Export Control
EAR Export Classification: Not subject to the EAR per 15 C.F.R. Chapter 1, Part 734.3(b)(3), except for the following Service Bulletins which are currently published as EAR Export Classification 9E991: SBE70-0992, SBE72-0483, SBE72-0580, SBE72-0588, SBE72-0640, SBE73-0209, SBE80-0024 and SBE80-0025.Copyright
© IAE International Aero Engines AG (2001, 2014 - 2021) The information contained in this document is the property of © IAE International Aero Engines AG and may not be copied or used for any purpose other than that for which it is supplied without the express written authority of © IAE International Aero Engines AG. (This does not preclude use by engine and aircraft operators for normal instructional, maintenance or overhaul purposes.).Applicability
All
Common Information
TASK 70-34-01-340-501 Application Of Sprayed Metal And Ceramic Coatings
General
This procedure gives instructions that can be used to apply metal, metal alloy, ceramic or composite coatings on to metal parts by flame spraying.
In general, flame sprayed coatings can be used on all metal materials, but not magnesium alloys or copper alloys. These materials must not be sprayed unless specified in the Engine Manual. The problem with magnesium is corrosion, and with copper the build up of surface oxides at low temperatures cause adhesion problems.
A part will not get back its initial strength when a flame sprayed coating is applied, to make up the material to its initial thickness. (That is, the strength will be the same as that of the base material.) A decrease in base material fatigue must also be considered, specially on primary parts that turn and other high stressed parts.
Build up of composite powder materials are also used to give abradable seal linings. (Refer to Step.) Materials used to make these linings do not have to have abradable qualities, this is given fully by the procedure and equipment used and these have been made for special application. The type of material for special applications is given in the Engine Manual.
Aluminium parts which have been sprayed must not be anodized unless specially instructed in the Engine Manual, they must usually be prepared with Alocrom (Refer to the SPM TASK 70-38-02-100-501).
Figure gives the temperature limits and coating thickness to be applied. Differences for these instructions must only be done, when specified in the Engine Manual.
The edge of a flame sprayed coating can easily become damaged, if hit, and when possible the coating must be set into the part. If this is not possible a sufficient radius, or alternatively chamfers, must be given to remove the edge from the work surface.
Three basic coating procedures are used:
Combustion flame coating
With combustion flame coating, wire and powder of the necessary coatings is fed at a controlled rate through the flame where it is melted. It is then sprayed on to the work piece by compressed air.
Plasma flame coating
With plasma flame coating a powder is supplied through a plasma flame where it becomes molten. It is then sprayed on to the work piece by a high speed gas flow. A gas mixture is ionized with an electric arc, to make the plasma flame.
Detonation flame coating
Detonation flame coating is a known procedure controlled by Union Carbide Limited; to who operators must apply for data about the procedure.
With detonation flame coating, specified quantities of oxygen, acetylene and powder are put into a special spray-gun. A timed spark detonates the mixture and sprays the powder, in a plastic condition onto the work piece.
Although flame spray coating by the above procedures uses high energy heat sources, to make semi-molten spray, the temperature of the part being sprayed must not usually be more than 302 deg F (150 deg C) and there must be no heat distortion problems. To make sure of this, the correct procedures (That is, a related movement between the spray-gun and the work piece together with the correct coolant) must always be used.
It is important that a sufficient supply of clean, dry, compressed air and the necessary gases are available before doing the spraying procedures.
Equipment maintenance
The performance and satisfactory operation of all flame spraying equipment is related to its condition. Regular maintenance must be done to make sure the best spraying conditions, specially on plasma spraying equipment, where careful maintenance is very important.
The performance of the plasma spraying equipment must be continuously monitored, with special detail given to the points that follow:
Low coating deposit efficiency, i.e., powder feed rate against the coating deposition rate, is usually caused by one or more of the defects that follow:
Worn or eroded nozzles
Damaged or pitted rear electrodes
Worn or eroded gas distribution ring
Incorrectly aligned electrodes
Worn or incorrectly aligned powder supply tubes
Leakage in the powder supply system
Operating voltage
The equipment operational voltage, for a given amperage must be in the range of 10 percent of the specified value. A incorrect voltage can cause one or more of the defects that follow:
Damaged or pitted rear electrodes
Worn or eroded gas distribution rings
Gas leakage
Changes in gas flow and/or pressure
To make sure that the equipment will continue to operate correctly, the basic maintenance procedures that follow are recommended.
Nozzles must be turned regularly (For example once per shift) to make sure that they wear equally.
The equipment must always be started and stopped correctly.
Clean and examine the electrodes, powder supply system and hoses regularly (For example once a week), by a scheduled strip and maintenance procedure. Electrodes which have been damaged can be repaired with emery paper as long as the initial shape is kept.
It is important to keep a record of all electrode operational and maintenance procedures to find the life of the electrodes and thus the correct time for replacement.
Storage
Wires
Some wires are supplied coated with protective coatings which is used as a lubricant, these coatings must not be removed.
The wires must always be kept where they can not get kinked or damaged by corrosion.
Powders
Powders must be kept in closed containers to prevent contamination by unwanted materials. If contamination is found the powder must be discarded.
Storage conditions must be installed for keeping powder free-flowing specially where humidity and/or temperature differences are high. Although, in practice, powder flow problems are caused by incorrect storage conditions, it is recommended that regular checks be made on the powder flow properties.
Test pieces
Test pieces are used to check coating adhesion and hardness. The test that follow are necessary.
Abradable coatings, those used for seal linings/rotor path linings are applied to hardness testing in line with Step.
All other coatings, which include bond coatings, must be tested as follows.
Prepare a test panel, with minimum dimensions of 2 x 3 in. (50 x 75 mm) and made from 18 S.W.G. mild steel or EBP sheet. Refer to TASK 70-31-02-310-501-001 for the part number of an applicable test panel.
Abrasive blast the panel with instructions fromStep.
Spray the test panel with the instructions referred to in Step.
Bend the panel mechanically through 90 degrees, at a slow and positive rate, around a 0.50 in. (12,5 mm) diameter mandrel, with the coating on the outside of the bend.
There must be no sign of lifting or spalling from the panel. A minimum quantity of cracking in the bend is permitted on some low ductility coatings if no lifting is shown. For example, molybdenum, tungsten carbide, cobalt or chromium carbide nichrome.
Parts must not be sprayed until a satisfactory bend test has been completed.
A powder must be fully mixed after storage, immediately before use. Containers are only two-thirds full to make easier this mixing.
When possible, spray samples of powder to do a test for deposition properties before using the applicable batch on engine parts.
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
Preliminary Requirements
Pre-Conditions
NONESupport Equipment
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wire spray guns | LOCAL | Wire spray guns | Metco 10E and 12E | |
| Thermospray powder spray guns | LOCAL | Thermospray powder spray guns | Metco 5P, 6P - For special use | |
| Plasma spray guns | LOCAL | Plasma spray guns | Metco 3M, 7M and 9M | |
| Plasma gun | LOCAL | Plasma gun | Metco 3APG | |
| F1 plasma gun - Plasma technik | LOCAL | F1 plasma gun - Plasma technik | ||
| P4 plasma gun - Plasma technik | LOCAL | P4 plasma gun - Plasma technik | ||
| Superficial hardness tester | LOCAL | Superficial hardness tester | Rockwell 15Y scale - 3JS or 3TT | |
| Indetec Hardness Tester | LOCAL | Indetec Hardness Tester | 4045 or 8150 SK |
Consumables, Materials and Expendables
| Name | Manufacturer | Part Number / Identification | Quantity | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoMat 02-001 ADHESIVE TAPE (MASKING) | LOCAL | CoMat 02-001 | ||
| CoMat 02-006 ADHESIVE TAPE ALUMINIUM FOIL | 76381 | CoMat 02-006 | ||
| CoMat 02-007 TEFLON TAPE | LOCAL | CoMat 02-007 | ||
| CoMat 02-198 ADHESIVE TAPE (MASKING METAL SPRAY) | LOCAL | CoMat 02-198 | ||
| CoMat 03-029 STOPPING-OFF PAINT | LOCAL | CoMat 03-029 | ||
| CoMat 03-033 DELETED | X111X | CoMat 03-033 | ||
| CoMat 03-034 METAL SPRAY MASKING COMPOUND | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-034 | ||
| CoMat 03-035 METAL SPRAY MASKING COMPOUND | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-035 | ||
| CoMat 03-036 METAL SPRAYING WIRE, Ni,Al | LOCAL | CoMat 03-036 | ||
| CoMat 03-037 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni Al | 08662 | CoMat 03-037 | ||
| CoMat 03-038 METAL SPRAYING POWDER NICKEL ALUMINIUM (95/5) | 00BB6 | CoMat 03-038 | ||
| CoMat 03-043 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Al OXIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 03-043 | ||
| CoMat 03-047 METAL SPRAYING POWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-047 | ||
| DELETED | X111X | CoMat 03-049 | ||
| CoMat 03-051 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,75CrC, 25 NiCr | LOCAL | CoMat 03-051 | ||
| CoMat 03-052 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,75CrC, 25NiCr | LOCAL | CoMat 03-052 | ||
| CoMat 03-053 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,25% Cr, 7% W | LOCAL | CoMat 03-053 | ||
| CoMat 03-054 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,25% Cr, 7% W | K1030 | CoMat 03-054 | ||
| CoMat 03-055 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,COBALTALLOY 25% CHROMIUM, 7% TUNGSTEN | LOCAL | CoMat 03-055 | ||
| CoMat 03-057 ALUMINIUM ALLOY/POLYESTERCOMPOSITE | LOCAL | CoMat 03-057 | ||
| CoMat 03-080 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co BASE ALLOY | IE426 | CoMat 03-080 | ||
| CoMat 03-089 METAL SPRAYING POWDER Ni/Al (95/5) | 33870 | CoMat 03-089 | ||
| CoMat 03-229 METAL SPRAYING POWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-229 | ||
| CoMat 03-235 DELETED | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-235 | ||
| CoMat 03-236 METAL SPRAYING POWDER-ALUMINUM | LOCAL | CoMat 03-236 | ||
| CoMat 03-237 DELETED | X111X | CoMat 03-237 | ||
| CoMat 03-238 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Ni-Cr-Al | LOCAL | CoMat 03-238 | ||
| CoMat 03-239 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE | 00BB6 | CoMat 03-239 | ||
| CoMat 03-240 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE | X111X | CoMat 03-240 | ||
| CoMat 03-248 METAL SPRAY POWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-248 | ||
| CoMat 03-261 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Cu,Ni, In | K1030 | CoMat 03-261 | ||
| CoMat 03-262 METAL SPRAY POWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-262 | ||
| CoMat 03-263 ALUMINIUM METAL SPRAYINGPOWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-263 | ||
| CoMat 03-265 NICKEL CHROMIUM ALUMINIUMPOWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-265 | ||
| CoMat 03-268 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni-Cr-ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-268 | ||
| CoMat 03-273 ALUMINIUM GRAPHITE COMPOSITEPOWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-273 | ||
| CoMat 03-277 METAL SPRAYING POWDER | 33870 | CoMat 03-277 | ||
| CoMat 03-278 METAL SPRAY POWDER, COBALTBASE ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-278 | ||
| CoMat 03-279 METAL SPRAY POWDER | IE441 | CoMat 03-279 | ||
| CoMat 03-298 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE | X111X | CoMat 03-298 | ||
| CoMat 03-299 DELETED | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-299 | ||
| CoMat 03-300 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,WC/Co | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-300 | ||
| CoMat 03-301 DELETED | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-301 | ||
| CoMat 03-302 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,WC/Co | LOCAL | CoMat 03-302 | ||
| CoMat 03-303 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Al OXIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 03-303 | ||
| CoMat 03-304 METAL SPRAYING POWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-304 | ||
| CoMat 03-305 DELETED | 0AM53 | CoMat 03-305 | ||
| CoMat 03-306 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Cu-,Ni-,In-ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-306 | ||
| CoMat 03-307 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co-BASE ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-307 | ||
| CoMat 03-308 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co BASE ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-308 | ||
| CoMat 03-309 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co-BASE ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-309 | ||
| CoMat 03-310 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni,Cr,Al | LOCAL | CoMat 03-310 | ||
| CoMat 03-311 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni-Cr-ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-311 | ||
| CoMat 03-312 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni-,Cr-ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-312 | ||
| CoMat 03-313 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co-BASE ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-313 | ||
| CoMat 03-314 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,75CrC, 25NiCr | LOCAL | CoMat 03-314 | ||
| CoMat 03-315 METAL SPRAYING POWDER | LOCAL | CoMat 03-315 | ||
| CoMat 03-316 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,75CrC, 25NiCr | LOCAL | CoMat 03-316 | ||
| CoMat 03-317 DELETED | X111X | CoMat 03-317 | ||
| CoMat 03-318 METAL SPRAY POWDER, COBALTBASE ALLOY | LOCAL | CoMat 03-318 | ||
| CoMat 03-319 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Al OXIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 03-319 | ||
| CoMat 03-320 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,WC/Co | LOCAL | CoMat 03-320 | ||
| CoMat 03-321 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,WC/Co | LOCAL | CoMat 03-321 | ||
| CoMat 03-322 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE | X111X | CoMat 03-322 | ||
| CoMat 03-323 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE | X111X | CoMat 03-323 | ||
| CoMat 03-324 DELETED | X111X | CoMat 03-324 | ||
| CoMat 03-325 DELETED | X111X | CoMat 03-325 | ||
| CoMat 05-001 ABRASIVE MEDIUM, ALUMINIUM OXIDE, 20/30 GRADE | LOCAL | CoMat 05-001 | ||
| CoMat 05-015 ABRASIVE MEDIUM, ALUMINUM OXIDE | LOCAL | CoMat 05-015 | ||
| CoMat 05-130 ABRASIVE DELETED | X111X | CoMat 05-130 | ||
| DELETED | LOCAL | DELETED | ||
| CoMat 05-192 ALUMINUM OXIDE GRIT | IE531 | CoMat 05-192 | ||
| CoMat 07-040 MASKING PAINT METAL SPRAY | X111X | CoMat 07-040 | ||
| CoMat 08-067 THREADLOCKING MATERIAL | LOCAL | CoMat 08-067 | ||
| CoMat 10-002 DRY FILM LUBRICANT | LOCAL | CoMat 10-002 | ||
| CoMat 10-004 DRY FILM LUBRICANT | LOCAL | CoMat 10-004 |
Spares
NONESafety Requirements
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
Procedure
Refer to SPM TASK 70-11-03-300-503. Vapor degrease then allow the parts to cool.
