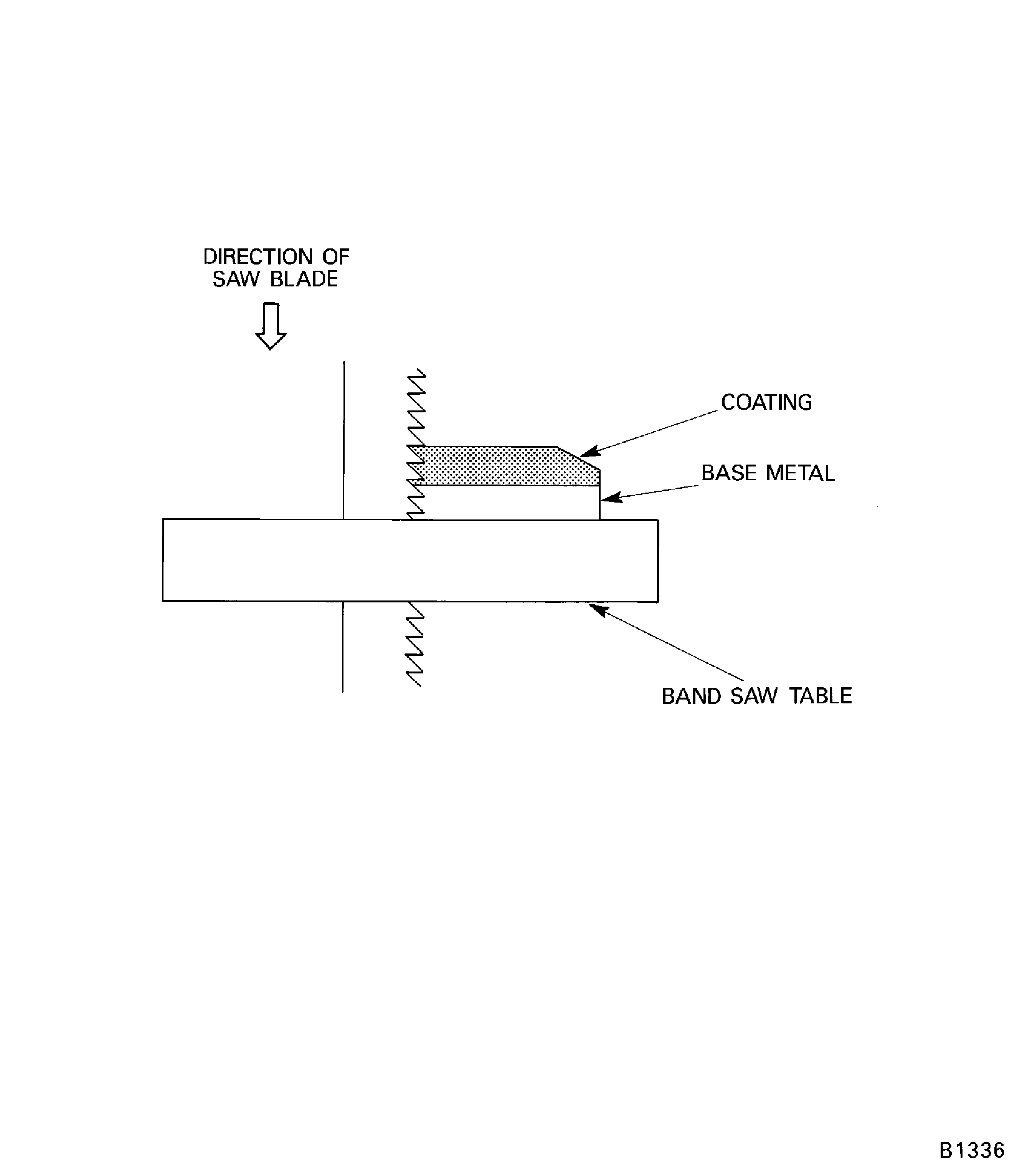
Figure: Satisfactory thermal shock test conditions in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X)
Satisfactory thermal shock test conditions in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X)

Figure: Satisfactory thermal shock test conditions (Slight