If small areas are to be coated locally degrease. Refer to SPM TASK 70-11-26-300-503.
Degrease the parts using one of the following methods:
NOTE
It is permitted to use TASK 70-34-18-380-501 as an alternative to Step.Condition of the part.
It is permitted to use SPM TASK 70-34-18-380-501 as an alternative to the specified surface preparation procedure in the applicable repair task, including source demonstration repairs, if the resulting thermal spray coating agrees with all specified quality requirements.
Do one of the procedures in the subsequent list:
Apply CoMat 02-001 ADHESIVE TAPE (MASKING) or CoMat 02-006 ADHESIVE TAPE ALUMINIUM FOIL or CoMat 02-198 ADHESIVE TAPE (MASKING METAL SPRAY) or mechanical masks. Apply protection to holes and passage ways with blanks or plugs.

CAUTION
REFER TO SPM TASK 70-12-01-120-501 FOR PRECAUTIONS NECESSARY WHEN DRY ABRASIVE BLASTING MAGNESIUM ALLOYS.Dry abrasive blast the surface to be prepared with CoMat 05-001 ABRASIVE MEDIUM, ALUMINIUM OXIDE, 20/30 GRADE, CoMat 05-015 ABRASIVE MEDIUM, ALUMINUM OXIDE or CoMat 05-192 ALUMINUM OXIDE GRIT. When thin parts are to be prepared, use CoMat 05-015 ABRASIVE MEDIUM, ALUMINUM OXIDE or CoMat 05-192 ALUMINUM OXIDE GRIT. Finer grades of abrasive media may be used provided that an acceptable bond strength can be achieved. Blast the surface for a sufficient length of time to get a constant, matt finish. Use an air pressure of 20 to 40 psi (138 to 276 kPa) when pressure pot abrasive blast equipment is used, and 70 to 80 psi (483 to 552 kPa) with vacuum pick-up abrasive blast equipment.
Abrasive blast the part.
NOTE
CoMat 02-001 ADHESIVE TAPE (MASKING) or CoMat 02-006 ADHESIVE TAPE ALUMINIUM FOIL or CoMat 02-198 ADHESIVE TAPE (MASKING METAL SPRAY) or mechanical masks permits blasting and spray coating to be done in one operation, which makes it not necessary to do the masking removal step at the end of this abrasive blast procedure.
Surface preparation.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-001 Preparation Procedures
Bond coat CoMat 03-038 METAL SPRAYING POWDER NICKEL ALUMINIUM (95/5) or CoMat 03-036 METAL SPRAYING WIRE, Ni,Al or CoMat 03-248 METAL SPRAY POWDER, have a top coat examples of abradable linings, Cu/Ni/In, Wc/Co for where general application bond coats are necessary.
Bond coat CoMat 03-262 METAL SPRAY POWDER or CoMat 03-265 NICKEL CHROMIUM ALUMINIUMPOWDER, have a top coat examples of ceramic coatings, magnesium zirconate or yttria stabilized zirconia.
Materials usually used for bond coating are as follows:
The thickness of the bond coating, unless used to limit the thickness of the top coating, must be sufficient to give a continuous coating of between 0.003 to 0.005 in. (0.07 to 0.13 mm) thick, unless differently specified in the Engine Manual.
NOTE
Because a blasted surface can easily become dirty again, it must be sprayed as quickly as possible after it is blasted. If the part is not sprayed in two hours after it is blasted all of the preparation work must be done again.The spraying procedure must be, when possible, be continuous. Short stops, to measure the applied coat thickness, can be accepted, but they must be kept to a minimum, to prevent 'layering'.Where it can be done, the spraying operation must be controlled automatically for the spray angle and distance and the motion between the gun and the work piece. For example, install the gun so as to get vertical or horizontal mechanical traverse and mechanically turn the work piece.The direction of spray must be kept as near as possible at right-angles to the surface being sprayed. The angle must not be less than 50 degrees. Work piece and coating temperatures must be kept below 338 deg F (170 deg C). This is specially important when spraying materials give an exothermic effect such as CoMat 03-037 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni Al or CoMat 03-038 METAL SPRAYING POWDER NICKEL ALUMINIUM (95/5). Facilities must be supplied to direct a clean, dry air flow over the component in such a way that the flow of sprayed material is not impeded, or a different spraying/cooling operation may be used. Remove all 'bloom' or 'smoke' with a clean, dry, air blast before more spraying.
Bond coatings.
Spray the test pieces (refer to General section, Test Pieces) to check the coating bond, hardness and the satisfactory condition as necessary.
NOTE
Parts must not be sprayed until satisfactory tests have been completed.The condition of the equipment is very important, if the adjustments found are to be used again. This is specially important for plasma equipment, where a high standard of inspection and maintenance is necessary. (Refer to Equipment Maintenance section.)Most components will require a preheat, and the preheat control must be specified in a local work instruction. Generally several passes of the flame (without powder) over the component will be satisfactory. If no preheat temperature is specified, use a preheat temperature that does not cause discoloration, oxidation, distortion, or other conditions that can have a bad effect on the coating or base metal; and is not more than 302 deg F (150 deg C).
To prevent coating/base material corrosion problems on magnesium alloy parts, sprayed coatings must be soaked to seal the coating and prevent entrance of water, immediately the part is cooled sufficiently to handle after spraying. CoMat 08-067 THREADLOCKING MATERIAL must be applied to the coating by brush.
CoMat 08-067 THREADLOCKING MATERIAL must be applied again after all post spraying machining operation.
Where necessary, after spraying, temporarily protect the areas which have not been sprayed on the work piece as specified in the SPM TASK 70-38-05-380-501.
Spraying operation.
After finishing, visually examine the coating by the use of a magnification of up to x7 where necessary. A satisfactory coating has a matt finish, in which the machining marks can easily be seen. There must be no color change, and the coating must not be cracked, spalled or polished. Less important chips, at the edge of the coating and not related to the condition of the bond, can be accepted for some uses. When necessary, the standard that can be accepted are given in the Engine Manual.
Remove most of the coating by machining followed by the chemical removal of the remaining material by the procedure given in the SPM TASK 70-33-59-300-503.
Remove the coating chemically as given in the SPM TASK 70-33-59-300-503.
Removal of defective coatings.
Remove all defecting coatings by one of the procedures that follow, unless specified differently in the Engine Manual.
Where necessary, apply temporary protection, between spraying and machining or after machining, as given in the SPM TASK 70-38-05-380-501.
Temporary protection.
Examine the sprayed parts.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-002 Spraying Procedures
Some coatings can be turned (Refer to Figure), when a tipped tool must be used.
Turning.
The depth of cut is different, for each coating and procedure used, but must be in the range of:
For surface grinding use a 'plunge' grinding rate of 0.00025 to 0.0005in./pass (0.006 to 0.013 mm/pass), with a movement or depth of cut of 0.00025 to 0.0005in./pass (0.006 to 0.013 mm/pass).
For cylindrical grinding use a 'plunge' grinding rate of 0.003 to 0.005 in./min (0.075 to 0.13 mm/min) on the diameter, with a movement or depth of cut of 0.0005 to 0.001 in./pass (0.013 to 0.025 mm/pass).
Matt or glossy wheels give a more shinny and lower surface finish indication; than the same wheel used in a clean, free-cutting condition. The surface if examined with a lens (10x) will look dirty and heat damaged. The parts must be examined, during and after the grinding operations, for signs of defects that can not be accepted.
Grinding.
If no special procedure is given in the Engine Manual, refer to Figure which gives the recommended procedure for each type of coating.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-003 Finishing Procedures
Clean nozzles.
NOTE
If a hardness test can not be done on the part, the integral test piece procedure must be used. A 0.98 x 0.59 x 0.06 in. (25 x 15 x 1.6 mm) minimum steel test piece attached to and sprayed with the work piece.Details of the spraying data are given in Figure. The system is identified by SUBTASK and CoMat numbers for the materials being sprayed
Spraying must be effected as in Step.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-004 Spraying Procedures for Abradable Coatings
NOTE
To keep the necessary quality standards the points that follow must be continuously monitored.Apply CoMat 03-261 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Cu,Ni, In and CoMat 03-306 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Cu-,Ni-,In-ALLOY - copper/nickel/indium, refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-005 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-262 METAL SPRAY POWDER or CoMat 03-299 DELETED, refer to Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-006 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-053 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,25% Cr, 7% W, CoMat 03-055 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,COBALTALLOY 25% CHROMIUM, 7% TUNGSTEN, CoMat 03-307 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co-BASE ALLOY, CoMat 03-308 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co BASE ALLOY or CoMat 03-309 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co-BASE ALLOY, refer to Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-009 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-036 METAL SPRAYING WIRE, Ni,Al, refer to Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-010 Application of Metal Spray Wire
To apply CoMat 03-047 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CoMat 03-304 METAL SPRAYING POWDER or CoMat 03-305 DELETED, refer to Figure and Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-011 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-047 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CoMat 03-304 METAL SPRAYING POWDER or CoMat 03-305 DELETED refer to Figure and Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-012 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-263 ALUMINIUM METAL SPRAYINGPOWDER, CoMat 03-235 DELETED or CoMat 03-236 METAL SPRAYING POWDER-ALUMINUM, refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-016 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-265 NICKEL CHROMIUM ALUMINIUMPOWDER or CoMat 03-310 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Ni,Cr,Al, refer to Figure, Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-018 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-057 ALUMINIUM ALLOY/POLYESTERCOMPOSITE, refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-020-002 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-273 ALUMINIUM GRAPHITE COMPOSITEPOWDER, refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-023 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-273 ALUMINIUM GRAPHITE COMPOSITEPOWDER, refer to Figure, Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-024 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-038 METAL SPRAYING POWDER NICKEL ALUMINIUM (95/5), or CoMat 03-089 METAL SPRAYING POWDER Ni/Al (95/5), refer to Figure, Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-025 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-239 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE, CoMat 03-240 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE, CoMat 03-298 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE, CoMat 03-322 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE and CoMat 03-323 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, CHROMIUM CARBIDE/NICHROME 75/25, FINE, refer to Figure, Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-026 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-277 METAL SPRAYING POWDER, refer to Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-027 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-238 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Ni-Cr-Al, or CoMat 03-324 DELETED, refer to Figure and Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-029 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-238 METAL SPRAY POWDER, Ni-Cr-Al, or CoMat 03-324 DELETED, refer to Figure and Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-030 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-229 METAL SPRAYING POWDER or CoMat 03-237 DELETED, refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-031 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-317 DELETED refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-032-002 Application of Metal Spray Powder
To apply CoMat 03-080 METAL SPRAYING POWDER,Co BASE ALLOY refer to Figure, Figure or Figure.
SUBTASK 70-34-01-340-033 Application of Metal Spray Powder
Figure: Finishing procedures for the different coatings
Finishing procedures for the different coatings
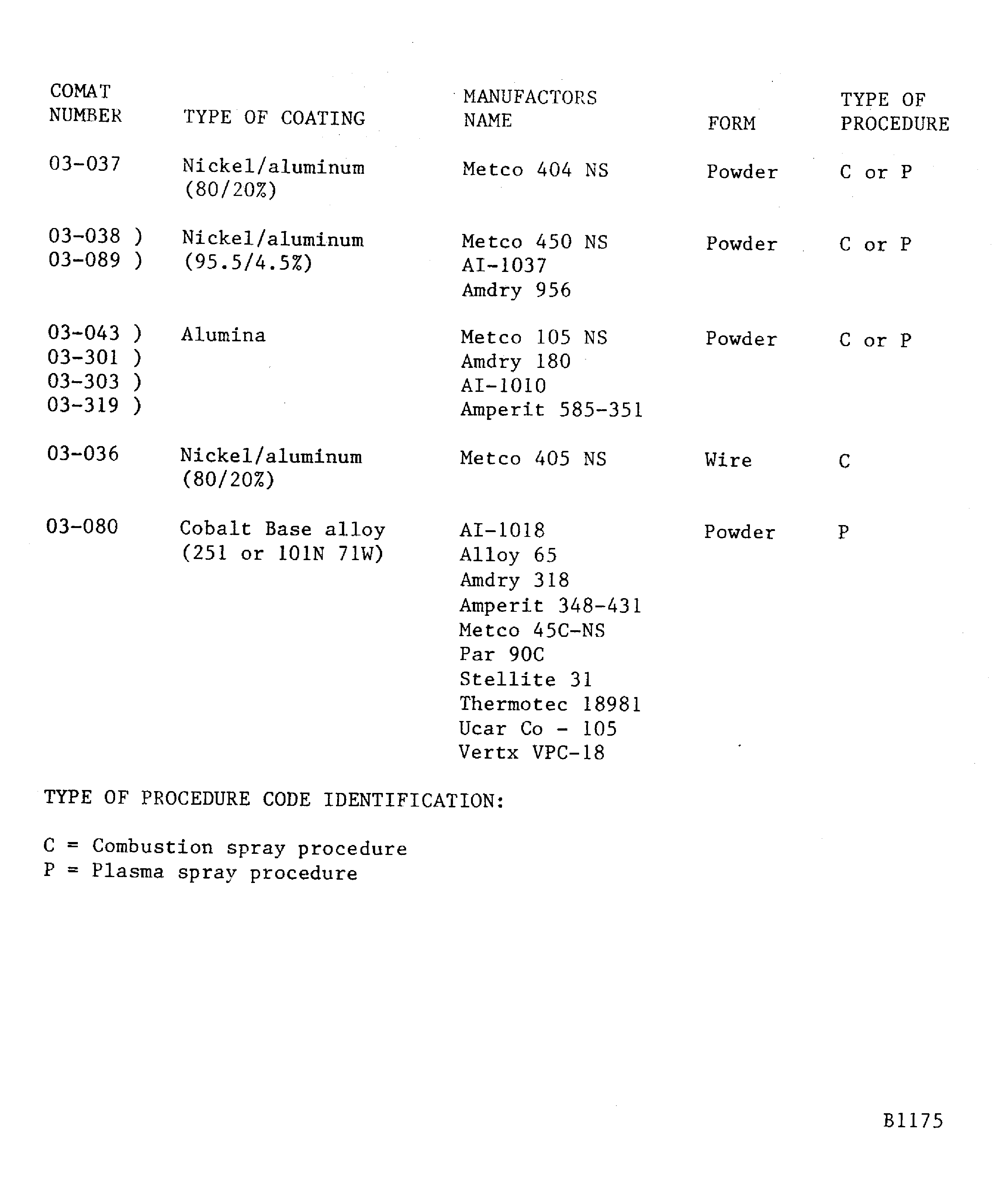
Figure: Finishing procedures for the different coatings
Finishing procedures for the different coatings
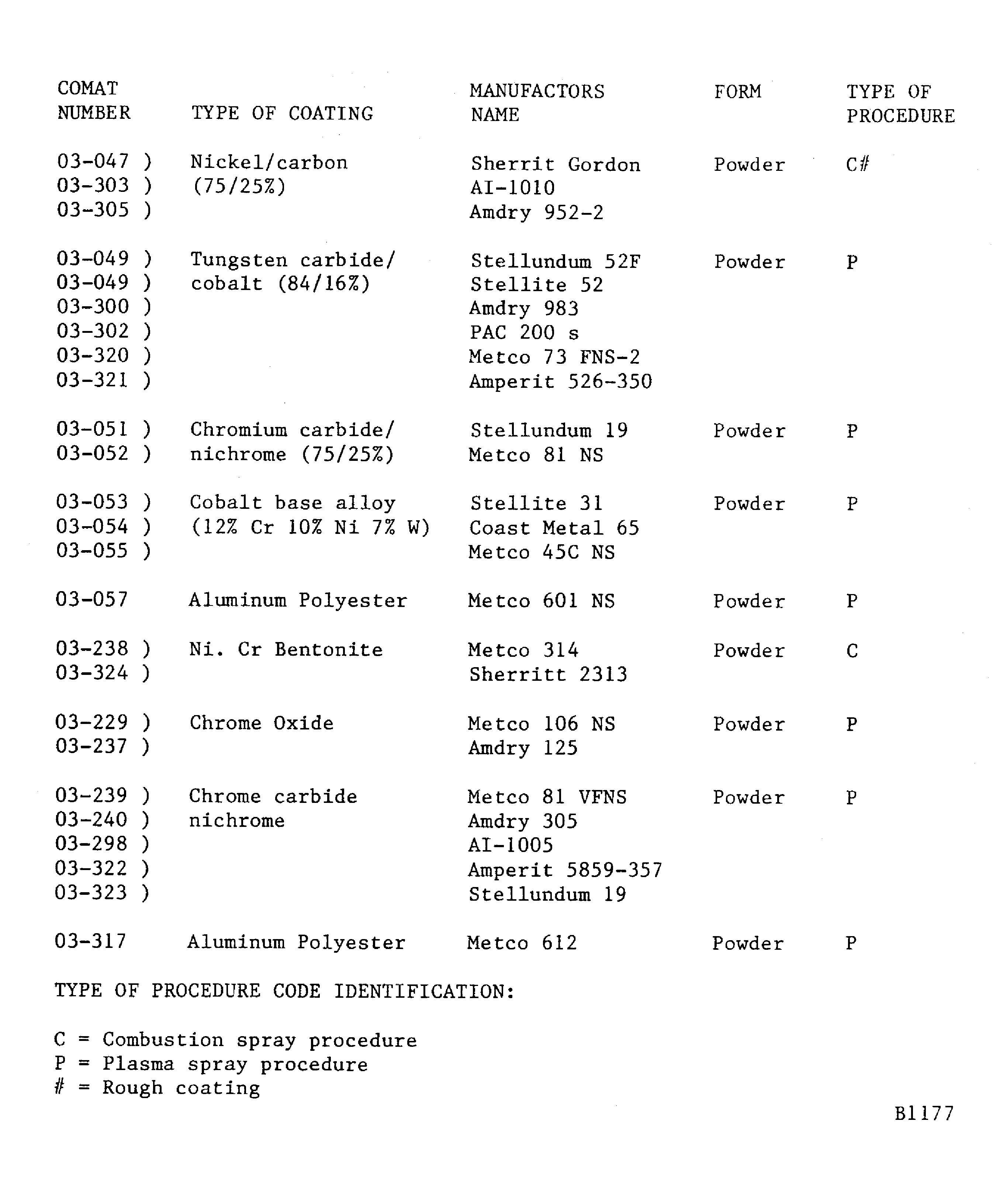
Figure: Finishing procedures for the different coatings
Finishing procedures for the different coatings

Figure: Finishing procedures for the different coatings