cracks) in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X)
Satisfactory thermal shock test conditions (Slight cracks) in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X)
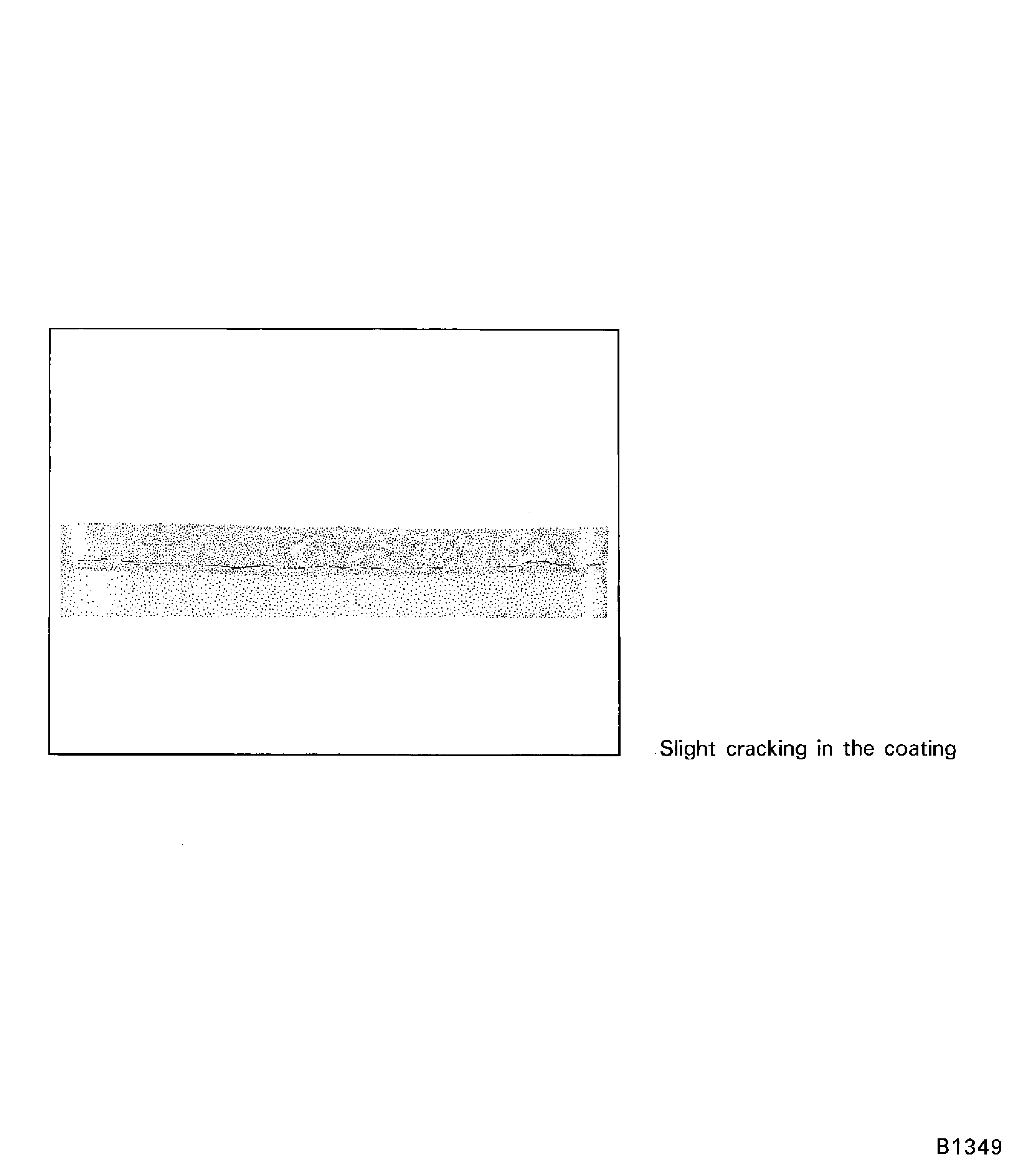
Figure: Thermal shock test conditions (Moderate cracks) in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X) to be re-evaluated