Finishing procedures for the different coatings
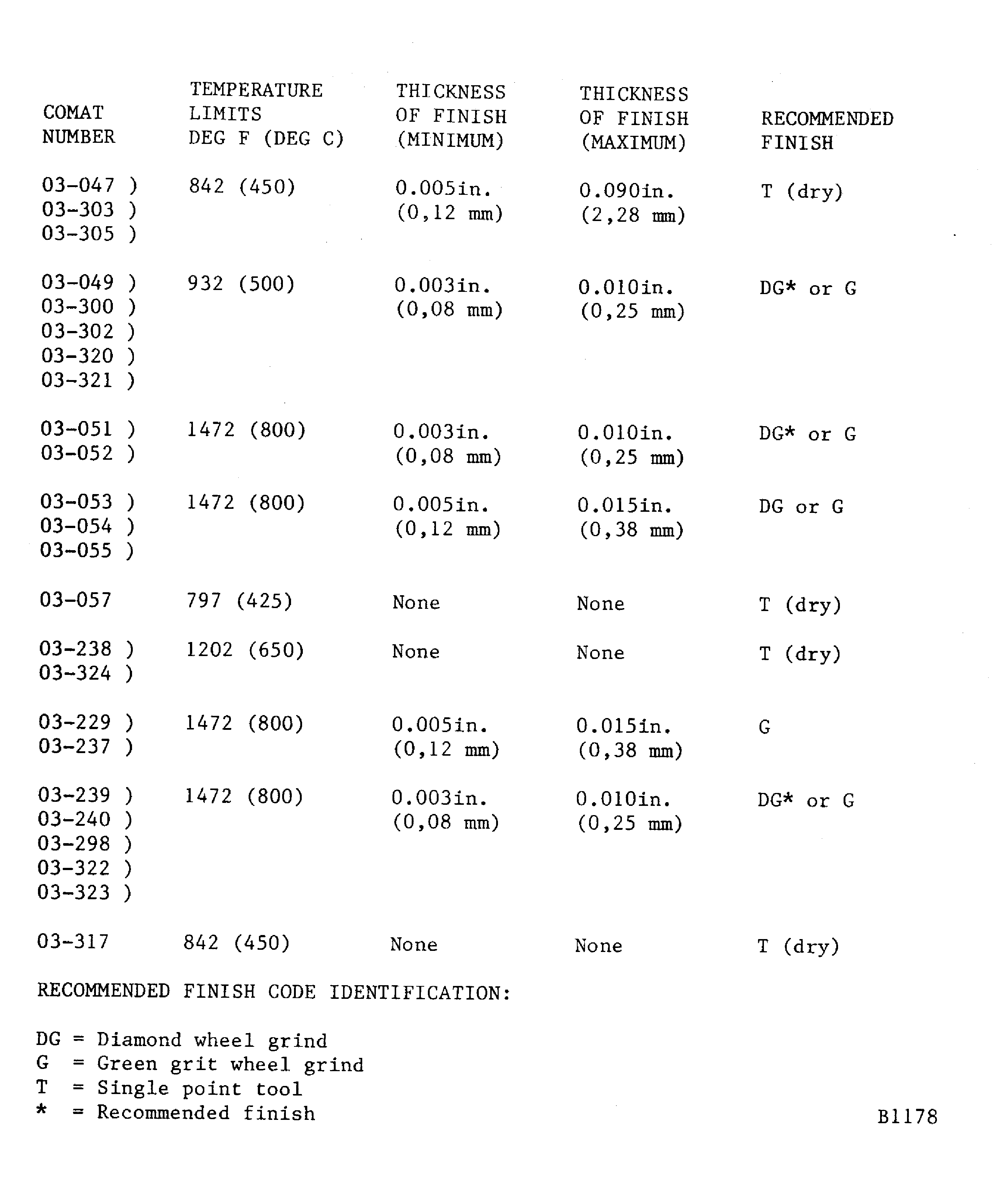
Figure: Abradable linings - hardness values
Abradable linings - hardness values
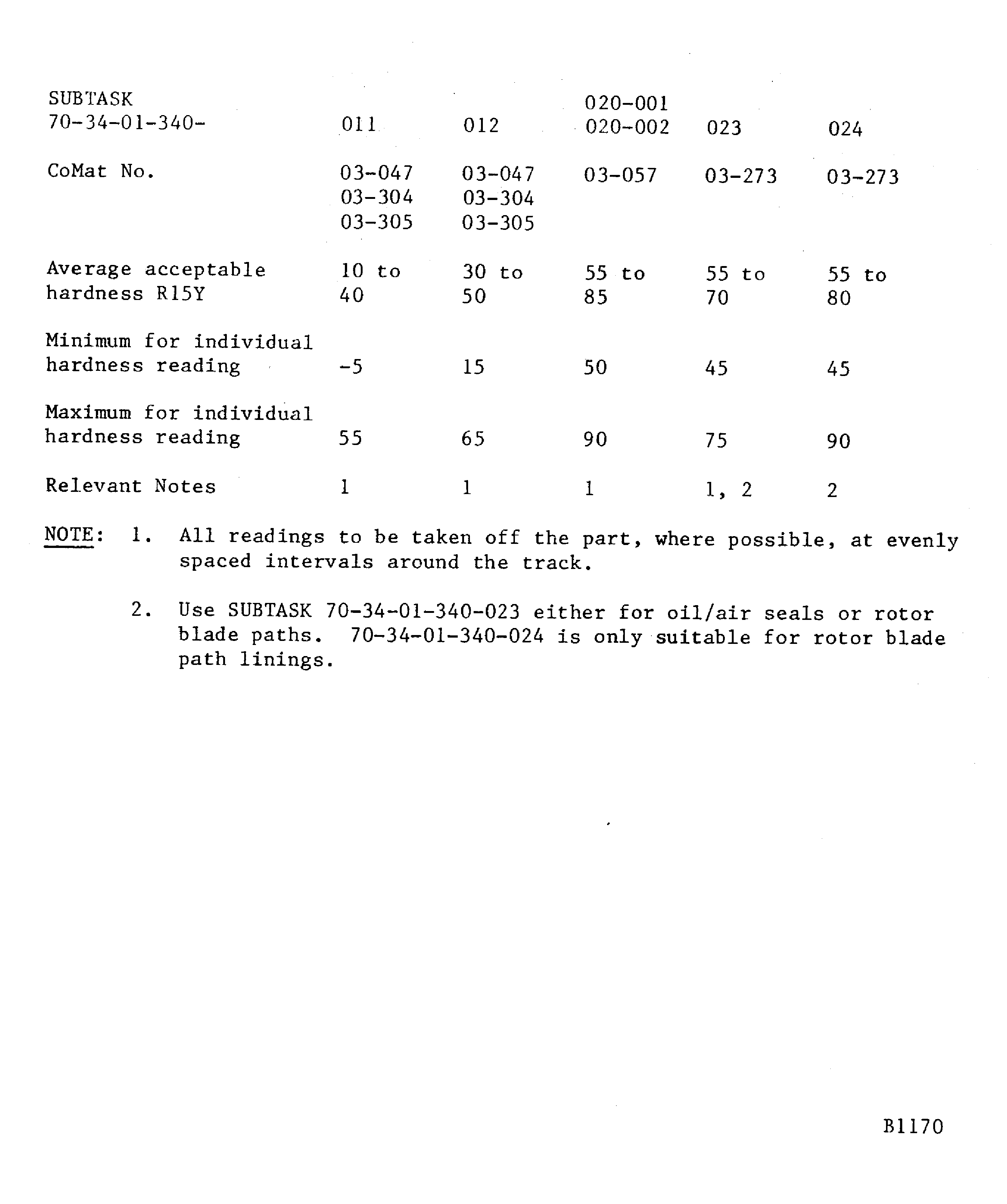
Figure: Abradable linings - hardness values
Abradable linings - hardness values
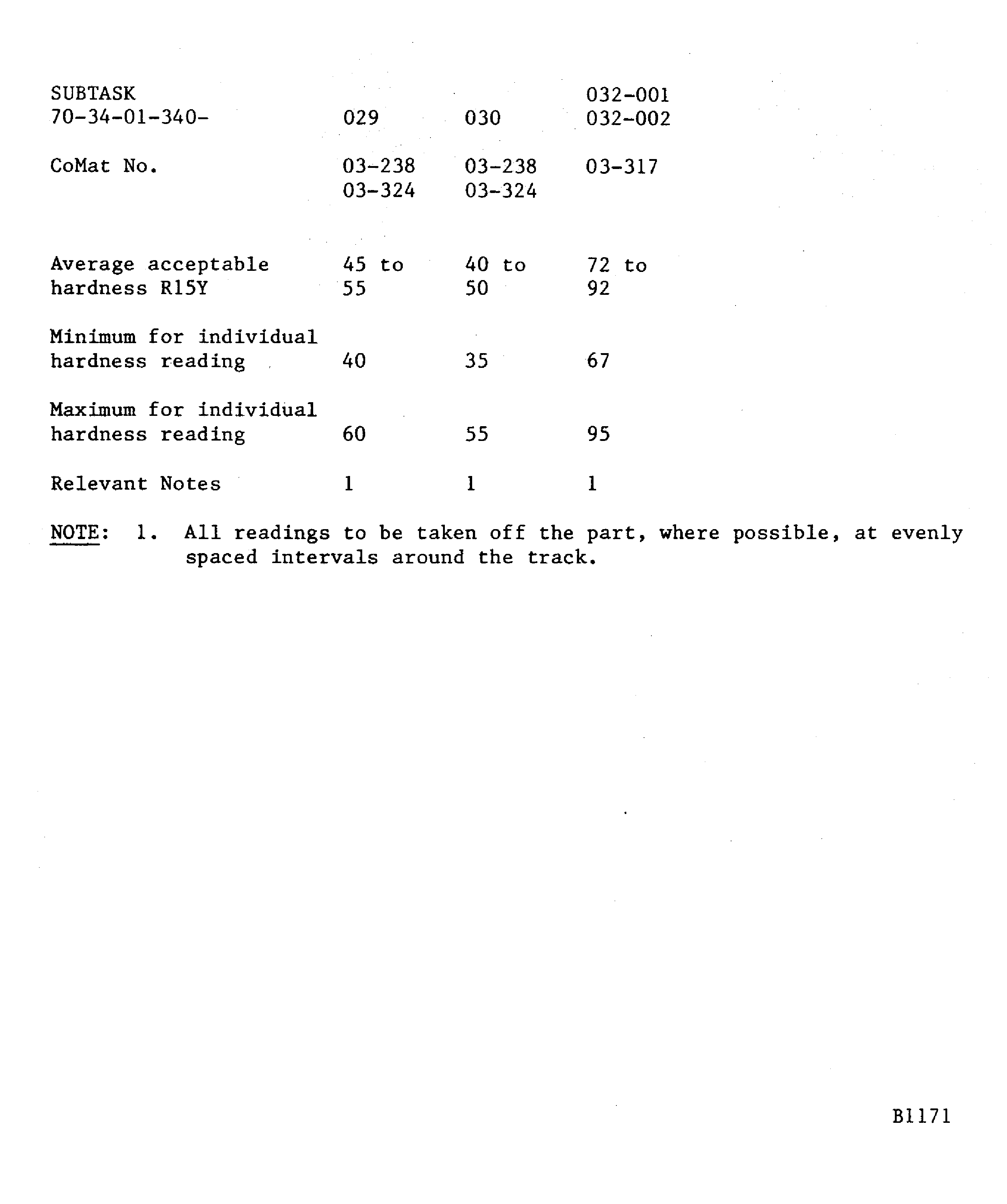
Figure: Combustion wire spray - METCO 10E or 12E
Combustion wire spray - METCO 10E or 12E

Figure: Powders - combustion spraying data - METCO 5P gun
Powders - combustion spraying data - METCO 5P gun
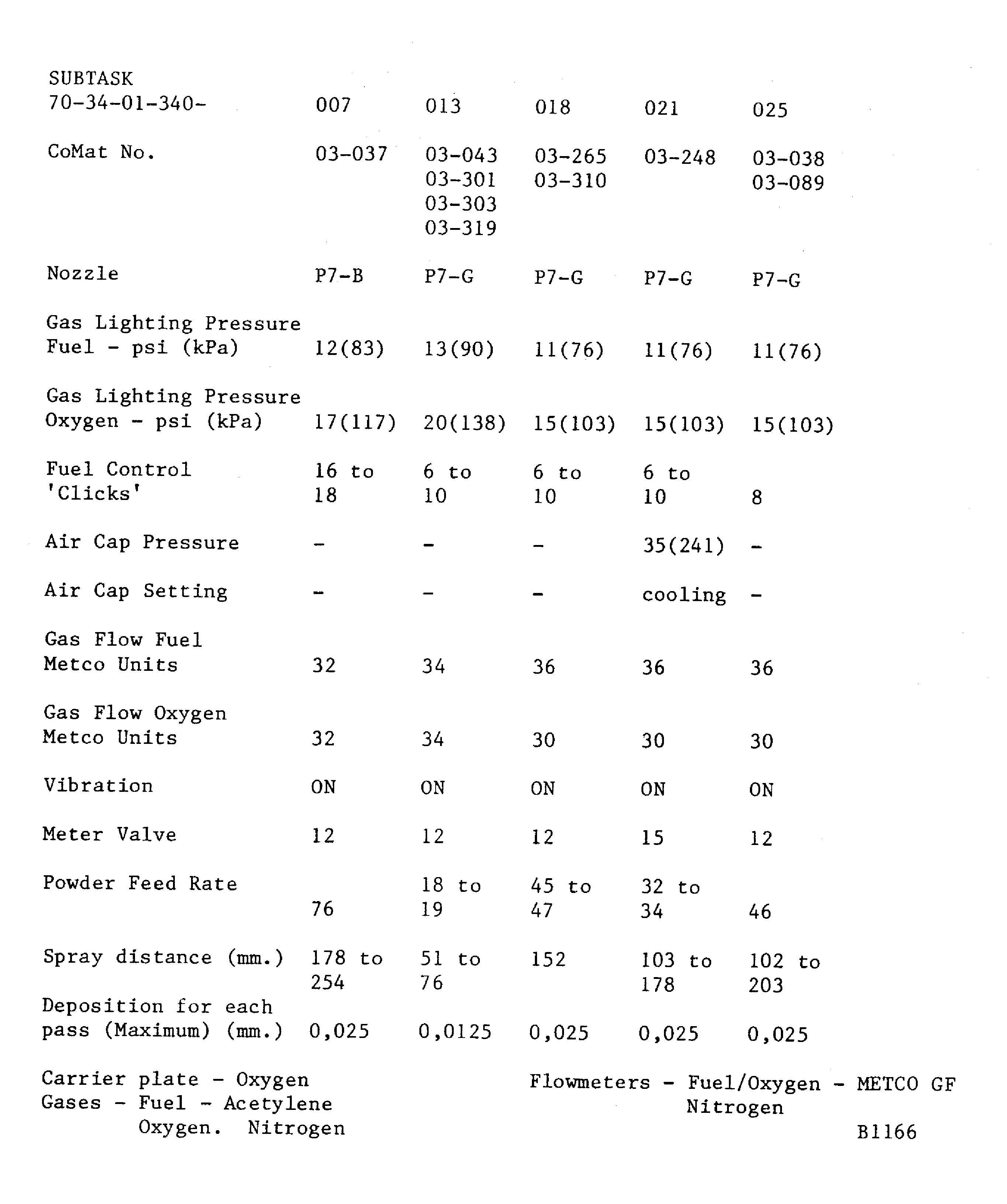
Figure: Powders - combustion spraying data - METCO 6P gun
Powders - combustion spraying data - METCO 6P gun
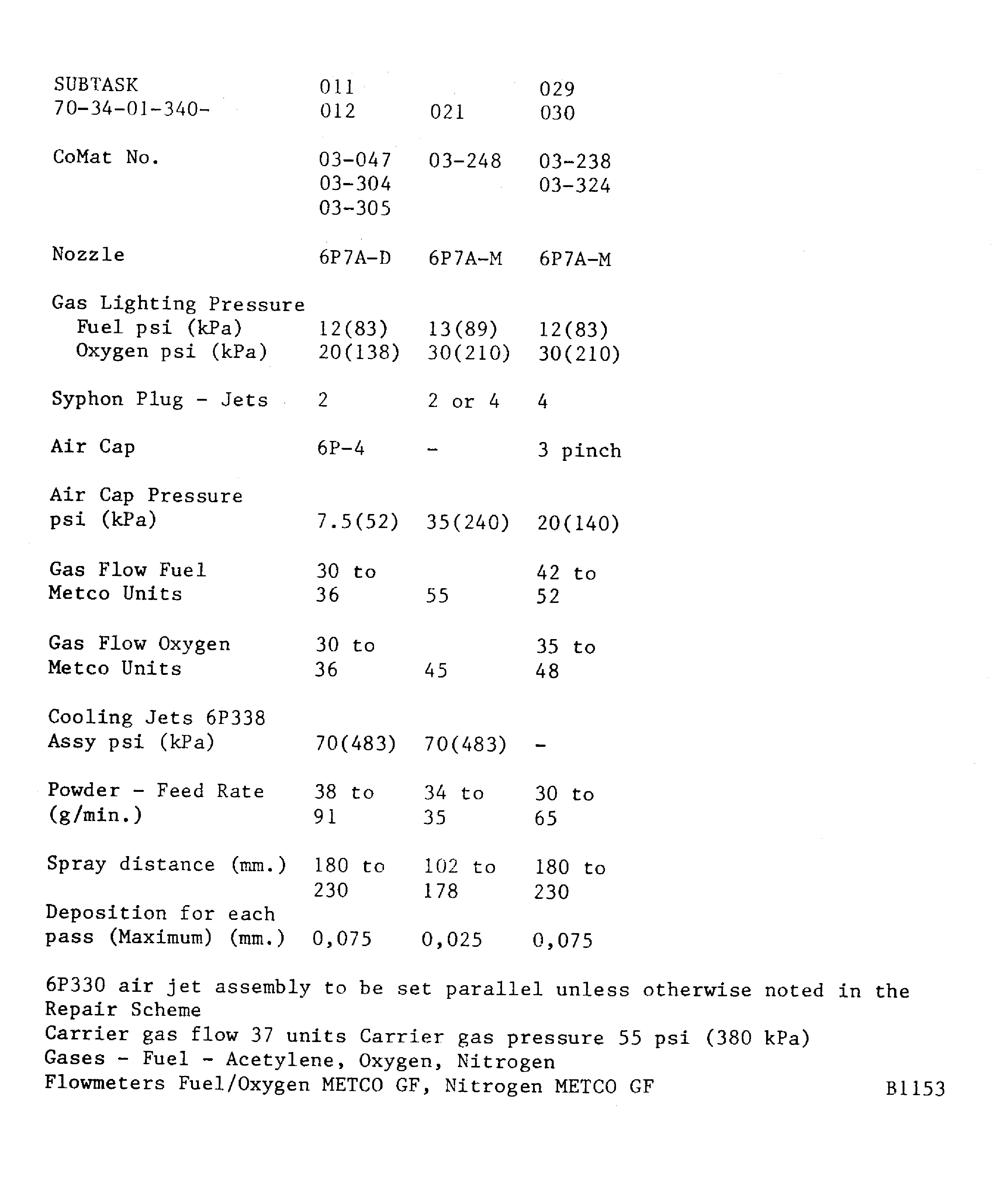
Figure: Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
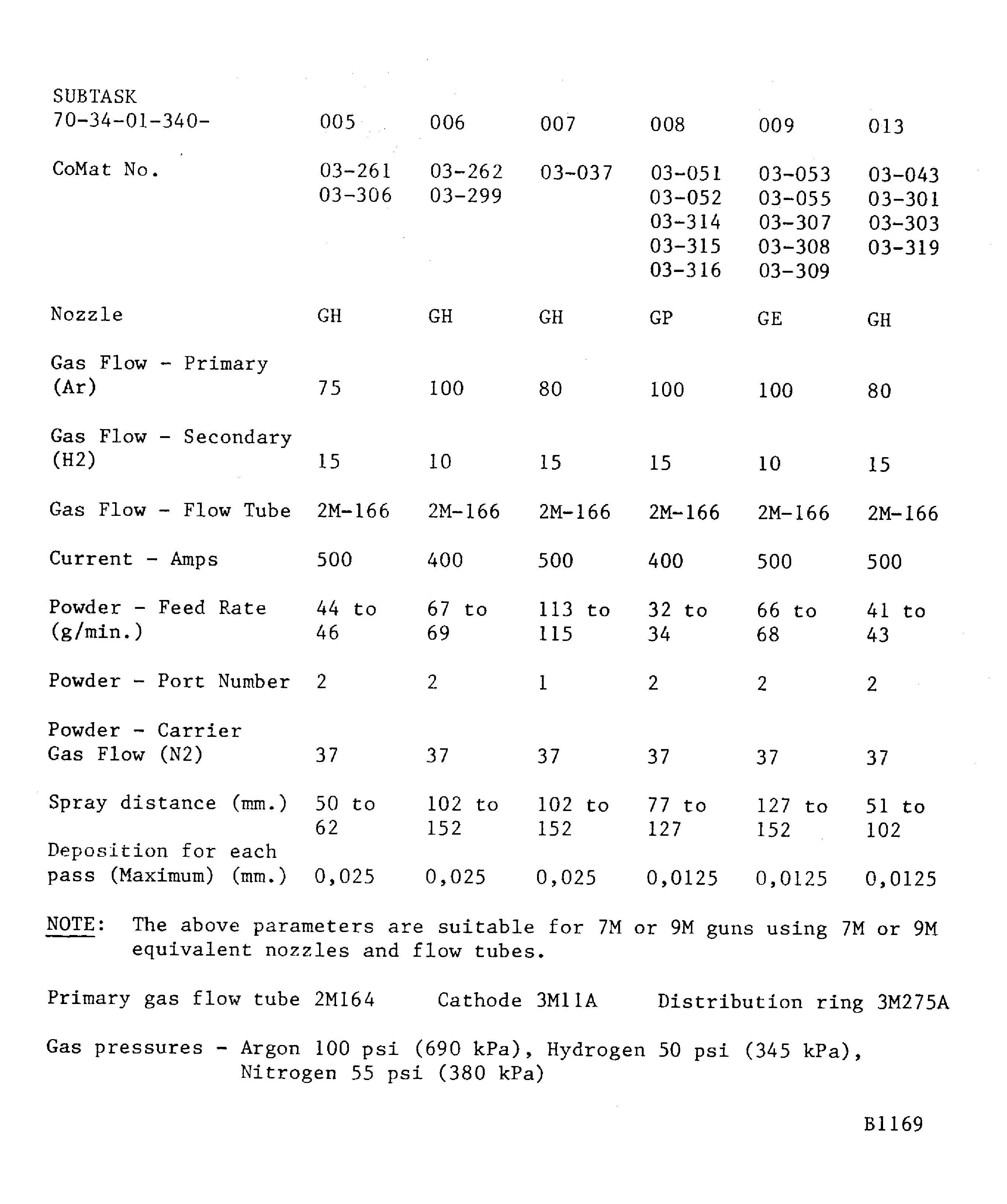
Figure: Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
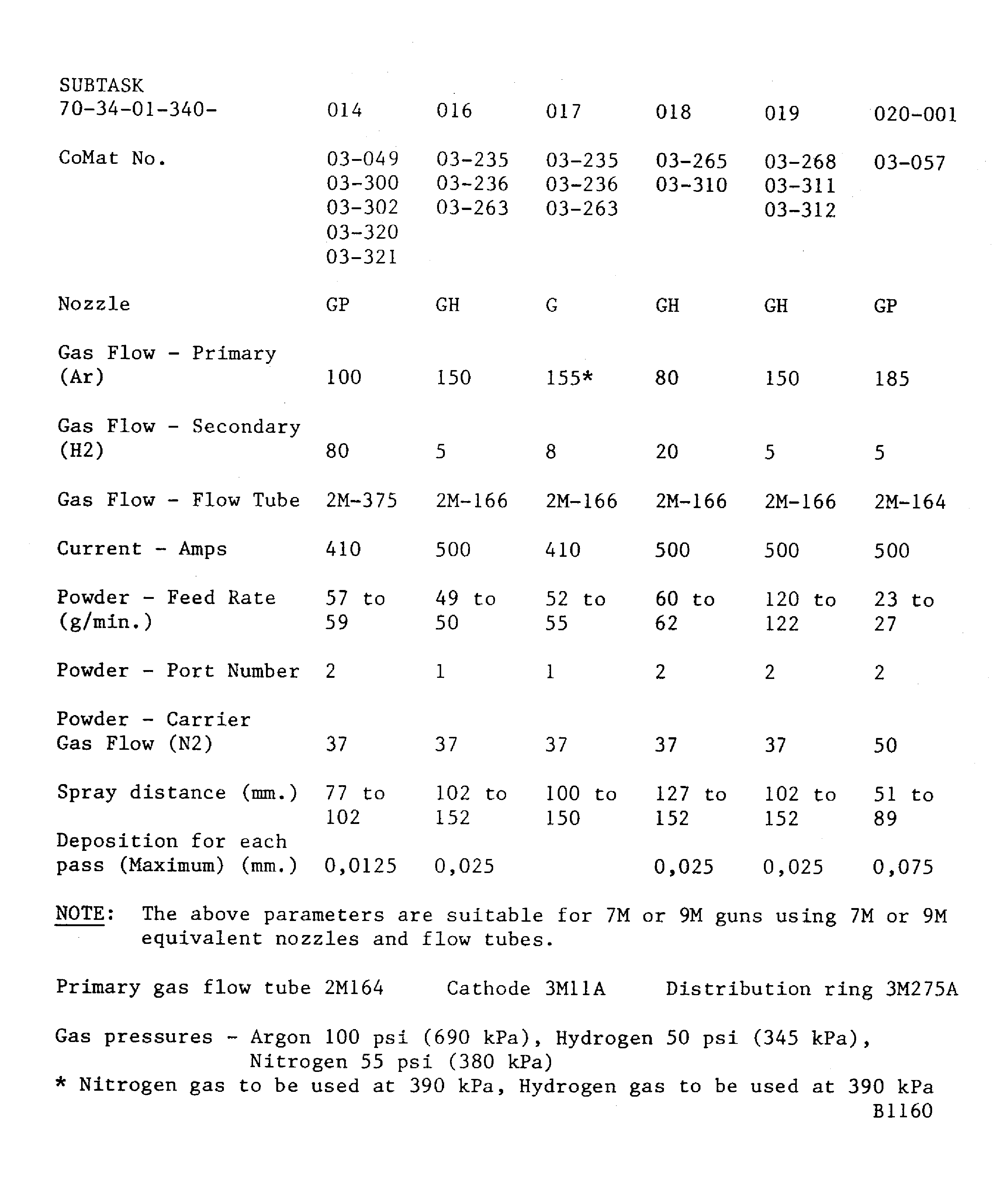
Figure: Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
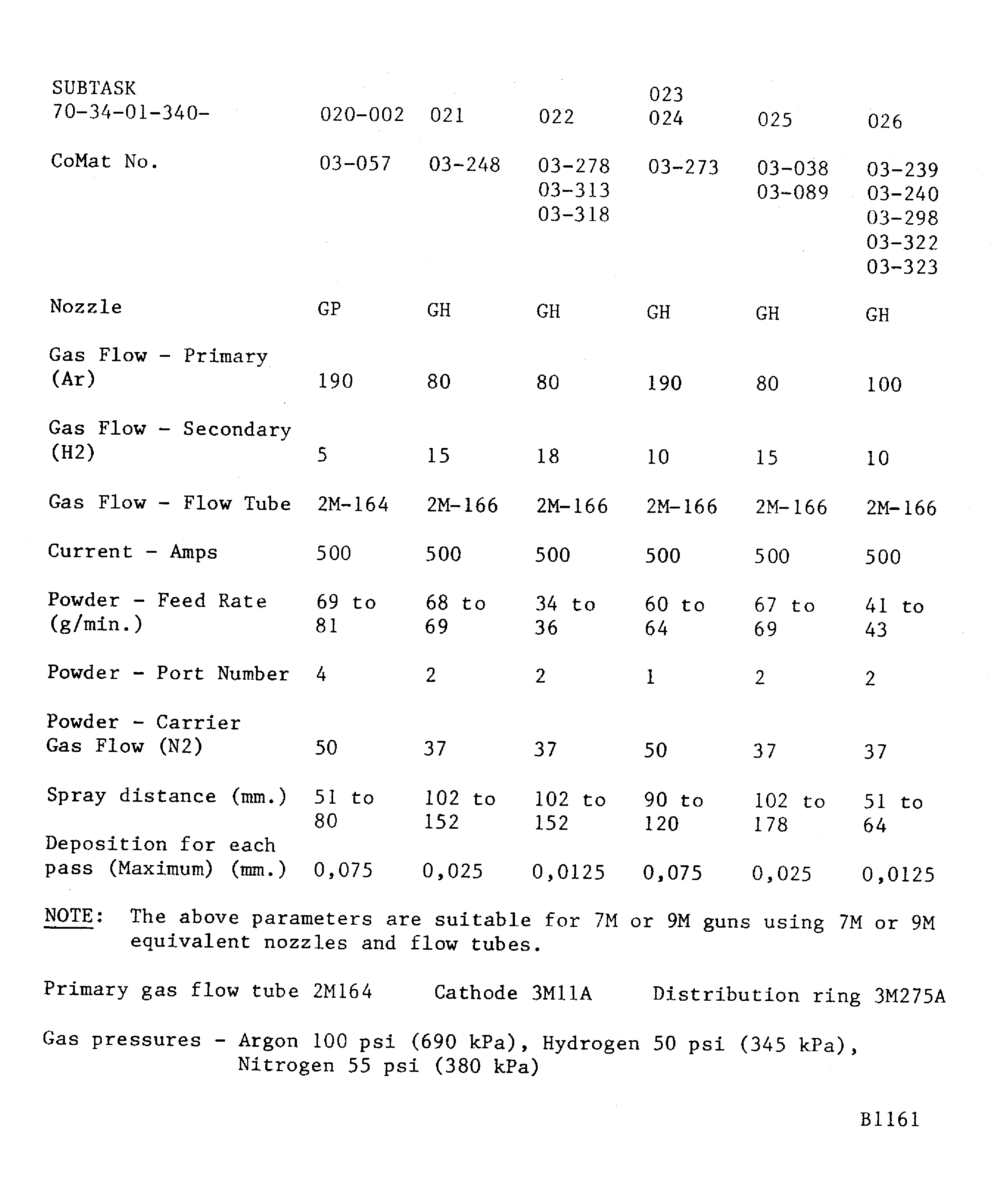