Thermal shock test conditions (Moderate cracks) in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X) to be re-evaluated

Figure: Unsatisfactory thermal shock test conditions (Severe cracks) in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X)
Unsatisfactory thermal shock test conditions (Severe cracks) in PWA 75-1 coating (3.5X)

Figure: Scratch hardness tester
Scratch hardness tester
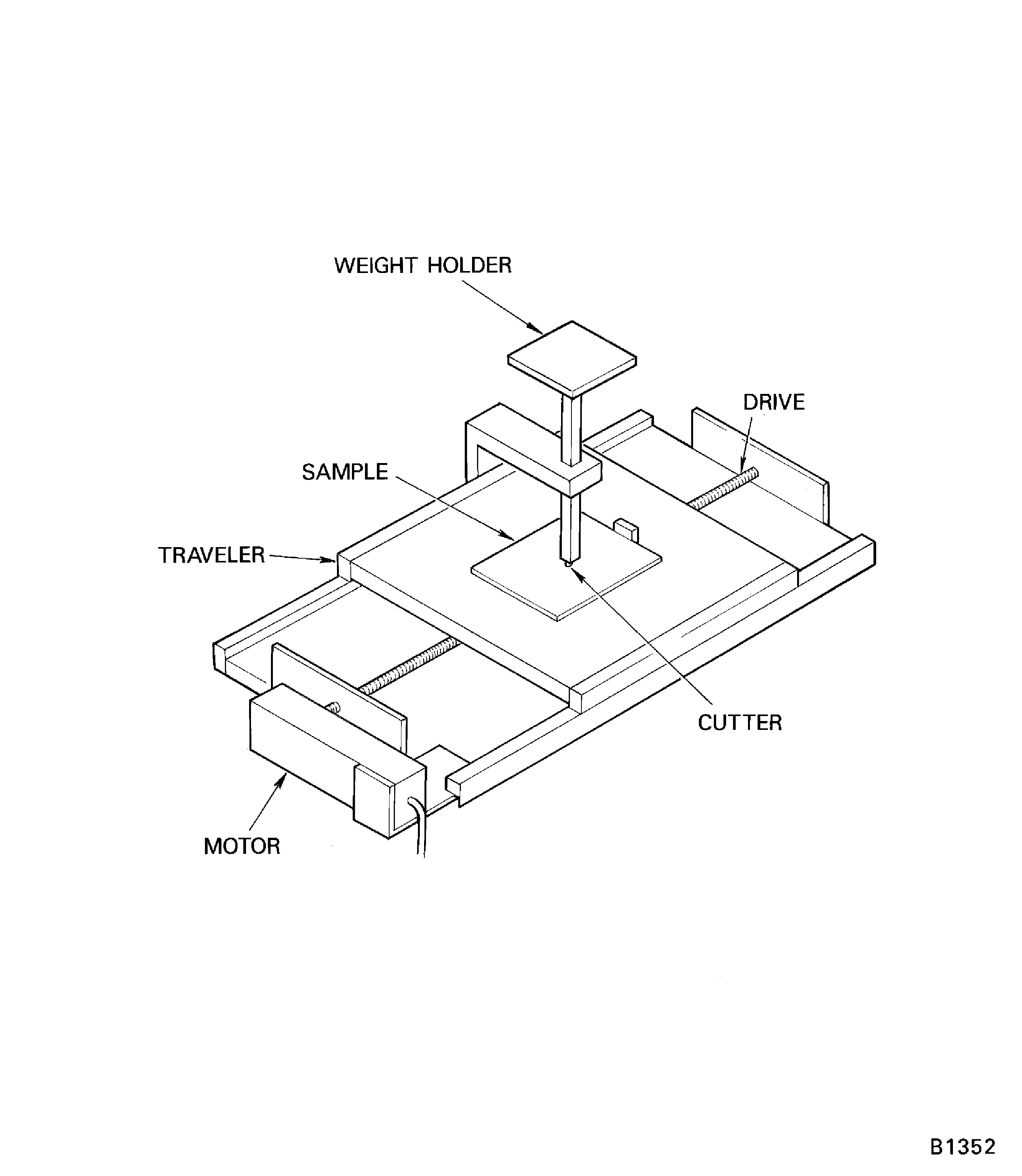
Figure: Typical specimen selection
Typical specimen selection
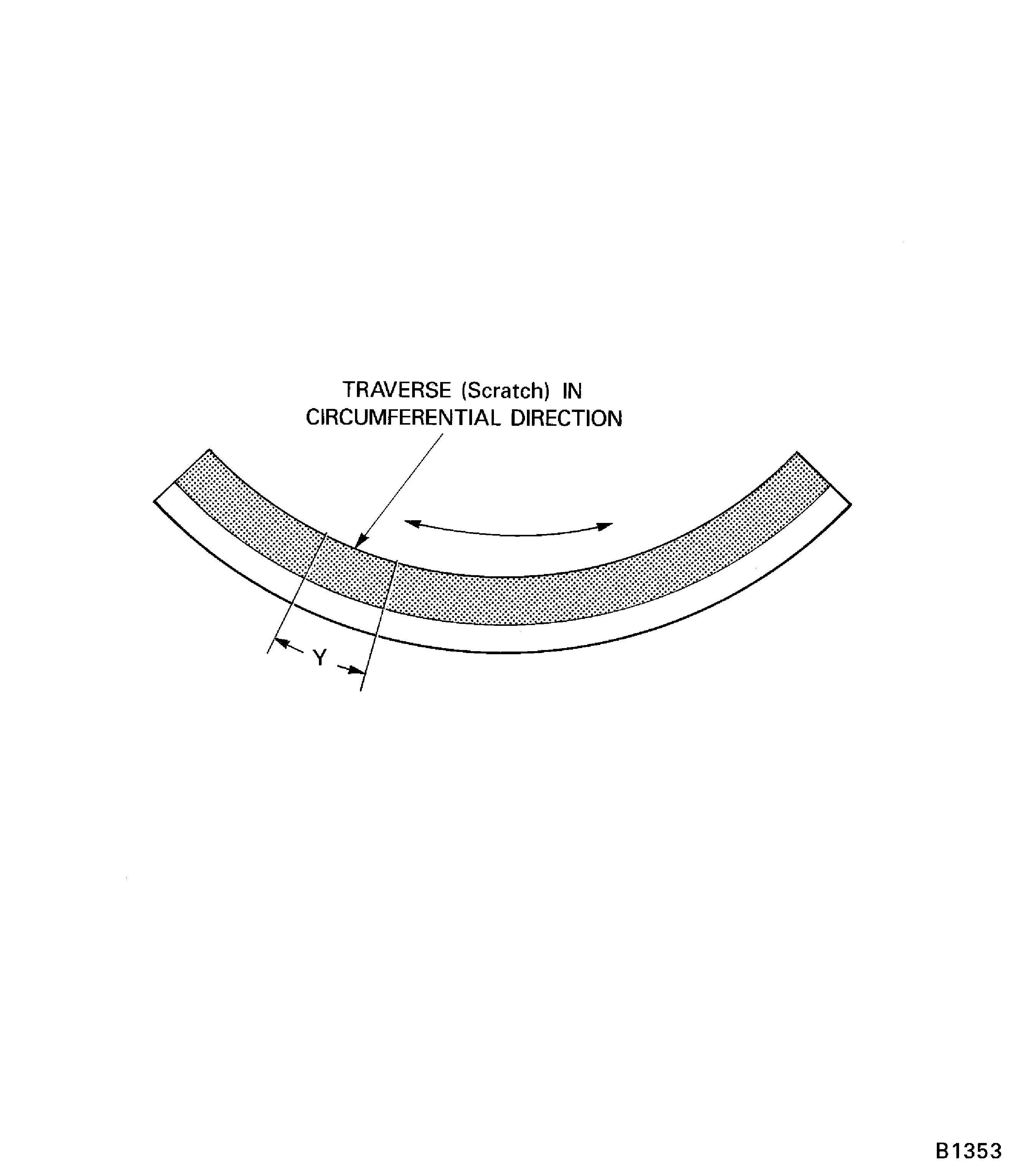
Figure: Scratch width measurement
Scratch width measurement