Figure: Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
Powder plasma data - METCO 3MB gun
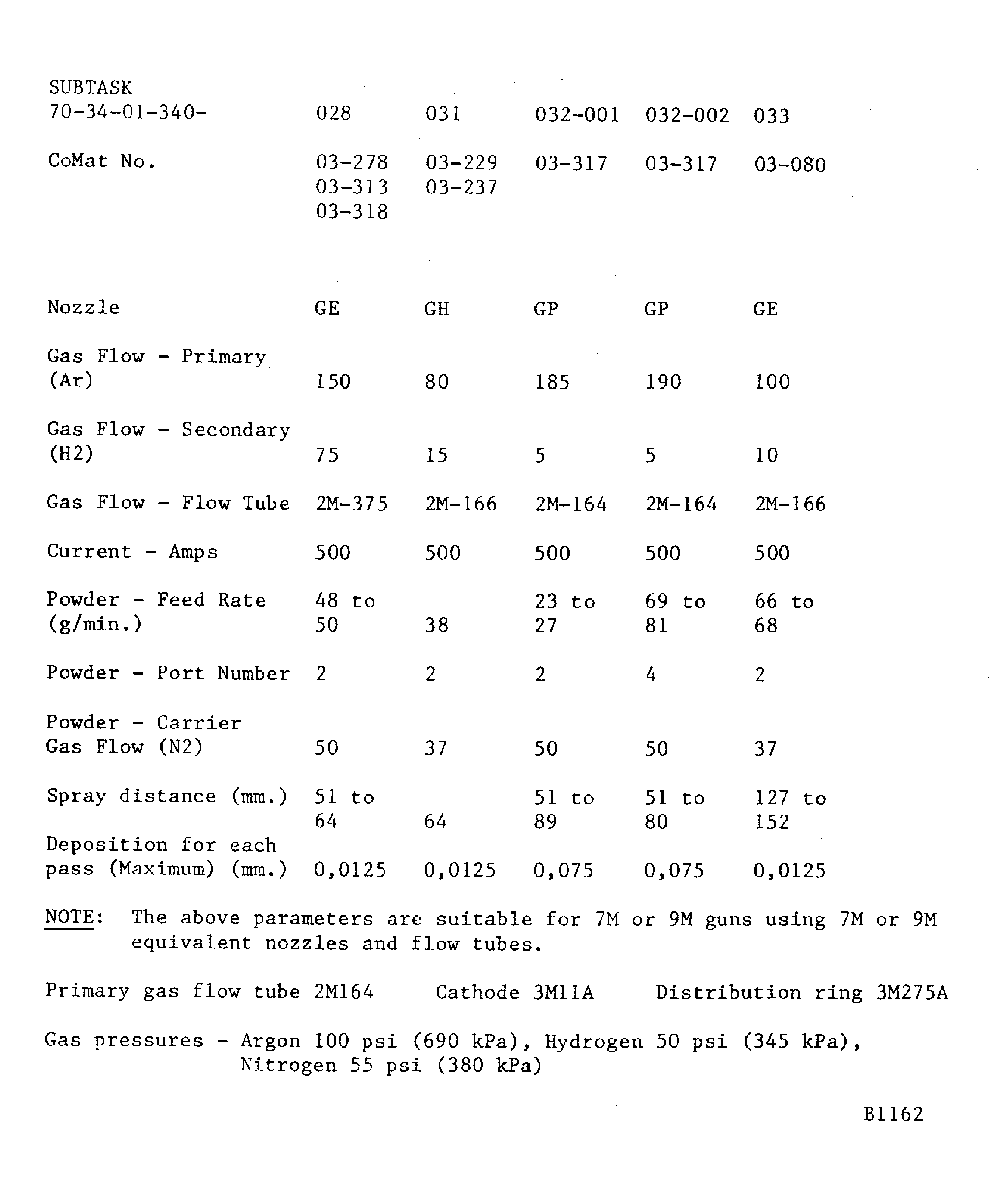
Figure: Powder plasma data - METCO 7MB (high energy coatings)
Powder plasma data - METCO 7MB (high energy coatings)
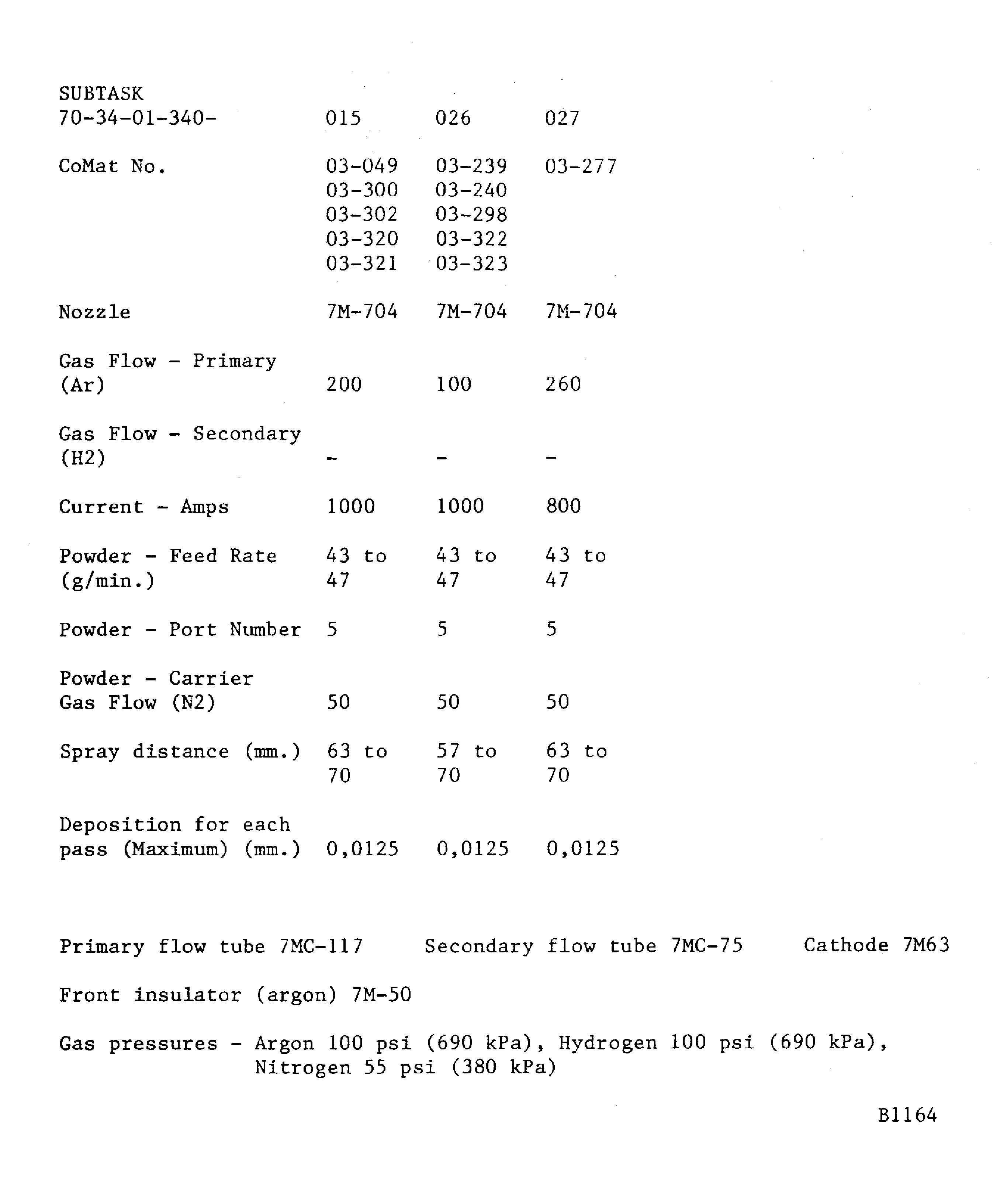
Figure: Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F1 gun
Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F1 gun
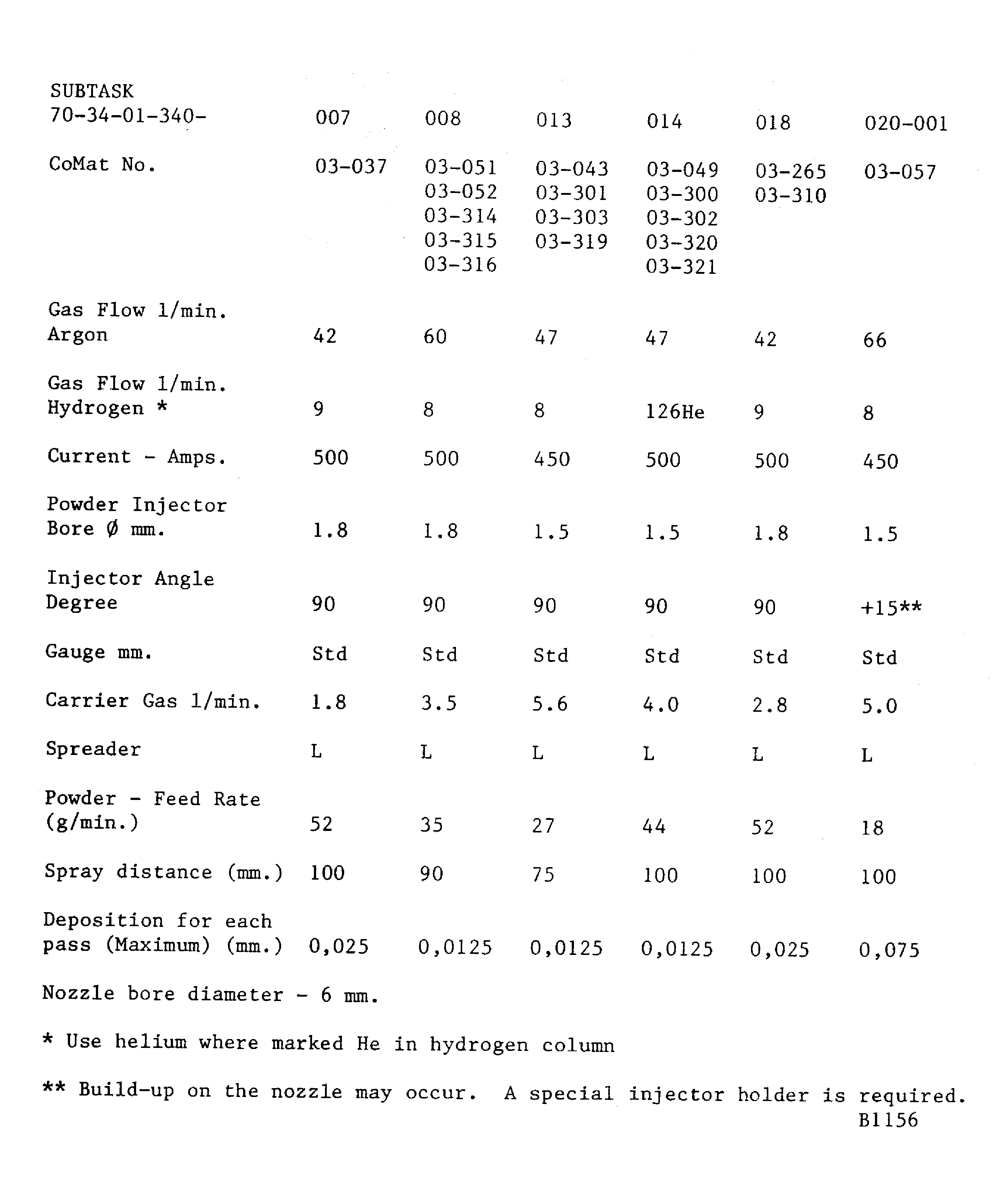
Figure: Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F1 gun
Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F1 gun
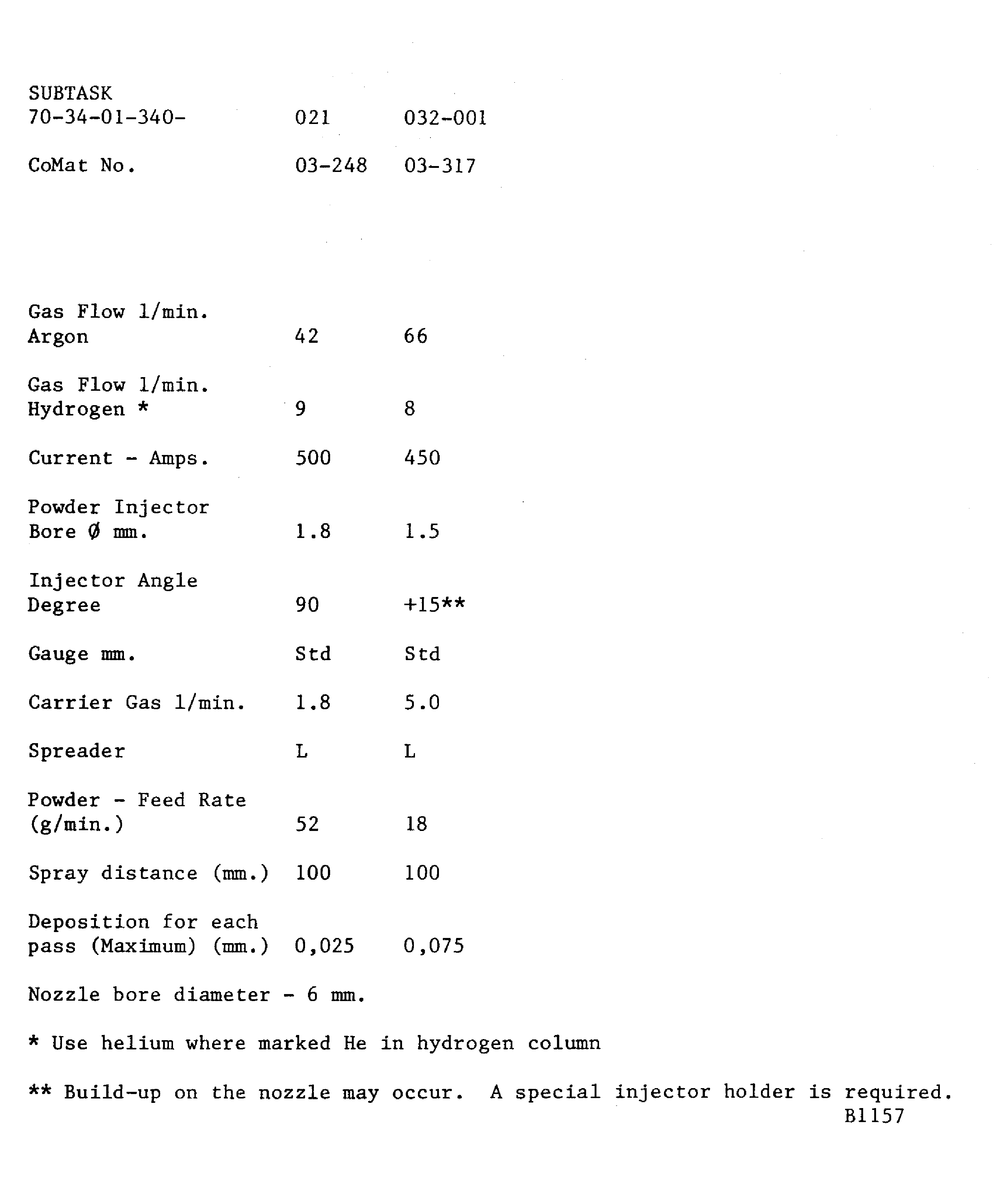
Figure: Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
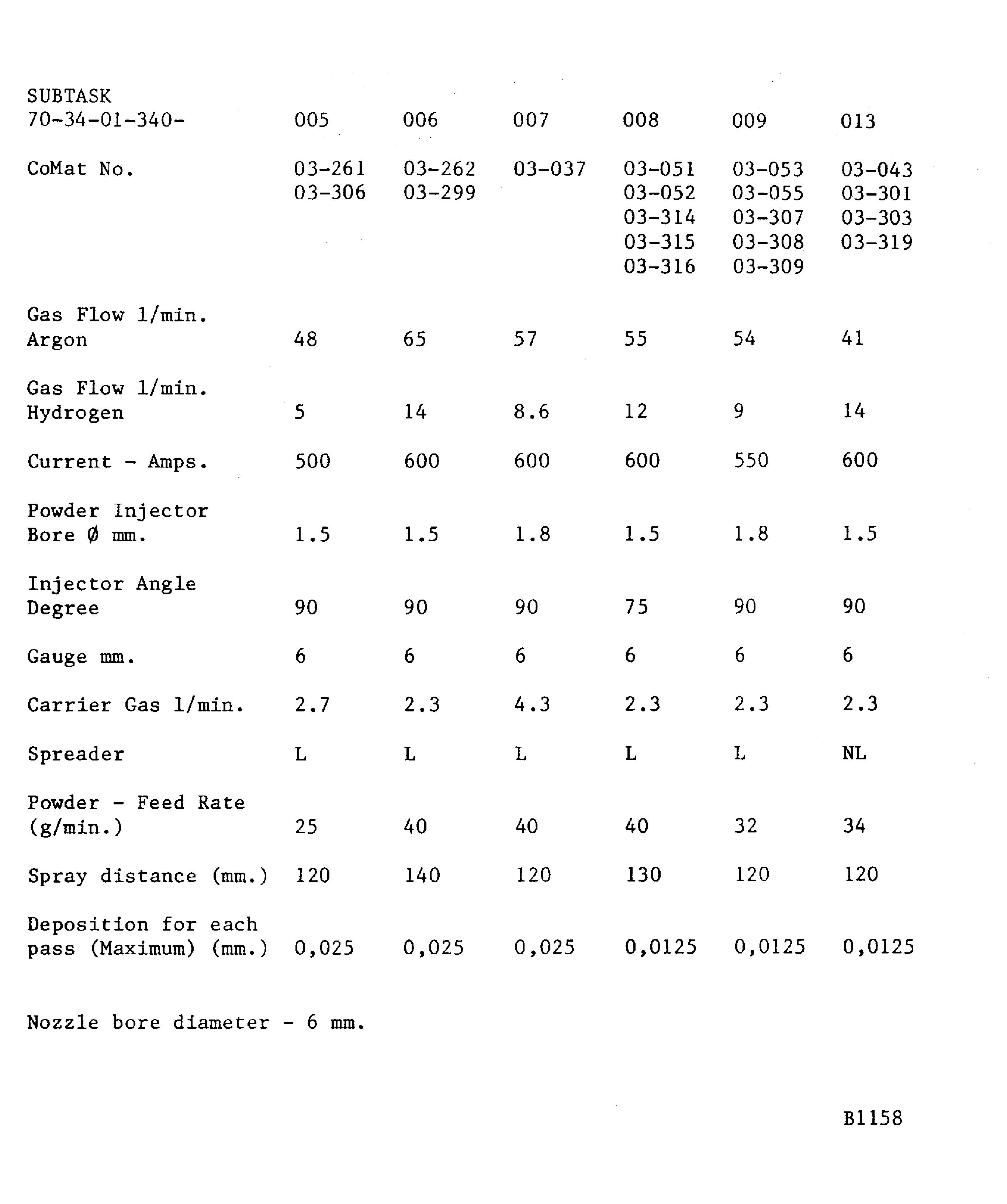
Figure: Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
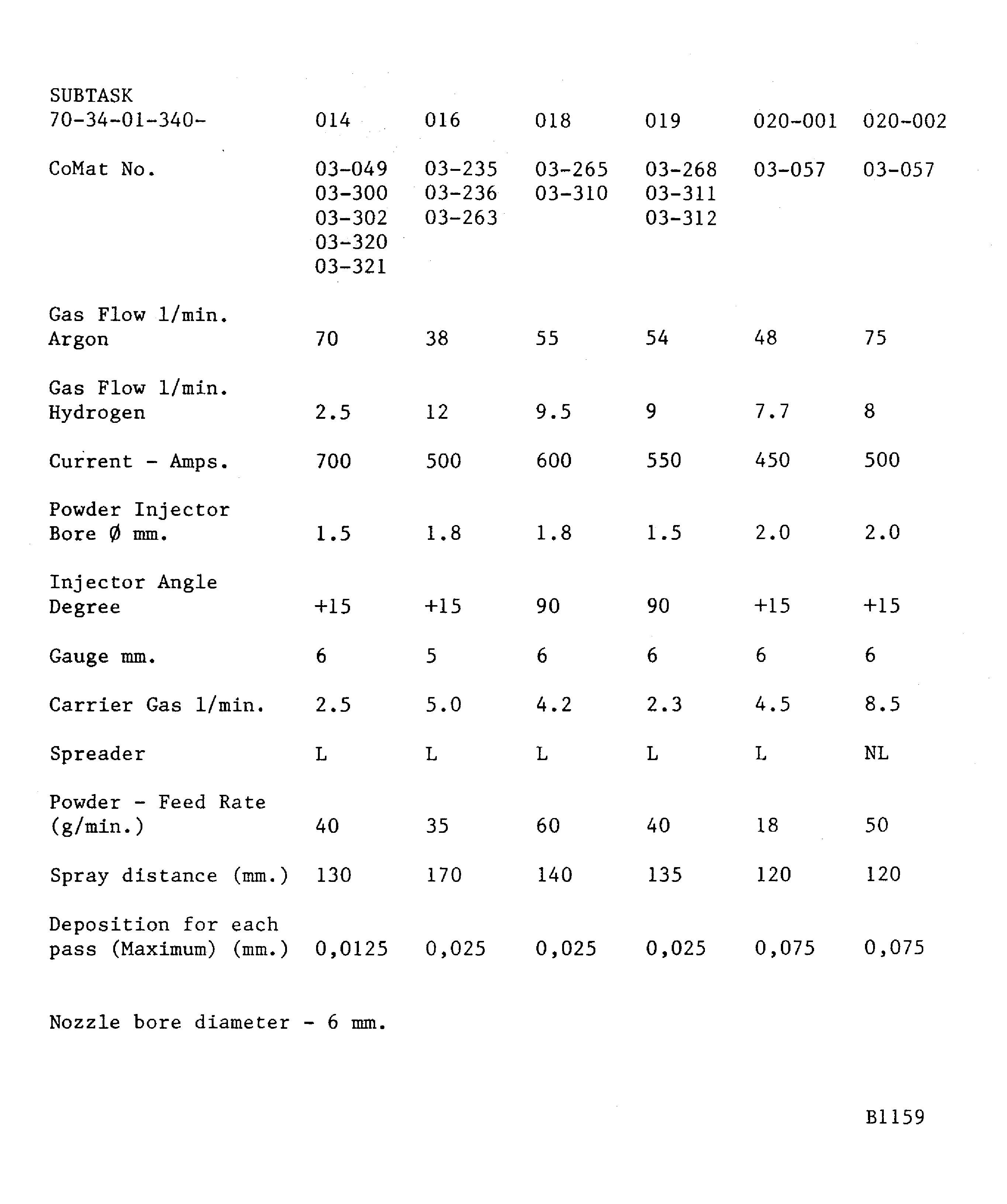
Figure: Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
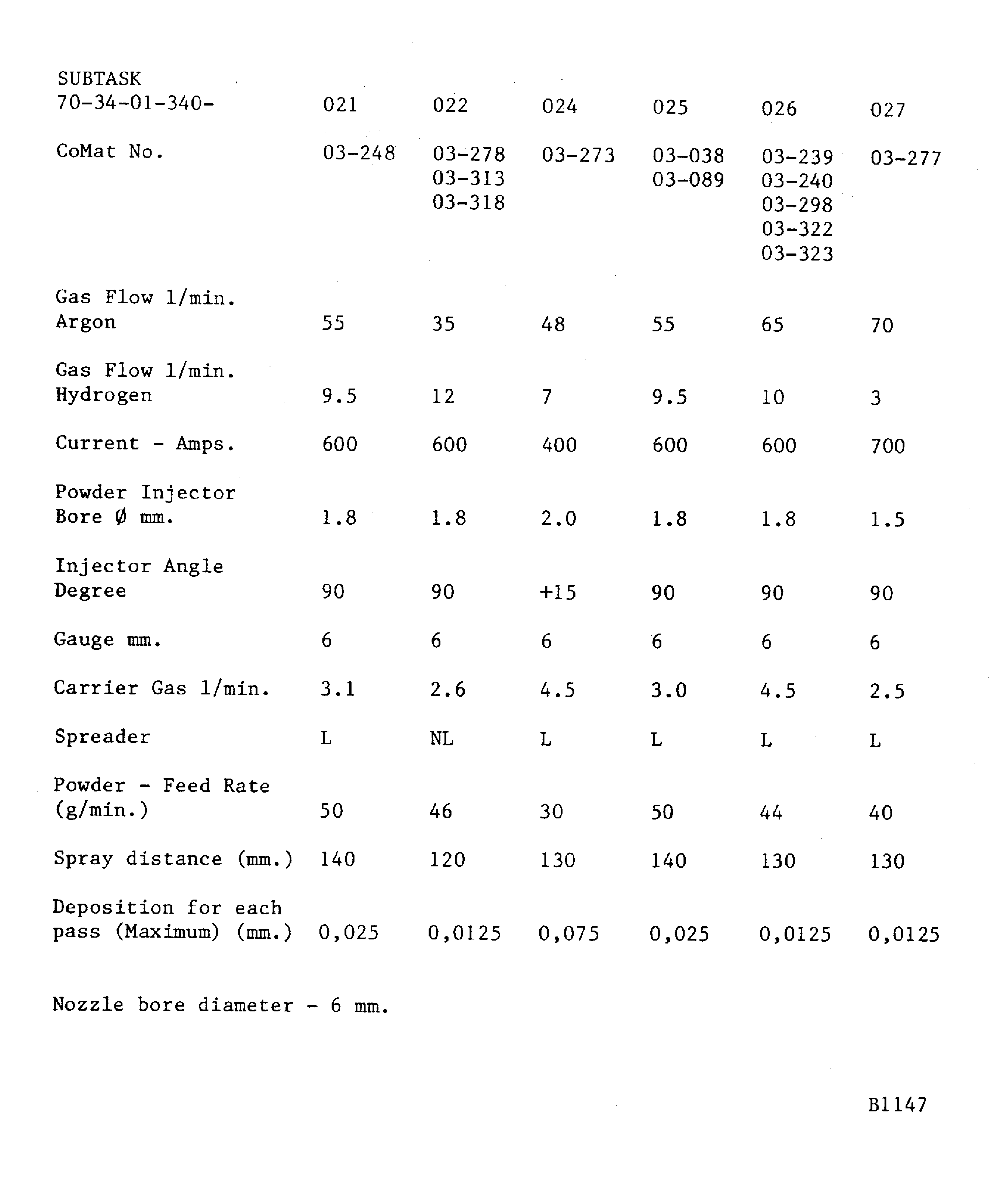
Figure: Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
Plasma data - Plasma Tecnik F4 gun
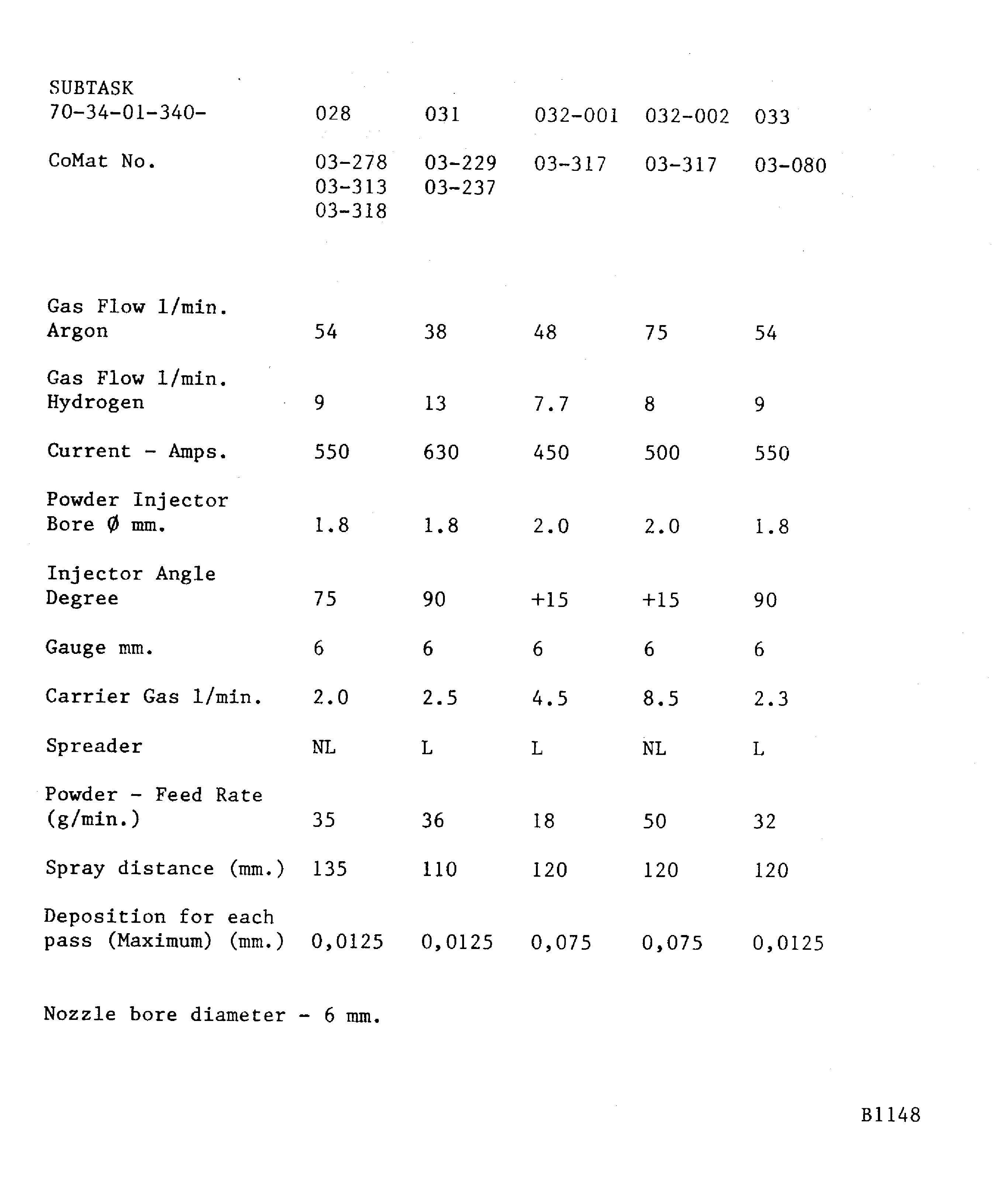
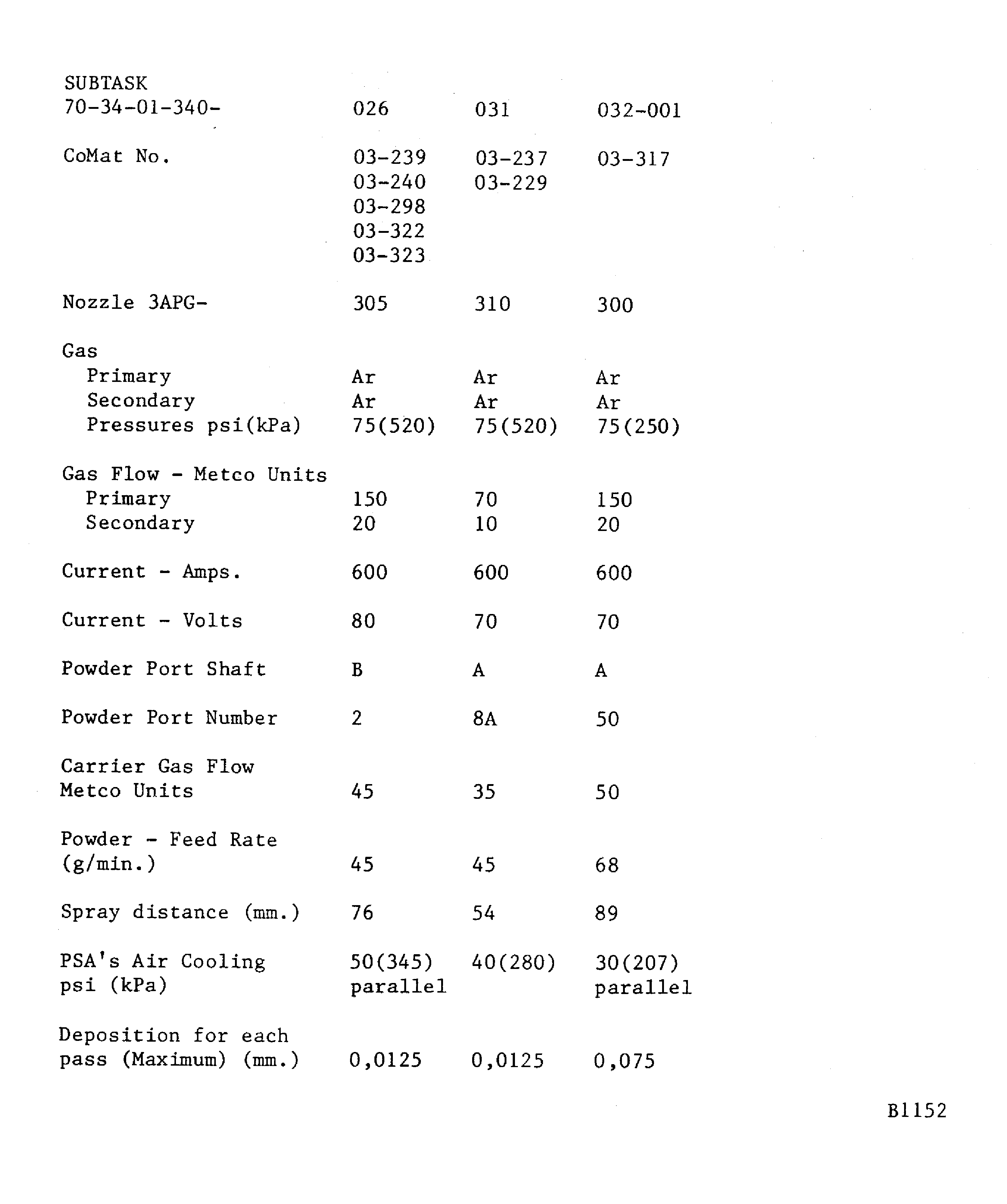
Figure: Plasma data - METCO 3APG (advanced plasma gun)
Plasma data - METCO 3APG (advanced plasma gun)
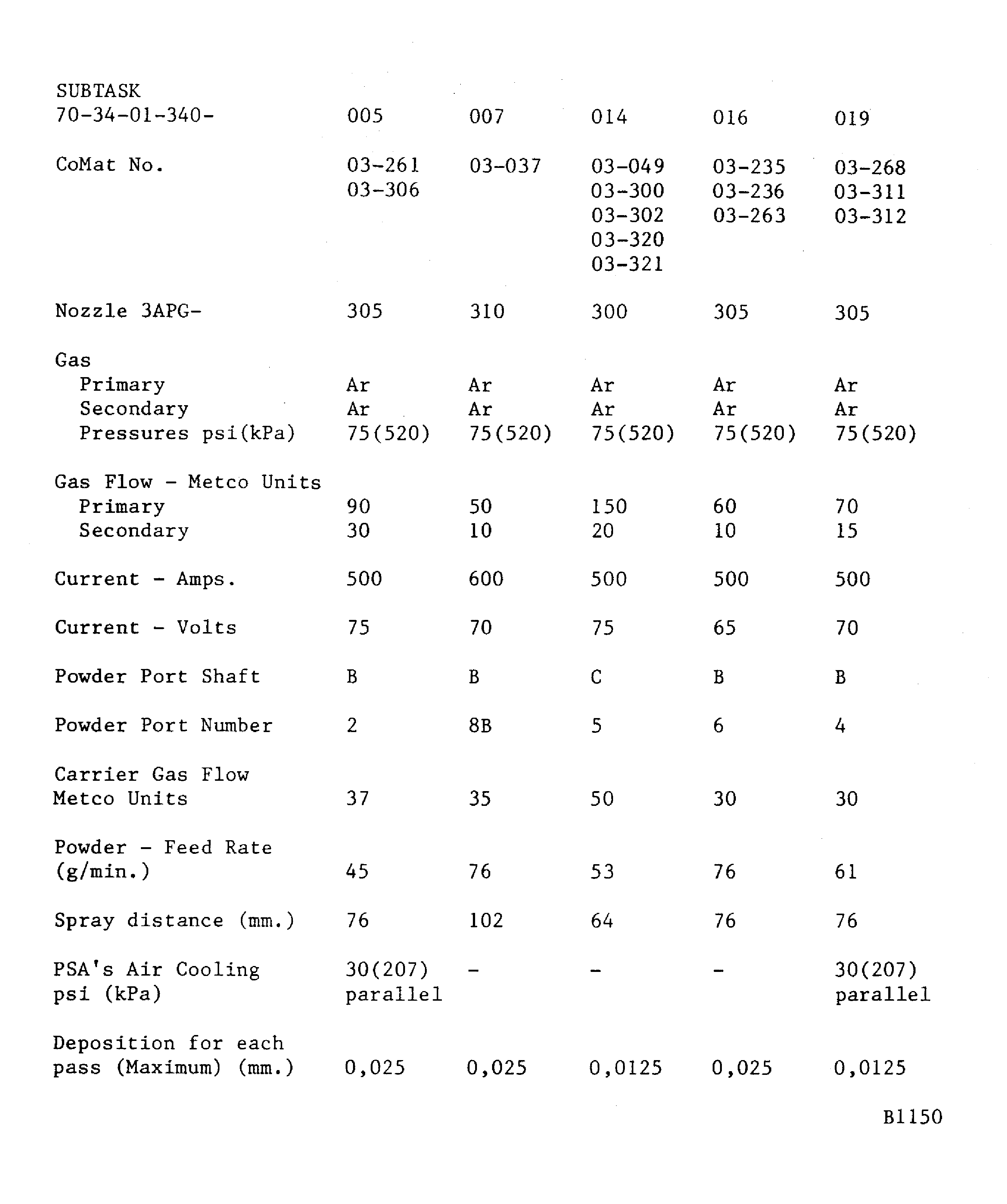
Figure: Plasma data - METCO 3APG (advanced plasma gun)
Plasma data - METCO 3APG (advanced plasma gun)
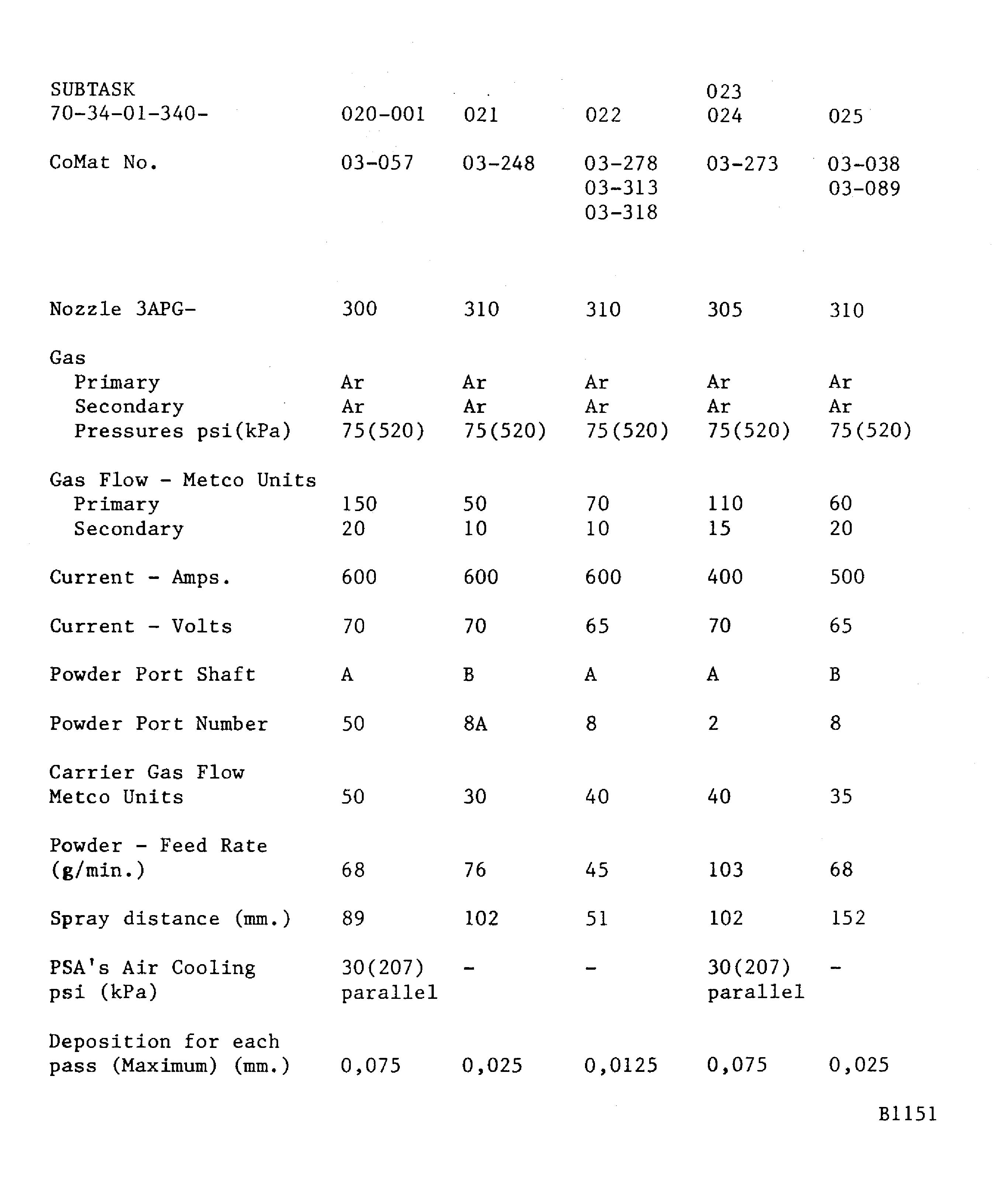
Figure: Plasma data - METCO 3APG (advanced plasma gun)
Plasma data - METCO 3APG (advanced plasma gun)